Abstract
We have used cDNAs for the human interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptor to study IL-2 receptor gene expression in normal activated T cells. Resting T cells do not contain detectable IL-2 receptor mRNA. Within 1 hr after stimulation with phytohemagglutinin (PHA), a large, presumably nuclear precursor RNA species is seen, which then gradually disappears. Mature IL-2 receptor mRNA forms appear within 8 hr after stimulation, reach peak levels between 8 and 24 hr, and then decline. Thus, in PHA-activated lymphocytes the rise and fall in IL-2 receptor mRNA levels precede by more than 24 hr the peak and decline of IL-2 receptor protein expression occurring at the cell surface. 4 beta-Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) also stimulates IL-2 receptor mRNA and protein expression by T cells. Combinations of optimal concentrations of PHA and PMA produce an additive effect on IL-2 receptor mRNA levels, suggesting that PHA and PMA may induce IL-2 receptor gene expression through different, complementary mechanisms. Nuclease S1-protection assays indicate that IL-2 receptor mRNAs may differ in length due to the use of three different polyadenylylation signals. Further, these assays demonstrate the presence of transcripts that lack a 216-base segment within the protein-coding region and thus do not encode a functional IL-2 receptor. Nuclear transcription assays indicate that the increase in IL-2 receptor mRNA is reflected at the level of transcription. Thus, IL-2 receptor gene regulation controls IL-2 receptor expression at the cell surface and is intimately linked to the control of T-cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Gallo R. C. Transcriptional modulation of human T-cell growth factor gene by phorbol ester and interleukin 1. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6685–6690. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D., Cerretti D. P., Larsen A., Park L., March C., Dower S., Gillis S., Urdal D. Cloning, sequence and expression of human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):768–771. doi: 10.1038/312768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Noguchi P. D., Cunningham R. E., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Regulation of interleukin 2 receptor expression: effects of phorbol diester, phospholipase C, and reexposure to lectin or antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3054–3061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Robb R. J., Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Drogula C., Svetlik P. B., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Waldmann T. A. Phorbol diester induces expression of Tac antigen on human acute T lymphocytic leukemic cells. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):1042–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Robb R. J., Svetlik P. B., Rusk C. M., Depper J. M., Leonard W. J. Stable expression of cDNA encoding the human interleukin 2 receptor in eukaryotic cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):363–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Cyclosporin A inhibits T-cell growth factor gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Krönke M., Robb R. J., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. The human receptor for T-cell growth factor. Evidence for variable post-translational processing, phosphorylation, sulfation, and the ability of precursor forms of the receptor to bind T-cell growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1872–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Robb R. J., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Characterization of the human receptor for T-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6957–6961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. A., Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1007–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.181845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Shimizu A., Ishida N., Sabe H., Teshigawara K., Maeda M., Uchiyama T., Yodoi J., Honjo T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):631–635. doi: 10.1038/311631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Trowbridge I. S. Induction of expression and phosphorylation of the human interleukin 2 receptor by a phorbol diester. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11706–11712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdal D. L., March C. J., Gillis S., Larsen A., Dower S. K. Purification and chemical characterization of the receptor for interleukin 2 from activated human T lymphocytes and from a human T-cell lymphoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6481–6485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
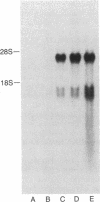
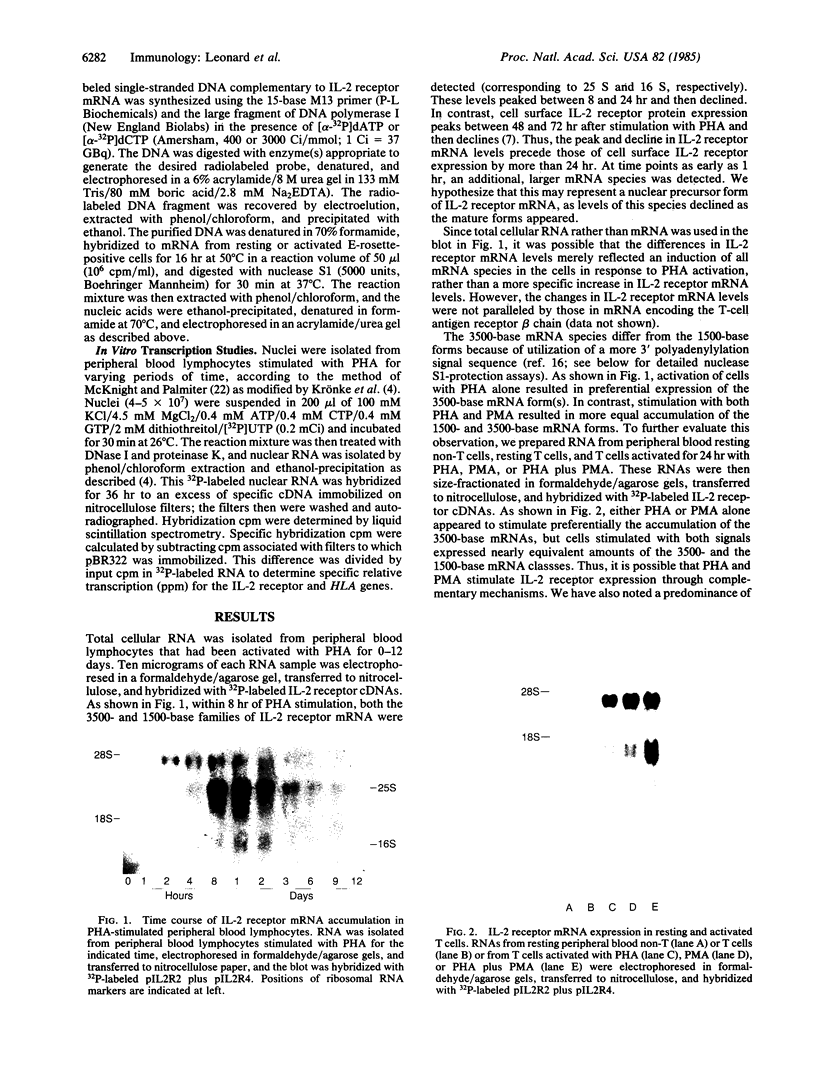
- Wano Y., Uchiyama T., Fukui K., Maeda M., Uchino H., Yodoi J. Characterization of human interleukin 2 receptor (Tac antigen) in normal and leukemic T cells: co-expression of normal and aberrant receptors on Hut-102 cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3005–3010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]