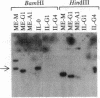
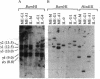
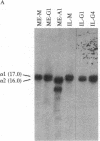
Abstract
During differentiation B lymphocytes may switch from the expression of surface IgM to the synthesis of IgG, IgA, or IgE isotypes by using a different heavy chain constant region (CH) gene. The molecular mechanisms by which switching occurs remain controversial. Rearrangements and deletions of CH genes 5' to the expressed gene have often been observed in the mouse and, more recently, in human cells that have switched isotypes. We have used human JH, C micro, C gamma, and C alpha probes to examine the extent of the deletions and rearrangements in clones of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human cells that produce IgG1, IgG3, IgG4, or IgA1. Though deletions of CH genes 5' to the expressed CH gene were consistently observed, the rearrangement process appeared to be highly variable for the nonproductive CH gene locus: deletion or persistence of 5' CH genes, combinations of deletion and duplication of 5' genes, and deletions extending to 3' CH genes. Our results reveal an unexpected lack of specificity in the DNA deletions in cells that have undergone isotype switching.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Rosenberg N., Casanova R. J., Thomas E., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain expression and class switching in a murine leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):325–331. doi: 10.1038/296325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold A., Cossman J., Bakhshi A., Jaffe E. S., Waldmann T. A., Korsmeyer S. J. Immunoglobulin-gene rearrangements as unique clonal markers in human lymphoid neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 29;309(26):1593–1599. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312293092601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Hansen N. T., Linsley P. S., Cox D. W. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin C gamma genes reveal linkage disequilibrium and genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6952–6956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. A., Liu C., Berenson J. R., Garcia C. R., Wang R., Calame K. L. Immunoglobulin JH, C mu, and C gamma gene rearrangements in human B lymphocytes clonally transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):556–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows P. D., Beck-Engeser G. B., Wabl M. R. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain class switching in a pre-B cell line is accompanied by DNA rearrangement. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):243–246. doi: 10.1038/306243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows P. D., Cooper M. D. The immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984 Sep;63(2):97–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00285216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C., Cooper D., Perry R. P. Rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes during B-lymphocyte development as revealed by studies of mouse plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1422–1426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M. Deletions are associated with somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R., Kruger K., Andrews N., Lutzker S., Baltimore D., Alt F. W. Molecular basis of heavy-chain class switching and switch region deletion in an Abelson virus-transformed cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2905–2910. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Buxbaum J., Hood L. Nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin C gamma 4 gene. DNA. 1981;1(1):11–18. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gathings W. E., Lawton A. R., Cooper M. D. Immunofluorescent studies of the development of pre-B cells, B lymphocytes and immunoglobulin isotype diversity in humans. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Nov;7(11):804–810. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Kataoka T. Organization of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes and allelic deletion model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona I. M., Urban J. F., Jr, Finkelman F. D. B cells that simultaneously express surface IgM and IgE in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis-infected SJA/9 mice do not provide evidence for isotype switching without gene deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):511–515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W., Lawton A. R., Bockman D. E., Cooper M. D. Suppression of immunoglobulin G synthesis as a result of antibody-mediated suppression of immunoglobulin M synthesis in chickens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1918–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A. Immunoglobulin genes: rearrangement and translocation in human lymphoid malignancy. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Jan;4(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00915280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubagawa H., Gathings W. E., Levitt D., Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D. Immunoglobulin isotype expression of normal pre-B cells as determined by immunofluorescence. J Clin Immunol. 1982 Oct;2(4):264–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00915065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubagawa H., Mayumi M., Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D. Immunoglobulin VH determinants defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1010–1024. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritani T., Cooper M. D. Human B cell differentiation. IV. Effect of monoclonal anti-immunoglobulin M and D antibodies on B cell proliferation and differentiation induced by T cell factors. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1306–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Lang R. B., Stanton L. W., Harris L. J. A model for the molecular requirements of immunoglobulin heavy chain class switching. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):87–89. doi: 10.1038/298087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayumi M., Kuritani T., Kubagawa H., Cooper M. D. IgG subclass expression by human B lymphocytes and plasma cells: B lymphocytes precommitted to IgG subclass can be preferentially induced by polyclonal mitogens with T cell help. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):671–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone N., Oliviero S., de Lange G., Delacroix D. L., Boschis D., Altruda F., Silengo L., DeMarchi M., Carbonara A. O. Multiple gene deletions within the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5811–5815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Comparison of the yield of infectious virus from clones of human and simian lymphoblastoid lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1398–1412. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Nakai S., Honjo T. Switch region of immunoglobulin Cmu gene is composed of simple tandem repetitive sequences. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):845–848. doi: 10.1038/292845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Dierich M. P., Reisfeld R. A. Enhancement of sheep red blood cell human lymphocyte rosette formation by the sulfhydryl compound 2-amino ethylisothiouronium bromide. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter A. P., Gilbert W. Antibodies of the secondary response can be expressed without switch recombination in normal mouse B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7189–7193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Hamlyn P. H., Matthyssens G., Roe B. A. The variability, arrangement, and rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes. Can J Biochem. 1980 Mar;58(3):176–187. doi: 10.1139/o80-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Sablitzky F. Deletion of Cmu genes in mouse B lymphocytes upon stimulation with LPS. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1929–1935. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kirsch I. R., Leder P. Evolutionary approach to the question of immunoglobulin heavy chain switching: evidence from cloned human and mouse genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6734–6738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Siebenlist U., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T., Leder P. Structure of the human immunoglobulin mu locus: characterization of embryonic and rearranged J and D genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):583–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L., Johnson G. D., MacLennan I. C. The IgG subclass responses of human lymphocytes to B-cell activators. Immunology. 1983 Oct;50(2):269–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb C. F., Gathings W. E., Cooper M. D. Effect of anti-gamma 3 antibodies on immunoglobulin isotype expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated cultures of mouse spleen cells. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jul;13(7):556–559. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Deletion of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes from expressed allelic chromosome. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):850–853. doi: 10.1038/286850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita Y., Kumagai Y., Okumura K., Honjo T. Expression of lymphocyte surface IgE does not require switch recombination. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):697–699. doi: 10.1038/297697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Tosato G., Blaese R. M., Simon R. M., Nelson D. L. Limiting dilution analysis of Epstein-Barr virus-induced immunoglobulin production by human B cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):1–14. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]