Abstract
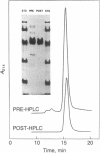
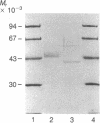
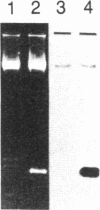
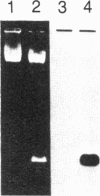
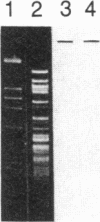
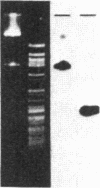
Fabry disease is an X-linked inborn error of metabolism resulting from the deficient activity of the lysosomal hydrolase, alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal A; alpha-D-galactoside galactohydrolase, EC 3.2.1.22). To investigate the structure, organization, and expression of alpha-Gal A, as well as the nature of mutations in Fabry disease, a clone encoding human alpha-Gal A was isolated from a lambda gt11 human liver cDNA expression library. To facilitate screening, an improved affinity purification procedure was used to obtain sufficient homogeneous enzyme for production of monospecific antibodies and for amino-terminal and peptide microsequencing. On the basis of an amino-terminal sequence of 24 residues, two sets of oligonucleotide mixtures were synthesized corresponding to adjacent, but not overlapping, amino acid sequences. In addition, an oligonucleotide mixture was synthesized based on a sequence derived from an alpha-Gal A internal tryptic peptide isolated by reversed-phase HPLC. Four positive clones were initially identified by antibody screening of 1.4 X 10(7) plaques. Of these, only one clone (designated lambda AG18) demonstrated both antibody binding specificity by competition studies using homogeneous enzyme and specific hybridization to synthetic oligonucleotide mixtures corresponding to amino-terminal and internal amino acid sequences. Nucleotide sequencing of the 5' end of the 1250-base-pair EcoRI insert of clone lambda AG18 revealed an exact correspondence between the predicted and known amino-terminal amino acid sequence. The insert of clone lambda AG18 appears to contain the full-length coding region of the processed, enzymatically active alpha-Gal A, as well as sequences coding for five amino acids of the amino-terminal propeptide, which is posttranslationally cleaved during enzyme maturation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J. Affinity purification of alpha-galactosidase A from human spleen, placenta, and plasma with elimination of pyrogen contamination. Properties of the purified splenic enzyme compared to other forms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1307–1316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Wampler D. E., Sgouris J. T., Bonefeld R. J., Anderson D. K., Hawley M. C., Sweeley C. C. Pilot scale purification of alpha-galactosidase A from Cohn fraction IV-1 of human plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 11;524(1):109–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady R. O., Tallman J. F., Johnson W. G., Gal A. E., Leahy W. R., Quirk J. M., Dekaban A. S. Replacement therapy for inherited enzyme deficiency. Use of purified ceramidetrihexosidase in Fabry's disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jul 5;289(1):9–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197307052890103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne C. A., Bennett H. P., Solomon S. The isolation of peptides by high-performance liquid chromatography using predicted elution positions. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 15;124(1):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall J. F., Leary S. L. Detection of early changes in androgen-induced mouse renal beta-glucuronidase messenger ribonucleic acid using cloned complementary deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6049–6053. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean K. J., Sweeley C. C. Studies on human liver alpha-galactosidases. I. Purification of alpha-galactosidase A and its enzymatic properties with glycolipid and oligosaccharide substrates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):9994–10000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean K. J., Sweeley C. C. Studies on human liver alpha-galactosidases. II. Purification and enzymatic properties of alpha-galactosidase B (alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase). J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10001–10005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnick R. J., Dean K. J., Grabowski G., Bishop D. F., Sweeley C. C. Enzyme therapy in Fabry disease: differential in vivo plasma clearance and metabolic effectiveness of plasma and splenic alpha-galactosidase A isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5326–5330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. F., DuToit D. L., Warnich L., Retief A. E. Regional localization of alpha-galactosidase (GLA) to Xpter----q22, hexosaminidase B (HEXB) to 5q13----qter, and arylsulfatase B (ARSB) to 5pter----q13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(1):45–49. doi: 10.1159/000132028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., de Wet J. R., O'Brien J. S. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for human alpha-L-fucosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1262–1265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginns E. I., Choudary P. V., Martin B. M., Winfield S., Stubblefield B., Mayor J., Merkle-Lehman D., Murray G. J., Bowers L. A., Barranger J. A. Isolation of cDNA clones for human beta-glucocerebrosidase using the lambda gt11 expression system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):574–580. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieber V. C. Cloning of a cDNA complementary to rat preputial gland beta-glucuronidase mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1271–1278. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Sarver N., Law M. F. Eukaryotic cloning vectors derived from bovine papillomavirus DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Protein sequence analysis: automated microsequencing. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):650–659. doi: 10.1126/science.6687410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw R. A., 3rd Dideoxy DNA sequencing with end-labeled oligonucleotide primers. Anal Biochem. 1984 Dec;143(2):298–303. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90666-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Proia R. L. cDNA clone for the alpha-chain of human beta-hexosaminidase: deficiency of alpha-chain mRNA in Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5394–5398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Quan F., Willard H. F., Lamhonwah A. M., Korneluk R. G., Lowden J. A., Gravel R. A., Mahuran D. J. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the beta subunit of human beta-hexosaminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. T., Fluharty A. L., Kihara H. Correction of abnormal cerebroside sulfate metabolism in cultured metachromatic leukodystrophy fibroblasts. Science. 1971 Jun 18;172(3989):1263–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3989.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Ho Y. S., Shatzman A. The use of pKc30 and its derivatives for controlled expression of genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:123–138. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWEELEY C. C., KLIONSKY B. FABRY'S DISEASE: CLASSIFICATION AS A SPHINGOLIPIDOSIS AND PARTIAL CHARACTERIZATION OF A NOVEL GLYCOLIPID. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3148–3150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schram A. W., Hamers M. N., Tager J. M. The identity of alpha-galactosidase B from human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 12;482(1):138–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90361-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Schlesinger P. H., Sigardson E., Rodman J. S., Lee Y. C. Receptor-mediated pinocytosis of mannose glycoconjugates by macrophages: characterization and evidence for receptor recycling. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Fukushima H., Dewji N. N., Wilcox E., O'Brien J. S., Helinski D. R. Chromogenic immunodetection of human serum albumin and alpha-L-fucosidase clones in a human hepatoma cDNA expression library. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):437–447. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]