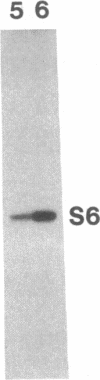
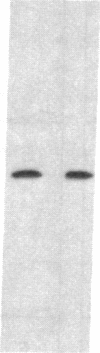
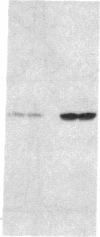
Abstract
Protein kinase capable of phosphorylating 40S ribosomal protein S6 on serine residues has been detected in chicken embryo fibroblasts. This activity appears to be regulated in direct response to expression of pp60v-src in chicken embryo fibroblasts infected with a temperature-sensitive transformation mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Partially purified S6 kinase was highly specific for S6 in 40S ribosomal subunits. The S6 kinase was not inhibited by calcium or by the heat-stable inhibitor of cAMP-dependent protein kinase, nor was it activated by phosphatidylserine, diacylglycerol, and calcium. Thus, it is distinct from protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which are capable of phosphorylating S6 in vitro. The tumor-promoter phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate also stimulated ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity in serum-starved chicken embryo fibroblasts, whereas phorbol, the inactive analog of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, had no effect. S6 kinase activity stimulated by expression of pp60v-src, by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, or by serum growth factors exhibited similar chromatographic properties upon ion-exchange chromatography. These results suggest that a common protein kinase may be activated by three diverse stimuli all involved in regulating cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF

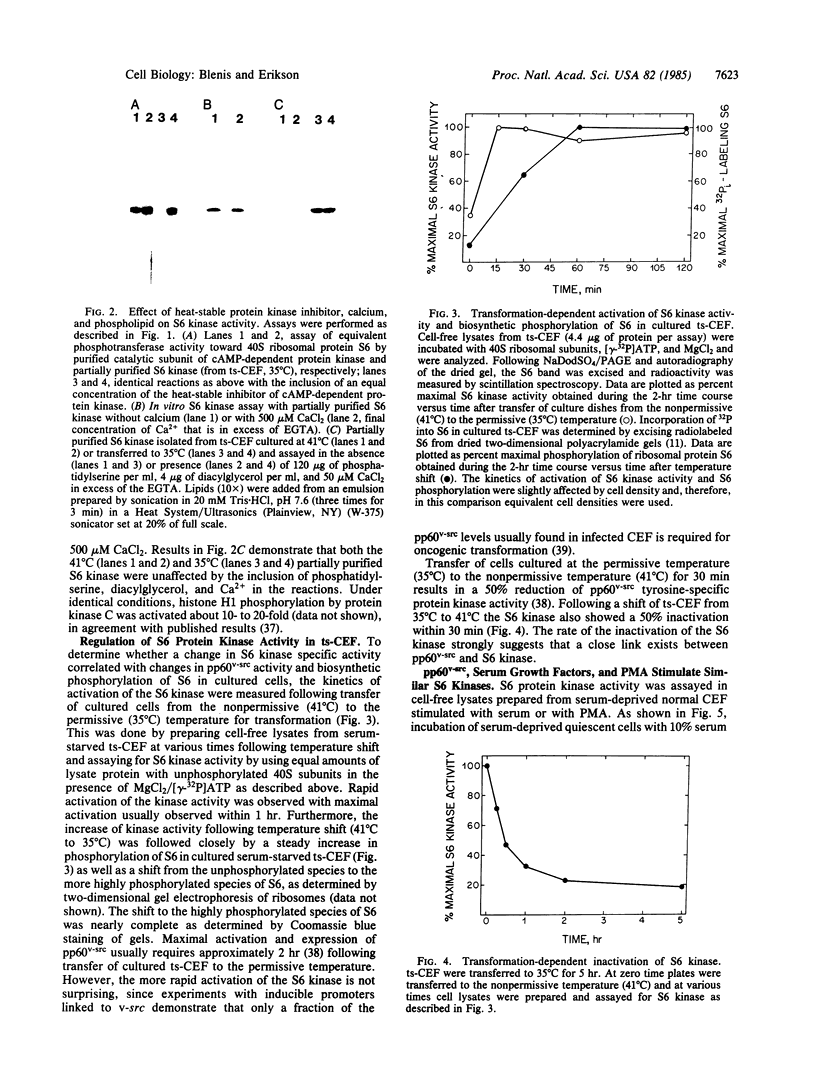

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R., Martinez R., Nakamura K. D., Weber M. J. A tumor promoter stimulates phosphorylation on tyrosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 15;115(2):536–543. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Phosphorylation of the ribosomal protein S6 is elevated in cells transformed by a variety of tumor viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):966–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.966-969.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Spivack J. G., Erikson R. L. Phorbol ester, serum, and rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product induce similar phosphorylations of ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommer U. A., Noll F., Lutsch G., Bielka H. Immunochemical detection of proteins in the small subunit of rat liver ribosomes involved in binding of the ternary initiation complex. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80785-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhard S. J., Traugh J. A. Changes in ribosome function by cAMP-dependent and cAMP-independent phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14003–14008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Le Cam A., Pouysségur J. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in G0/G1-arrested fibroblasts. Two distinct classes of growth factors with potentiating effects. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1706–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Rosen O. M. Description of a protein kinase derived from insulin-treated 3T3-L1 cells that catalyzes the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and casein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12472–12481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Diverse mitogenic agents induce the phosphorylation of two related 42,000-dalton proteins on tyrosine in quiescent chick cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in avian sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4112–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., McConkey E. H. Preferential utilization of phosphorylated 40-S ribosomal subunits during initiation complex formation. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):535–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. A protein kinase from Xenopus eggs specific for ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Collett M. S., Brugge J. S. Molecular events in cells transformed by Rous Sarcoma virus. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):319–325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli B., Wettenhall R. E., Kemp B. E., Quinn M., Bizonova L. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and a peptide analogue of S6 by a protease-activated kinase isolated from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80740-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Phorbol ester and diacylglycerol induce protein phosphorylation at tyrosine. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):487–490. doi: 10.1038/306487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Humbel R. E., Thomas G. Insulin-like growth factor: insulin or serum increase phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of stationary chick embryo fibroblasts into early G1 phase of the cell cycle. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Tyrosine protein kinases and their substrates: an overview. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:443–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Hormonal regulation of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene via a heterologous promoter defines a threshold dose for cellular transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Cooperative roles of various membrane phospholipids in the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7146–7149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisilevsky R., Treloar M. A., Weiler L. Ribosome conformational changes associated with protein S6 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1351–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastick S. M., McConkey E. H. Control of ribosomal protein phosphorylation in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):917–923. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91560-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Purified rat brain calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Foulkes J. G., Erikson E., Baltimore D. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 on serine after microinjection of the Abelson murine leukemia virus tyrosine-specific protein kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):272–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Thomas G., Maller J. L. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen-Hamilton M., Hamilton R. T., Allen W. R., Potter-Perigo S. Synergistic stimulation of S6 ribosomal protein phosphorylation and DNA synthesis by epidermal growth factor and insulin in quiescent 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 30;156(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Traugh J. A. Protease-activated kinase II as the potential mediator of insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9589–9592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes and cell-free extracts derived from them incorporate 32P into ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2641–2645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Wejksnora P. J., Warner J. R., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2725–2729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terao K., Ogata K. Proteins of small subunits of rat liver ribosomes that interact with poly(U). II. Cross-links between poly(U) and ribosomal proteins in 40 S subunits induced by UV irradiation. J Biochem. 1979 Sep;86(3):605–617. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Gordon J. Multiple phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of quiescent 3T3 cells into early G1, and cellular compartmentalization of the phosphate donor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevillyan J. M., Kulkarni R. K., Byus C. V. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in quiescent Reuber H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):897–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Ashby C. D., Gonzalez C., Calkins D., Fischer E. H. Krebs EG: Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1977–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Cohen P. Isolation and characterisation of cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation sites from rat liver ribosomal protein S6. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]