Abstract
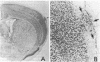
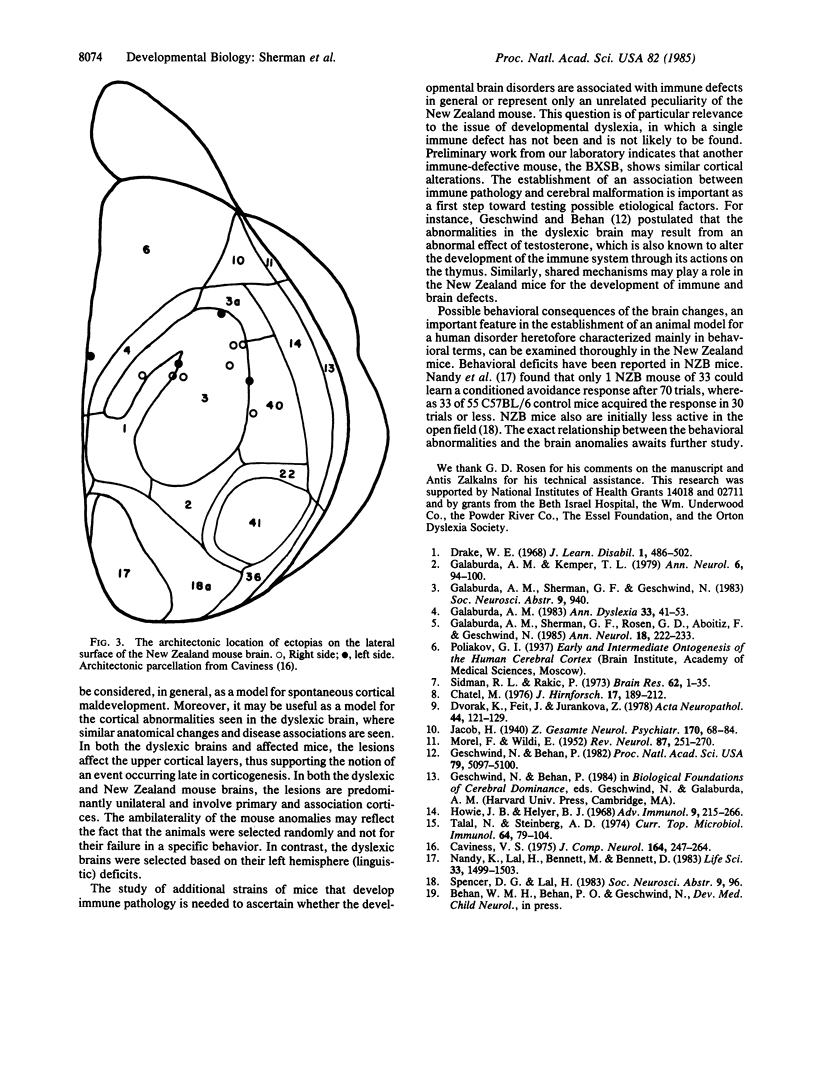
Cortical anomalies have been reported in the brains of dyslexic individuals. In addition, dyslexic and left-handed individuals have a higher than expected rate of some immune-related diseases. The possible association between immune and cerebrocortical pathology was investigated in the immune-defective New Zealand Black mouse and its hybrid with the New Zealand White mouse. Structural anomalies similar to those present in the dyslexic brain were seen in the brains of these mice.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caviness V. S., Jr Architectonic map of neocortex of the normal mouse. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Nov 15;164(2):247–263. doi: 10.1002/cne.901640207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatel M. Développement de l'isocortex du cerveau humain pendant les périodes embryonnaires et foetales jusqu'à la 24 éme semaine de gestation. J Hirnforsch. 1976;17(3):189–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak K., Feit J., Juránková Z. Experimentally induced focal microgyria and status verrucosus deformis in rats--pathogenesis and interrelation. Histological and autoradiographical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1978 Nov 15;44(2):121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00691477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galaburda A. M., Kemper T. L. Cytoarchitectonic abnormalities in developmental dyslexia: a case study. Ann Neurol. 1979 Aug;6(2):94–100. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galaburda A. M., Sherman G. F., Rosen G. D., Aboitiz F., Geschwind N. Developmental dyslexia: four consecutive patients with cortical anomalies. Ann Neurol. 1985 Aug;18(2):222–233. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geschwind N., Behan P. Left-handedness: association with immune disease, migraine, and developmental learning disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5097–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie J. B., Helyer B. J. The immunology and pathology of NZB mice. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:215–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOREL F., WILDI E. Dysgénésie nodulaire disséminée de l'écorce frontale. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1952;87(3):251–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandy K., Lal H., Bennett M., Bennett D. Correlation between a learning disorder and elevated brain-reactive antibodies in aged C57BL/6 and young NZB mice. Life Sci. 1983 Oct 10;33(15):1499–1503. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90853-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman R. L., Rakic P. Neuronal migration, with special reference to developing human brain: a review. Brain Res. 1973 Nov 9;62(1):1–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90617-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Steinberg A. D. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand black mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;64(0):79–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65848-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]