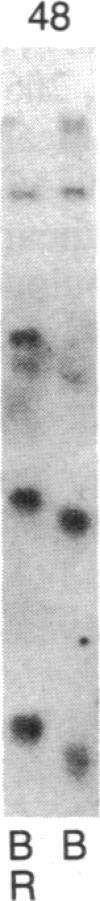
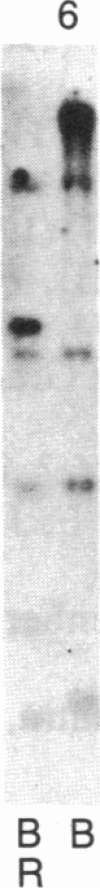
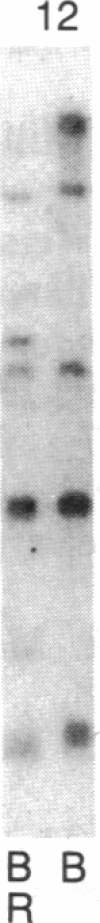
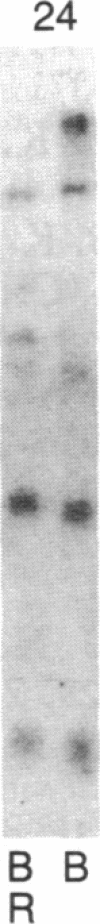
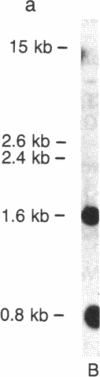
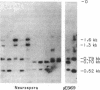
Abstract
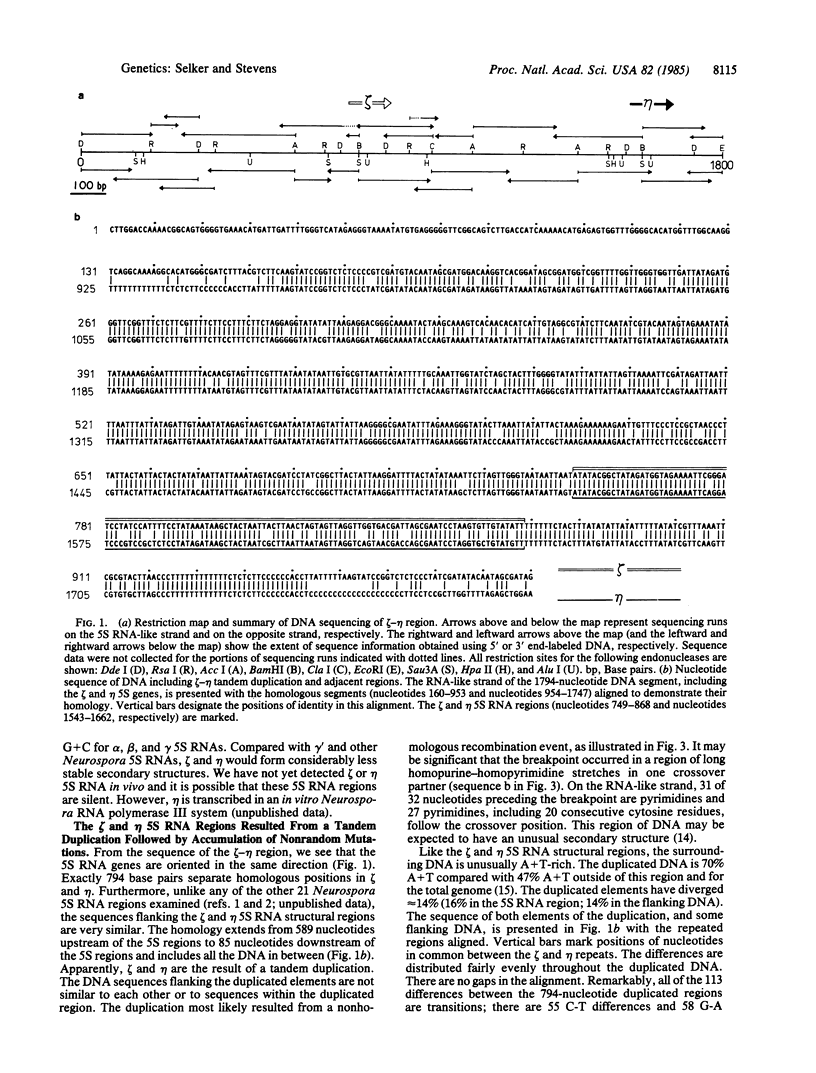
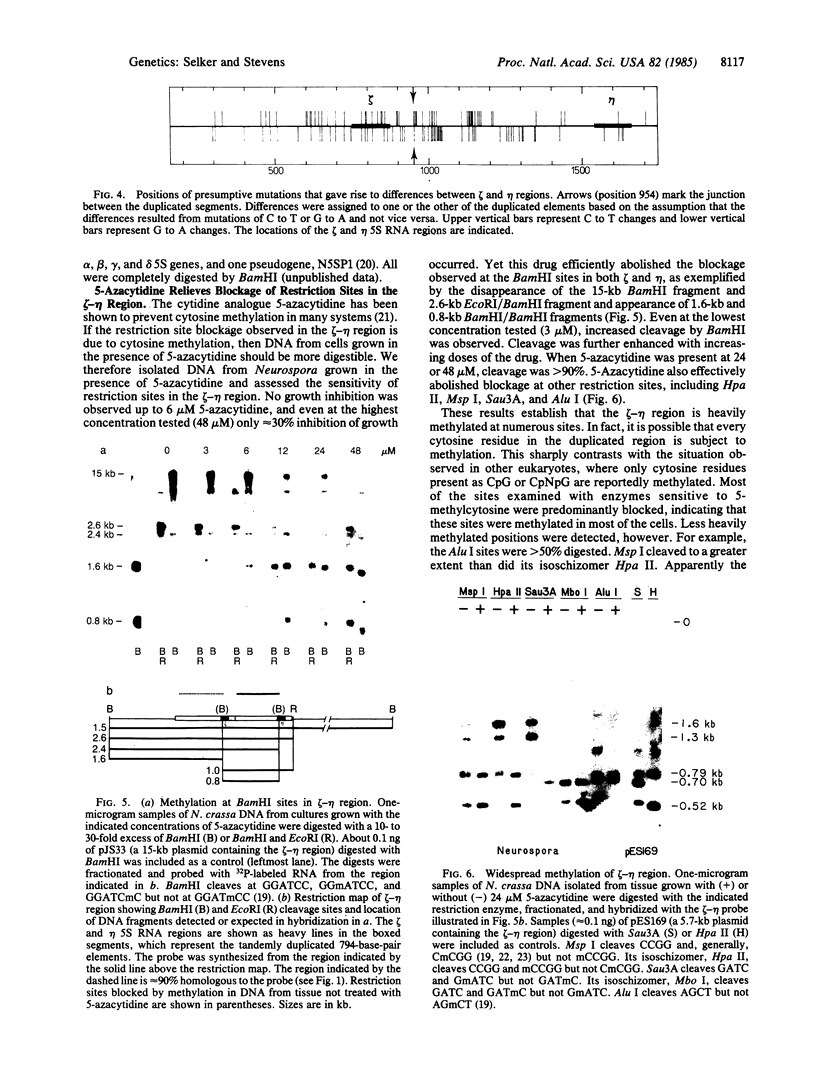
We describe two unusual 5S RNA regions from Neurospora crassa that are tightly linked. Sequence analysis suggests that these genes or pseudogenes, which we designate zeta (zeta) and eta (eta), arose by a 794-base-pair tandem duplication followed by hundreds of exclusively cytosine to thymine mutations. The duplication was most likely generated by nonhomologous recombination involving a DNA segment having a striking purine-pyrimidine strand asymmetry. Restriction analysis of genomic DNA from tissue grown in the presence or absence of 5-azacytidine indicates that many, and perhaps all, cytosines in the duplicated region are methylated in most cells. This is in contrast to the situation typically observed in eukaryotes, where 5-methylcytosine is found only at positions one or two nucleotides preceding guanine residues. No DNA methylation was detected in the unique DNA flanking the zeta-eta duplication. Thus the "signal" for methylation may be the duplication itself. The numerous transition mutations in this region probably occurred by deamination of 5-methylcytosines. Our results suggest that DNA methylation can have important evolutionary consequences in eukaryotes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busslinger M., deBoer E., Wright S., Grosveld F. G., Flavell R. A. The sequence GGCmCGG is resistant to MspI cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. K., Miller J. H. Mutagenic deamination of cytosine residues in DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):560–561. doi: 10.1038/287560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. K., Weiss B. Specific mutator effects of ung (uracil-DNA glycosylase) mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):750–755. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.750-755.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Anatomy of hypersensitive sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):213–214. doi: 10.1038/309213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Huysmans E., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S ribosomal RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r105–r133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Cedar H. Effect of CpG methylation on Msp I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3571–3580. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Wu C. I., Luo C. C. Nonrandomness of point mutation as reflected in nucleotide substitutions in pseudogenes and its evolutionary implications. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(1):58–71. doi: 10.1007/BF02100628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Nelson M. The effect of site specific methylation on restriction endonuclease digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r201–r207. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L., Stevens J. N., Selker E. U., Morzycka-Wroblewska E. Identification and chromosomal distribution of 5S rRNA genes in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Selker E. U., Stevens J. N., Metzenberg R. L. Concerted evolution of dispersed Neurospora crassa 5S RNA genes: pattern of sequence conservation between allelic and nonallelic genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):46–51. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Structure and function of 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. II. Partial digestion with ribonucleases and derivation of the complete sequence. J Biochem. 1974 Nov;76(5):935–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Free S. J., Metzenberg R. L., Yanofsky C. An isolated pseudogene related to the 5S RNA genes in Neurospora crassa. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):576–578. doi: 10.1038/294576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Stevens J. N., Metzenberg R. L. Heterogeneity of 5S RNA in fungal ribosomes. Science. 1985 Mar 15;227(4692):1340–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.2579431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Yanofsky C., Driftmier K., Metzenberg R. L., Alzner-DeWeerd B., RajBhandary U. L. Dispersed 5S RNA genes in N. crassa: structure, expression and evolution. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):819–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]