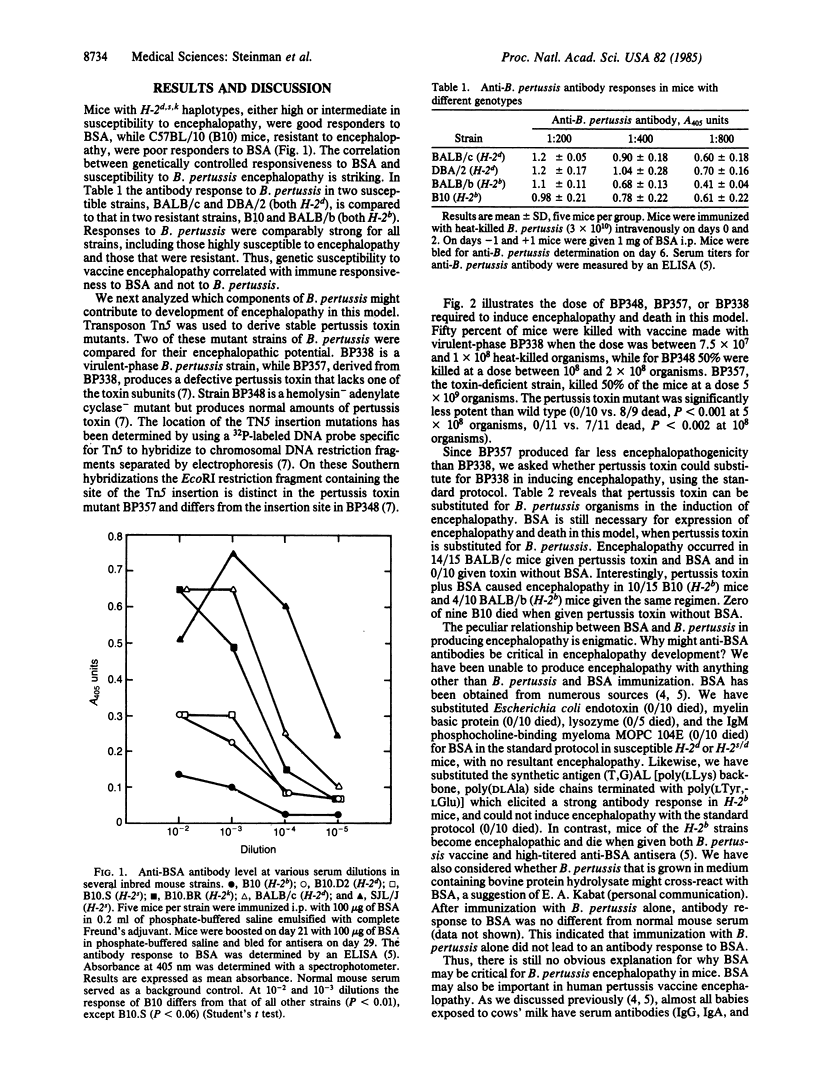
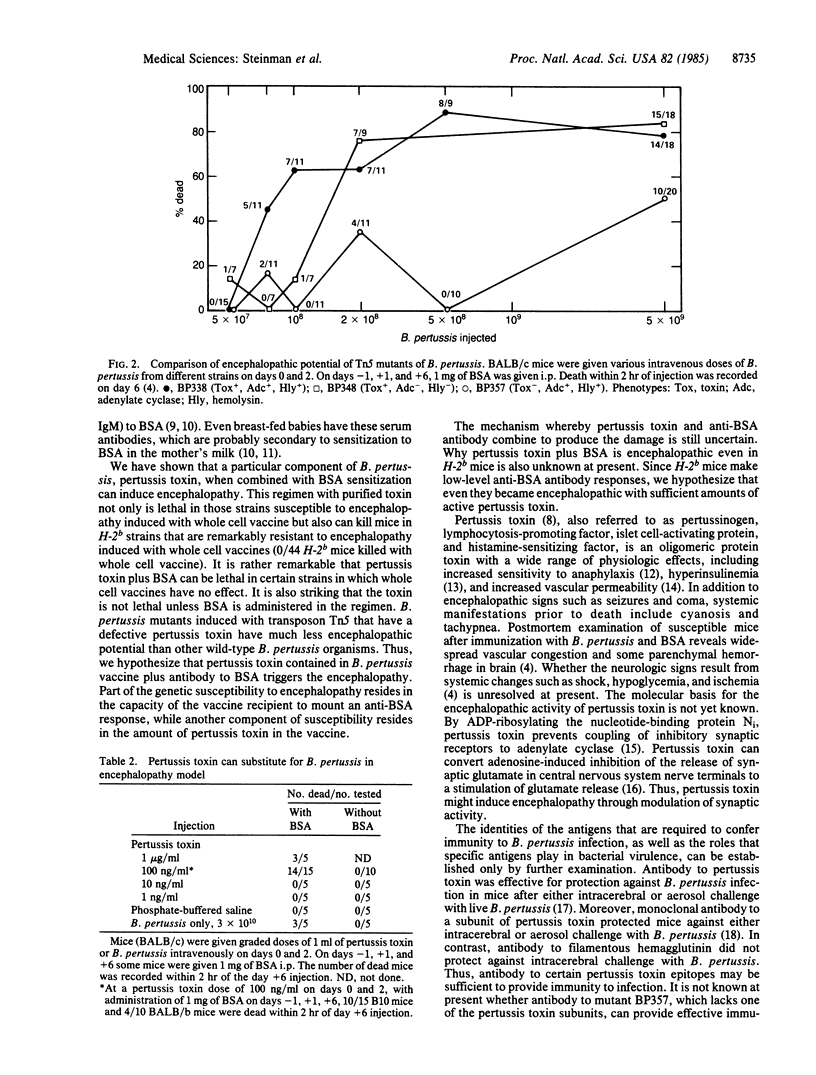
Abstract
A mouse model for encephalopathy induced by pertussis immunization has been described; it has features that closely resemble some of the severe reactions, including seizures and a shock-like state leading to death, occasionally seen after administration of Bordetella pertussis (whooping cough) vaccine. Susceptibility to encephalopathy maps to genes of the major histocompatibility complex and correlates as well with the genetic regulation of the level of antibody response to bovine serum albumin. In this study we have investigated which bacterial determinant is responsible for the encephalopathy. Two lines of evidence implicate pertussis toxin as the active bacterial component. Single-site mutants of B. pertussis with single affected virulence factors were tested. A mutant that produces a defective pertussis toxin had greatly diminished capacity to induce encephalopathy, whereas a hemolysin- and adenylate-cyclase-deficient avirulent mutant had the same activity in the mouse model as a virulent strain. Purified pertussis toxin plus bovine serum albumin was tested and found to induce the lethal encephalopathy, demonstrating that the toxin was the critical constituent of B. pertussis responsible for encephalopathy.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cody C. L., Baraff L. J., Cherry J. D., Marcy S. M., Manclark C. R. Nature and rates of adverse reactions associated with DTP and DT immunizations in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1981 Nov;68(5):650–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Prestwich S. A. Pertussis toxin reverses adenosine inhibition of neuronal glutamate release. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):148–150. doi: 10.1038/316148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNTHER M., ASCHAFFENBURG R., MATTHEWS R. H., PARISH W. E., COOMBS R. R. The level of antibodies to the proteins of cow's milk in the serum of normal human infants. Immunology. 1960 Oct;3:296–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Sauer K. T., Myers G. A., Cowell J. L., Guerrant R. L. Induction of a novel morphological response in Chinese hamster ovary cells by pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1198-1203.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinman A. R., Koplan J. P. Pertussis and pertussis vaccine. Reanalysis of benefits, risks, and costs. JAMA. 1984 Jun 15;251(23):3109–3113. doi: 10.1001/jama.251.23.3109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletter B., Gery I., Freier S., Davies A. M. Immune responses of normal infants to cow milk. I. Antibody type and kinetics of production. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(4-5):656–666. doi: 10.1159/000230447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Ross E. M., Alderslade R., Bellman M. H., Rawson N. S. Pertussis immunisation and serious acute neurological illness in children. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 16;282(6276):1595–1599. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6276.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Arai H., Bergman R. K., Sadowski P. L. Biological activities of crystalline pertussigen from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J. J., Bernard C. C., Mackay I. R. Elicitation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice with the aid of pertussigen. Cell Immunol. 1984 Jan;83(1):92–100. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBERG R. M., FARR R. S. ANTI-BOVINE SERUM ALBUMIN AND ANTI-ALPHA LACTALBUMIN IN THE SERUM OF CHILDREN AND ADULTS. Pediatrics. 1965 Apr;35:571–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley R. L., Wilson L. D., Germain R. N., Benjamin D. C. Immune responses to complex protein antigens I. MHC control of immune responses to bovine albumin. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1553–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Ito A., Chiba J., Sato Y. Monoclonal antibody against pertussis toxin: effect on toxin activity and pertussis infections. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):422–428. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.422-428.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y. Bordetella pertussis infection in mice: correlation of specific antibodies against two antigens, pertussis toxin, and filamentous hemagglutinin with mouse protectivity in an intracerebral or aerosol challenge system. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):415–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.415-421.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Sriram S., Adelman N. E., Zamvil S., McDevitt H. O., Urich H. Murine model for pertussis vaccine encephalopathy: linkage to H-2. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):738–740. doi: 10.1038/299738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima M., Hosoda K., Kanbayashi Y., Nakamura T., Nogimori K., Mizushima Y., Nakase Y., Ui M. Islets-activating protein (IAP) in Bordetella pertussis that potentiates insulin secretory responses of rats. Purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1978 Jan;83(1):295–303. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


