Abstract
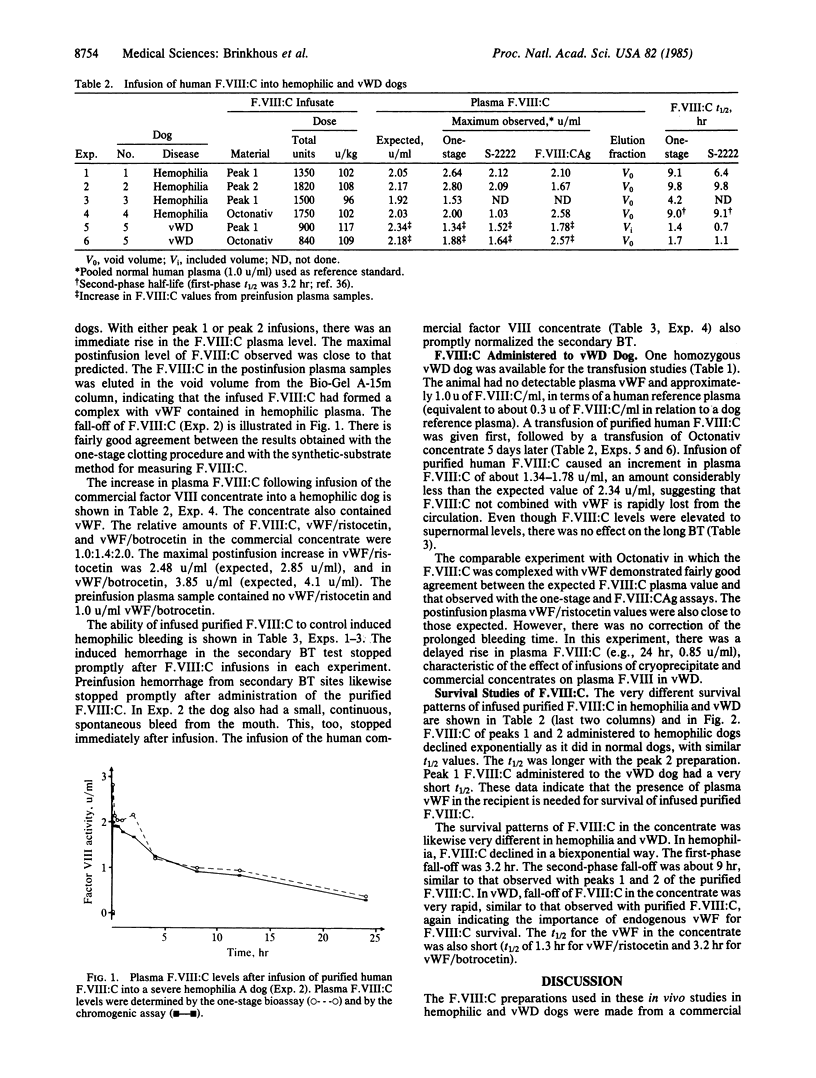
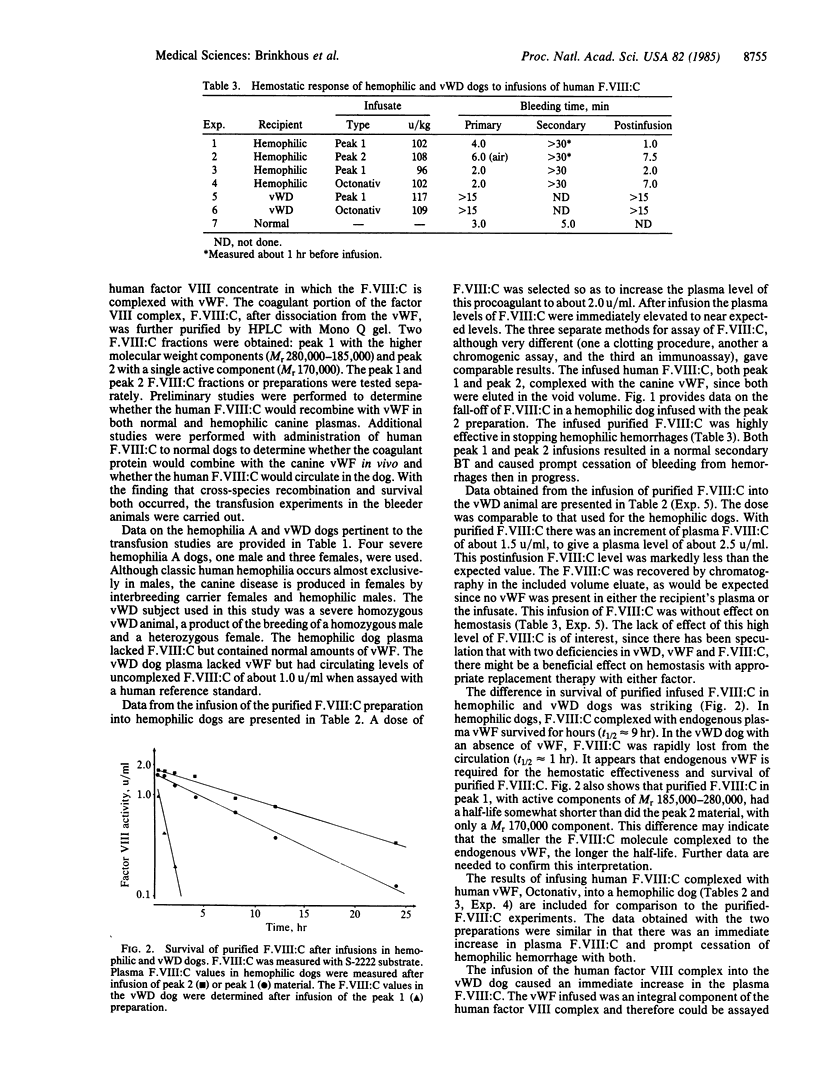
The procoagulant protein F.VIII:C is noncovalently bound to von Willebrand factor (vWF) to give the factor VIII macromolecular complex. New highly purified preparations of isolated human F.VIII:C, devoid of vWF and about 500,000-fold purified, were administered to hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease (vWD) dogs to determine their hemostatic effectiveness and survival in the circulation. Two preparations of F.VIII:C were used: peak 1, with active components of Mr 185,000-280,000, and peak 2, with a single component of Mr 170,000. In hemophilic dogs, with no plasma F.VIII:C but normal vWF, both preparations immediately elevated plasma F.VIII:C to expected levels, promptly stopped induced and spontaneous hemorrhages, and gave sustained plasma levels of F.VIII:C. The isolated F.VIII:C immediately complexed with endogenous vWF in hemophilic plasma and was eliminated exponentially, with a half-life (t1/2) of about 9 hr. Survival of peak 2 F.VIII:C was longer than that of peak 1 material. In contrast, F.VIII:C complexed to vWF in a therapeutic concentrate administered to hemophilic dogs was eliminated biexponentially with first-phase t1/2 of 3.2 hr and second-phase t1/2 of 9 hr. In vWD dogs with no vWF and reduced F.VIII:C levels, the isolated F.VIII:C produced supernormal levels of F.VIII:C without effect on induced bleeding. It was rapidly eliminated from plasma with a t1/2 of about 1 hr, as was the complexed F.VIII:C in the concentrate. These data indicate that isolated F.VIII:C promptly complexes with vWF and in this form is highly effective in controlling hemophilic hemorrhages with good survival in plasma. Without endogenous vWF with which to complex, the F.VIII:C is promptly eliminated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton P. G. Sequence theories of blood coagulation re-evaluated with reference to lipid-protein interactions. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1508–1509. doi: 10.1038/2151508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt P. M., Brinkhous K. M., Culp H. R., Krauss J. S., Roberts H. R. Antihemophilic factor concentrate therapy in von Willebrand disease. Dissociation of bleeding-time factor and ristocetin-cofactor activities. JAMA. 1976 Dec 13;236(24):2770–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S., Reddick R. L., Griggs T. R. Pathophysiology of platelet-aggregating von Willebrand factor: applications of the venom coagglutinin vWF assay. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:191–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S. Use of venom coagglutinin and lyophilized platelets in testing for platelet-aggregating von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):517–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang T. F., Sargeant R. B., Hougie C. The intrinsic activation of factor X in blood coagulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 19;273(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Griggs T. R., Wagner R. H. Factor VIII recombination after dissociation by CaCl12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2326–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H. The defect in hemophilic and von Willebrand's disease plasmas studied by a recombination technique. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1093–1099. doi: 10.1172/JCI107853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K. Basic mechanisms in blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:799–829. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Chavin S. I., Schroeder D., Young F. E., Marder V. J. Purification and characterization of a highly purified human factor VIII consisting of a single type of polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7200–7204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Zimmerman T. S. Characterization of the human factor VIII procoagulant protein with a heterologous precipitating antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles A. R., Tinlin S., Greenwood R. A canine model of hemophilic (factor VIII:C deficiency) bleeding. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):727–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs T. R., Cooper H. A., Webster W. P., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Plasma aggregating factor (bovine) for human platelets: a marker for study of antihemophilic and von Willebrand Factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemker H. C., Kahn M. J. Reaction sequence of blood coagulation. Nature. 1967 Sep 9;215(5106):1201–1202. doi: 10.1038/2151201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Borge L., Ljung R., Nilsson I. M. Measurement of antihaemophilic factor A antigen (VII:CAg) with a solid phase immunoradiometric method based on homologous non-haemophilic antibodies. Scand J Haematol. 1979 Jul;23(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb02847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Ljung R. Purification of F.VIII:C by antigen-antibody chromatography. Thromb Res. 1978 Apr;12(4):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90256-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougie C., Denson K. W., Biggs R. A study of the reaction product of factor 8 and factor IX by gel filtration. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Aug 15;18(1-2):211–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson G. J., Fass D. N. Porcine factor VIII:C prepared by affinity interaction with von Willebrand factor and heterologous antibodies: sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel analysis. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):615–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBLAD R. L., DAVIE E. W. THE ACTIVATION OF ANTIHEMOPHILIC FACTOR (FACTOR 8) BY ACTIVATED CHRISTMAS FACTOR (ACTIVATED FACTOR9 9). Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1720–1725. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Synthesis of intrinsic factor X activator. Inhibition of the function of formed activator by antibodies to factor VIII and to factor IX. Biochemistry. 1970 Apr 14;9(8):1854–1861. doi: 10.1021/bi00810a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Wagner R. H. Antihemophilic factor: separation of an active fragment following dissociation by salts or detergents. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):502–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Potter J. Y., Brinkhous K. M. Venom coagglutinin for detection of von Willebrand factor activity in animal plasmas. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Jan;101(1):74–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). V. Immunologic properties of AHF subunits produced by salt dissociation. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):737–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Molecular weight of human factor VIII procoagulant activity. Thromb Res. 1975 Dec;7(6):909–916. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosén S. Assay of factor VIII:C with a chromogenic substrate. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1984;40:139–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1984.tb02556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THELIN G. M., WGNER R. H. Sedimentation of plasma antihemophilic factor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Oct;95:70–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuddenham E. G., Trabold N. C., Collins J. A., Hoyer L. W. The properties of factor VIII coagulant activity prepared by immunoadsorbent chromatography. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jan;93(1):40–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. E., Webster W. P., Strike L. E., Brinkhous K. M. Survival of transfused factor VIII in hemophilic patients treated with epsilon aminocaproic acid. Transfusion. 1976 May-Jun;16(3):209–214. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1976.16376225490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Hoyer I. W. Von Willebrand factor: dissociation from antihemophilic factor procoagulant activity. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Kochwa S. Molecular forms of antihaemophilic globulin in plasma, cryoprecipitate and after thrombin activation. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jan;18(1):89–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Phillips L. L., Rosner W. Separation of sub-units of antihemophilic factor (AHF) by agarose gel chromatography. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Apr 30;27(2):212–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Capon D. J., Simonsen C. C., Eaton D. L., Gitschier J., Keyt B., Seeburg P. H., Smith D. H., Hollingshead P., Wion K. L. Expression of active human factor VIII from recombinant DNA clones. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):330–337. doi: 10.1038/312330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M., Fulcher C. A. Factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Prog Hematol. 1983;13:279–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Soberano M. E., Johnson A. J., Fulton A. J., Kowalski S., Adler M. The in vitro association of antihemophilic factor and von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Feb 28;49(1):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


