Abstract
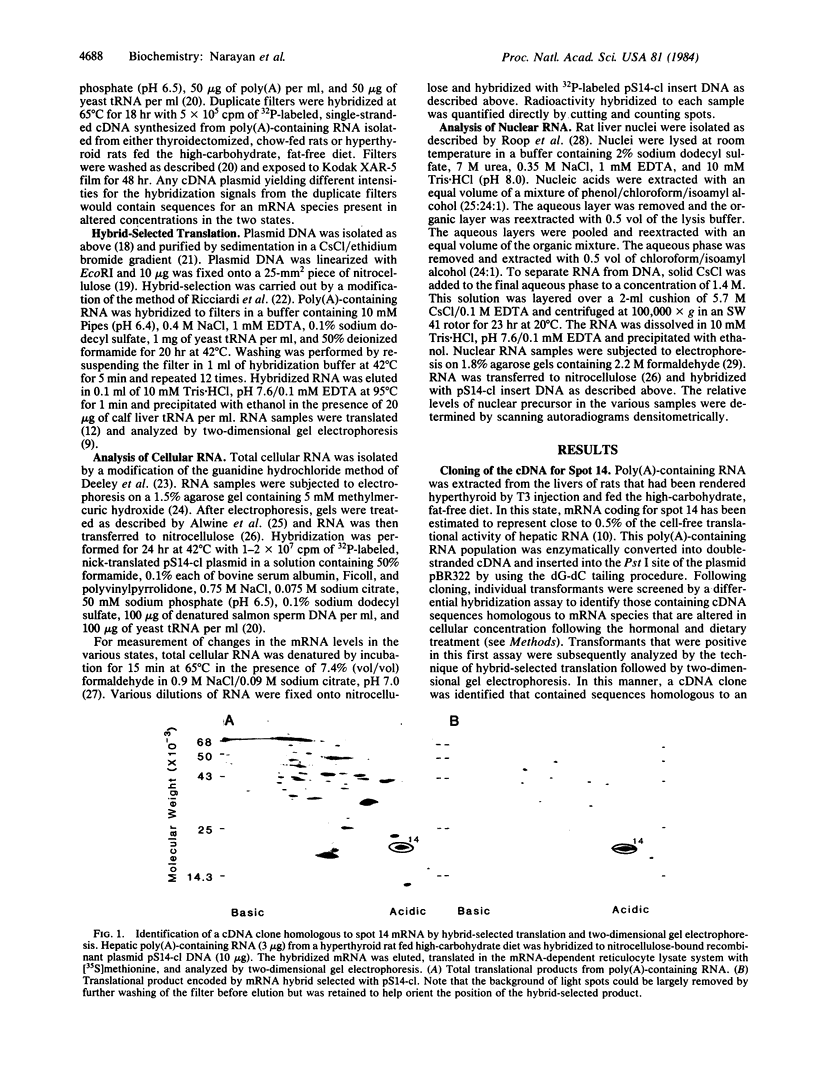
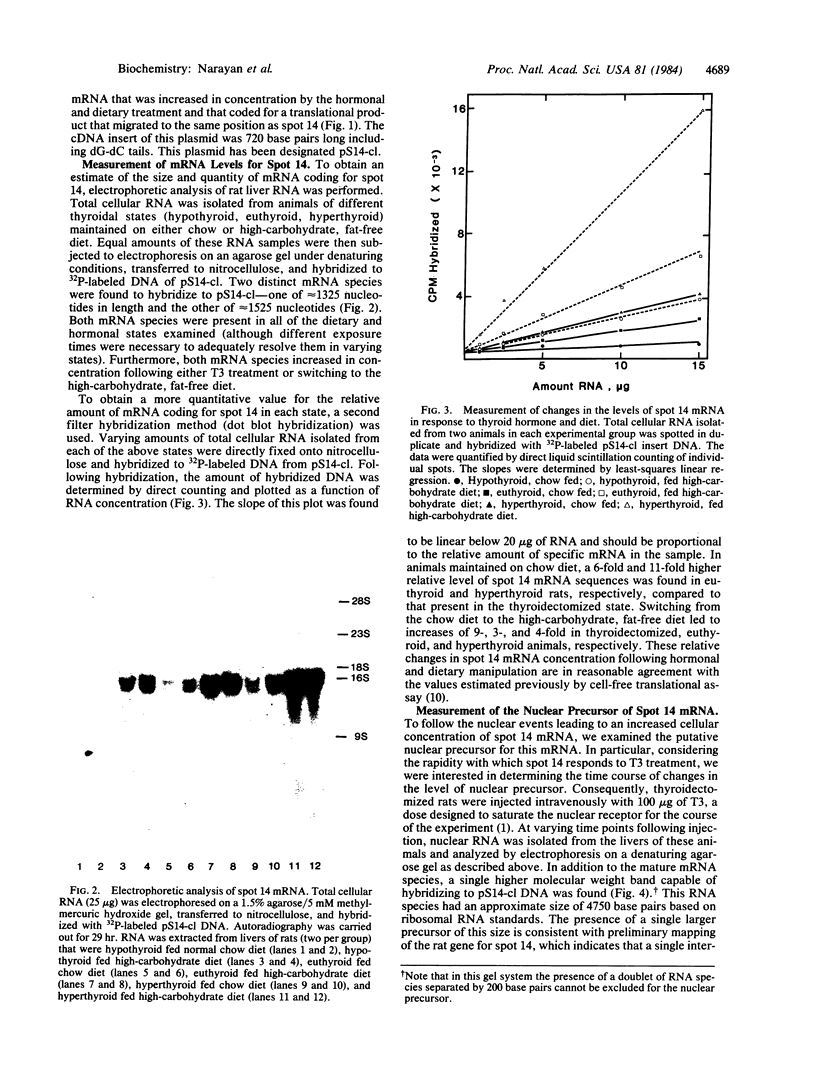
Administration of thyroid hormone to the thyroidectomized rat results in a rapid and dramatic increase in the relative amount of hepatic mRNA coding for spot 14--a translational product with an approximate Mr of 17,500 and isoelectric point of 4.9. We have now isolated a cDNA clone containing sequences homologous to this thyroid hormone-responsive mRNA. Two distinct mRNA species that differed by 200 nucleotides in length were found to be capable of hybridizing to the cDNA probe. Both mRNA species were proportionally elevated in relative concentration in rats with increasing plasma levels of thyroid hormone. The earliest change in the levels of mature mRNA occurred at 20 minutes following thyroid hormone treatment of the thyroidectomized rat. Analysis of nuclear RNA revealed a single higher molecular weight species that was homologous to spot 14 mRNA. An increase in the nuclear level of this putative precursor occurred by 10 minutes following thyroid hormone administration, a time preceding the earliest change in mature mRNA. Thus, thyroid hormone appears to act at least in part at a nuclear level in altering the cellular concentration of this mRNA species. The rapidity of this change suggests that it may reflect a direct response to the binding of thyroid hormone to its nuclear receptor.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Gordon J. I., Burns A. T., Mullinix K. P., Binastein M., Goldberg R. F. Primary activation of the vitellogenin gene in the rooster. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8310–8319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Birnberg N. C., Rosenfeld M. G. Glucocorticoid and thyroid hormones transcriptionally regulate growth hormone gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7659–7663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz D. T. Rat alpha 2u globulin is encoded by a multigene family. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(1):29–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liaw C. W., Towle H. C. Characterization of a thyroid hormone-responsive gene from rat. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7253–7260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liaw C., Seelig S., Mariash C. N., Oppenheimer J. H., Towle H. C. Interactions of thyroid hormone, growth hormone, and high carbohydrate, fat-free diet in regulating several rat liver messenger ribonucleic acid species. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):213–221. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martial J. A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M., Seeburg P. H. Regulation of growth hormone messenger RNA by thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R. J., Towle H. C. Changes in the rates of synthesis and messenger RNA levels of hepatic glucose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases following induction by diet or thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11829–11835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan J. J., Harris S. E., Woo S. L., Robberson D. L., O'Malley B. W. The synthesis and properties of the complete complementary DNA transcript of ovalbumin mRNA. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):223–233. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H. Thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Science. 1979 Mar 9;203(4384):971–979. doi: 10.1126/science.218285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock S. L., McIver C. M., Monahan J. J. Transformation of E. coli using homopolymer-linked plasmid chimeras. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 28;655(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Nordstrom J. L., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Transcription of structural and intervening sequences in the ovalbumin gene and identification of potential ovalbumin mRNA precursors. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):671–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):101–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Perlman A. J., Raaka B. M., Stanley F. Organization of the thyroid hormone receptor in chromatin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1982;38:557–599. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571138-8.50018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig S., Jump D. B., Towle H. C., Liaw C., Mariash C. N., Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Paradoxical effects of cycloheximide on the ultra-rapid induction of two hepatic mRNA sequences by triiodothyronine (T3). Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):671–673. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig S., Liaw C., Towle H. C., Oppenheimer J. H. Thyroid hormone attenuates and augments hepatic gene expression at a pretranslational level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4733–4737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo H., Vassart G., Brocas H., Refetoff S. Triiodothyronine stimulates specifically growth hormone mRNA in rat pituitary tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2054–2058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. E., Samuels H. H., Yaffe B. M. Thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones synergistically control growth hormone mRNA in cultured GH1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):45–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui U. A., Goldflam T., Goodridge A. G. Nutritional and hormonal regulation of the translatable levels of malic enzyme and albumin mRNAs in avian liver cells in vivo and in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4544–4550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Rosenbaum J. L. Multiple alpha- and beta-tubulin genes in Chlamydomonas and regulation of tubulin mRNA levels after deflagellation. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90503-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler S. R., Mellon S. H., Baxter J. D. Growth hormone gene transcription is regulated by thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones in cultured rat pituitary tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11627–11632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle H. C., Mariash C. N., Oppenheimer J. H. Changes in the hepatic levels of messenger ribonucleic acid for malic enzyme during induction by thyroid hormone or diet. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):579–585. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterman R. D., Lynch K. R., Nakhasi H. L., Dolan K. P., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V., Feigelson P. Cloning and sequence of several alpha 2u-globulin cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3478–3482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Broome S., Lomedico P., Tizard R., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Gilbert W. A bacterial clone synthesizing proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3727–3731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]