Abstract
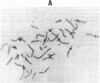
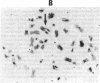
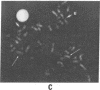
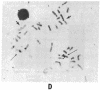
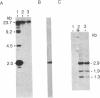
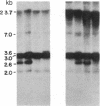
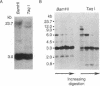
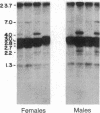
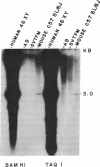
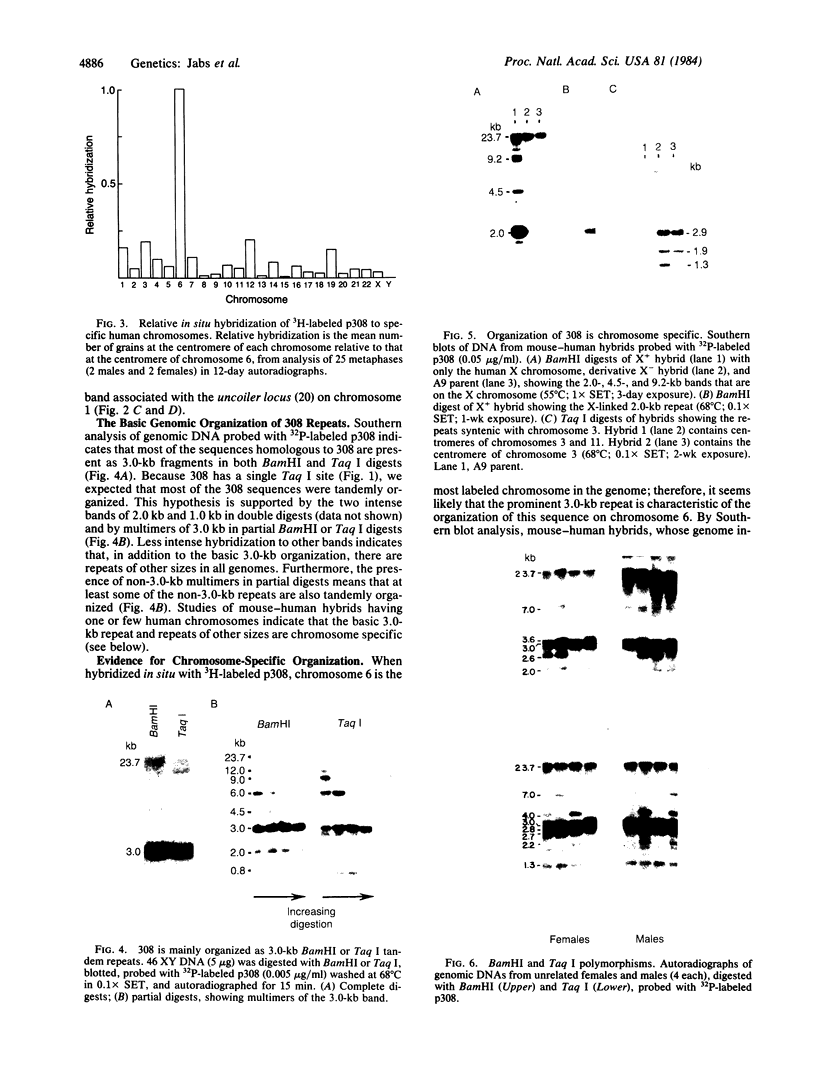
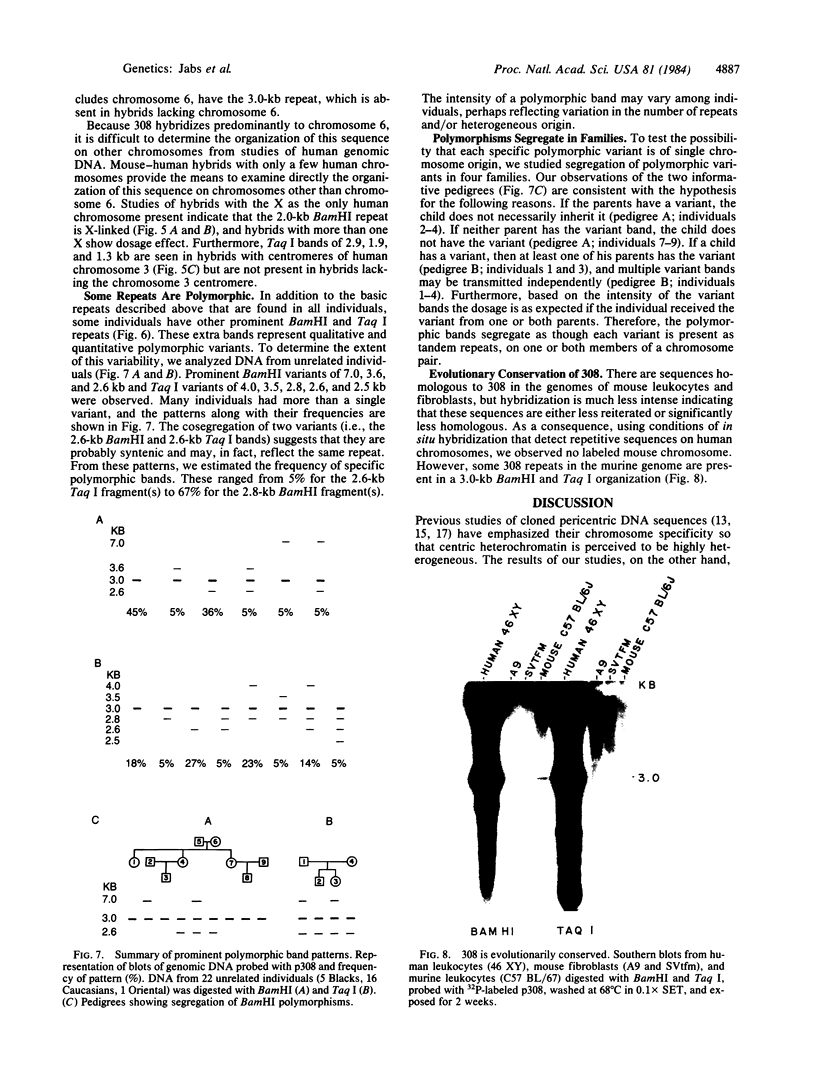
We have identified a human DNA recombinant (p308) with a 3.0-kilobase (kb) BamHI insert that hybridizes in situ exclusively to the centromeric region of all human autosomes and the X chromosome. This highly repetitive sequence is significantly enriched on several chromosomes, most prominently on chromosome 6. In all individuals, the majority of genomic repeats are organized as tandem 3.0-kb BamHI repeats, each containing one Taq I site; the others are organized into BamHI and Taq I repeats of variable size that have some chromosome specificity. Using mouse-human hybrids, we have defined the specific organization of this sequence on chromosomes 6, 3, and X. In some individuals, there are differences in the number and nature of the tandem repeats. These polymorphisms segregate in families as if chromosome specific. Although variable from one chromosome to another, 308 contains sequences homologous to DNA present in centric heterochromatin of essentially all human chromosomes and is evolutionarily conserved. Therefore, a significant component of pericentric DNA is similar for all human chromosomes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Lomakka G., Zech L. The 24 fluorescence patterns of the human metaphase chromosomes - distinguishing characters and variability. Hereditas. 1972;67(1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1971.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Mechanisms of chromosome banding and implications for chromosome structure. Annu Rev Genet. 1978;12:25–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.12.120178.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Hindley J. Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3177–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue R. P., Bias W. B., Renwick J. H., McKusick V. A. Probable assignment of the Duffy blood group locus to chromosome 1 in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):949–955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Clarke L., Carbon J. Nucleotide sequence comparisons and functional analysis of yeast centromere DNAs. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommer M., Prosser J., Tkachuk D., Reisner A. H., Vincent P. C. Simple repeated sequences in human satellite DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):547–563. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Lawrie S. S., Cooke H. J. A cloned repeated DNA sequence in human chromosome heteromorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1981;29(1):32–39. doi: 10.1159/000131549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Mitchell A. R., Buckland R. A., Clayton R. P., Evans H. J. The location of four human satellite DNAs on human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Apr;92(1):148–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90648-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Mitchell A. R., Seuanez H. N., Gosden C. M. The distribution of sequences complementary to human satellite DNAs I, II and IV in the chromosomes of chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes), gorilla (Gorilla gorilla) and orang utan (Pongo pygmaeus). Chromosoma. 1977 Sep 27;63(3):253–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00327453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Ullrich A., Saunders G. F. Localization of the human insulin gene to the distal end of the short arm of chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4458–4460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Characterization of reiterated human DNA with respect to mammalian X chromosome homology. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Jan;10(1):93–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01534476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John B., Miklos G. L. Functional aspects of satellite DNA and heterochromatin. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;58:1–114. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61473-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., Musich P. R. Toward a molecular paleontology of primate genomes. I. The HindIII and EcoRI dimer families of alphoid DNAs. Chromosoma. 1981;83(1):103–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00286019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma. 1978 Mar 22;66(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00285813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Complex and simple sequences in human repeated DNAs. Chromosoma. 1978 Mar 22;66(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00285812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Brown T. R., Axelman J., Migeon C. J. Studies of the locus for androgen receptor: localization on the human X chromosome and evidence for homology with the Tfm locus in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6339–6343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. R., Beauchamp R. S., Bostock C. J. A study of sequence homologies in four satellite DNAs of man. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):127–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90344-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Blank D., Fahrner K., Hereford L., Ricciardi R., Roberts B., Ruby S., Woolford J. R-looping and structural gene indentification of recombinant DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:454–469. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarto G. E., Therman E. Replication and inactivation of a dicentric X formed by telomeric fusion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Apr 1;136(7):904–911. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Smith K. D., Sutherland J. Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2017–2033. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Mareni C. E., Migeon B. R. Isolation and characterization of cloned DNA sequences that hybridize to the human X chromosome. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. P., Hansen S. K., Oishi K. K., Ryder O. A., Hamkalo B. A. Characterization of a cloned repetitive DNA sequence concentrated on the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6593–6597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]