Abstract
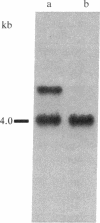
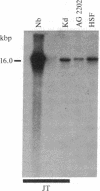
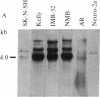
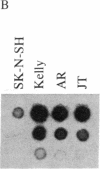
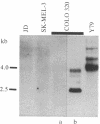
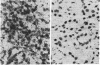
Previous studies had revealed that DNA with partial similarity to the myc oncogene (N-myc) is frequently amplified in human neuroblastoma cell lines and neuroblastoma tumors. We show here for one patient that N-myc amplification is confined to the neuroblastoma tumor and is not present in normal tissue. N-myc mRNA approximately equal to 4.0 kilobases in size is detectable in neuroblastoma cell lines and tumors and in a retinoblastoma cell line. By contrast, appreciable amounts of this RNA were not present in a number of cell lines derived from other human tumors and in fibroblasts from a normal individual and from a neuroblastoma patient. Low levels of N-myc RNA were found in human and murine neuroblastoma cell lines lacking amplification of this gene, up to 80-fold greater levels in all cell lines carrying amplified N-myc. In situ hybridization to sections of neuroblastoma tumors revealed high expression of N-myc predominantly in undifferentiated neuroblasts. We hypothesize that amplification and consequent elevated expression of N-myc may be related to malignant progression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Winqvist R., Lin C. C., de la Chapelle A., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Aberrant expression of an amplified c-myb oncogene in two cell lines from a colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4534–4538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban-Malenbaum G., Gilbert F. Double minute chromosomes and the homogeneously staining regions in chromosomes of a human neuroblastoma cell line. Science. 1977 Nov 18;198(4318):739–741. doi: 10.1126/science.71759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker L. E., Hinton D. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the central nervous system. Hum Pathol. 1983 Jun;14(6):538–550. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Spengler B. A. Metaphase chromosome anomaly: association with drug resistance and cell-specific products. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.942798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.6719137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX D., YUNCKEN C., SPRIGGS A. I. MINUTE CHROMATIN BODIES IN MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF CHILDHOOD. Lancet. 1965 Jul 10;1(7402):55–58. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casper J. T., Trent J. M., Harb J., Piaskowski V., Helmsworth M., Finlan J., Von Hoff D. D. Distinguishing characteristics of a new neuroblastoma cell line. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1983 Oct;10(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(83)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Groudine M. T. Rearrangement and amplification of c-abl sequences in the human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K-562. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4813–4817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Groudine M. Amplification of endogenous myc-related DNA sequences in a human myeloid leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):679–681. doi: 10.1038/298679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Onc gene amplification in promyelocytic leukaemia cell line HL-60 and primary leukaemic cells of the same patient. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):61–63. doi: 10.1038/299061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke F., Lampert F. Chromosomenuntersuchungen beim metastasierten Neuroblastom. Onkologie. 1982 Dec;5(6):268–272. doi: 10.1159/000215020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Specific chromosomal translocations and the genesis of B-cell-derived tumors in mice and men. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Kanda N., Schreck R. R., Bruns G., Latt S. A., Gilbert F., Alt F. W. Transposition and amplification of oncogene-related sequences in human neuroblastomas. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Battey J., Lenoir G., Moulding C., Murphy W., Potter H., Stewart T., Taub R. Translocations among antibody genes in human cancer. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):765–771. doi: 10.1126/science.6356357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levan A., Manolov G., Clifford P. Chromosomes of a human neuroblastoma: a new case with accessory minute chromosomes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Dec;41(6):1377–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. D., Nau M. M., Carney D. N., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. Amplification and expression of the c-myc oncogene in human lung cancer cell lines. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):194–196. doi: 10.1038/306194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. A., Sakurai M., Holdsworth R. N. Chromosomes and causation of human cancer and leukemia. 8. DMS chromosomes in a neuroblastoma. Cancer. 1972 Jun;29(6):1671–1679. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197206)29:6<1671::aid-cncr2820290635>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Kaufman R. J., Alt F. W., Kellems R. F. Gene amplification and drug resistance in cultured murine cells. Science. 1978 Dec 8;202(4372):1051–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.715457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Grzeschik K. H., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Brodeur G., Trent J. Chromosome localization in normal human cells and neuroblastomas of a gene related to c-myc. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):288–291. doi: 10.1038/308288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]