Abstract
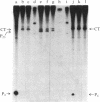
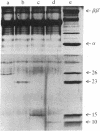
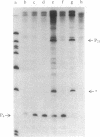
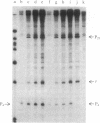
The RNA polymerase from bacteriophage T4-infected Escherichia coli, which specifically initiates transcription at phage T4 late promoters, is extensively modified by ADP-ribosylation of core subunits and by binding several virus-encoded subunits. We show here that one of these subunits, the phage T4 gene 55 protein, designated gp55, alone endows unmodified RNA polymerase core enzyme from uninfected E. coli with the ability to selectively initiate transcription at the phage T4 late promoters, without participation by E. coli RNA polymerase o- subunit.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., Kingston R., Gilman M., Wiggs J., deVera A. Isolation of bacterial and bacteriophage RNA polymerases and their use in synthesis of RNA in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:540–568. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. C., Young E. T. T4 late transcripts are initiated near a conserved DNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):369–371. doi: 10.1038/299369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Leighton T., Rabinowitz J. C. Purification of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with heparin-agarose. In vitro transcription of phi 29 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9220–9226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Geiduschek E. P. Purification of a positive regulatory subunit from phage SP01-modified RNA polymerase. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):28–32. doi: 10.1038/270028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
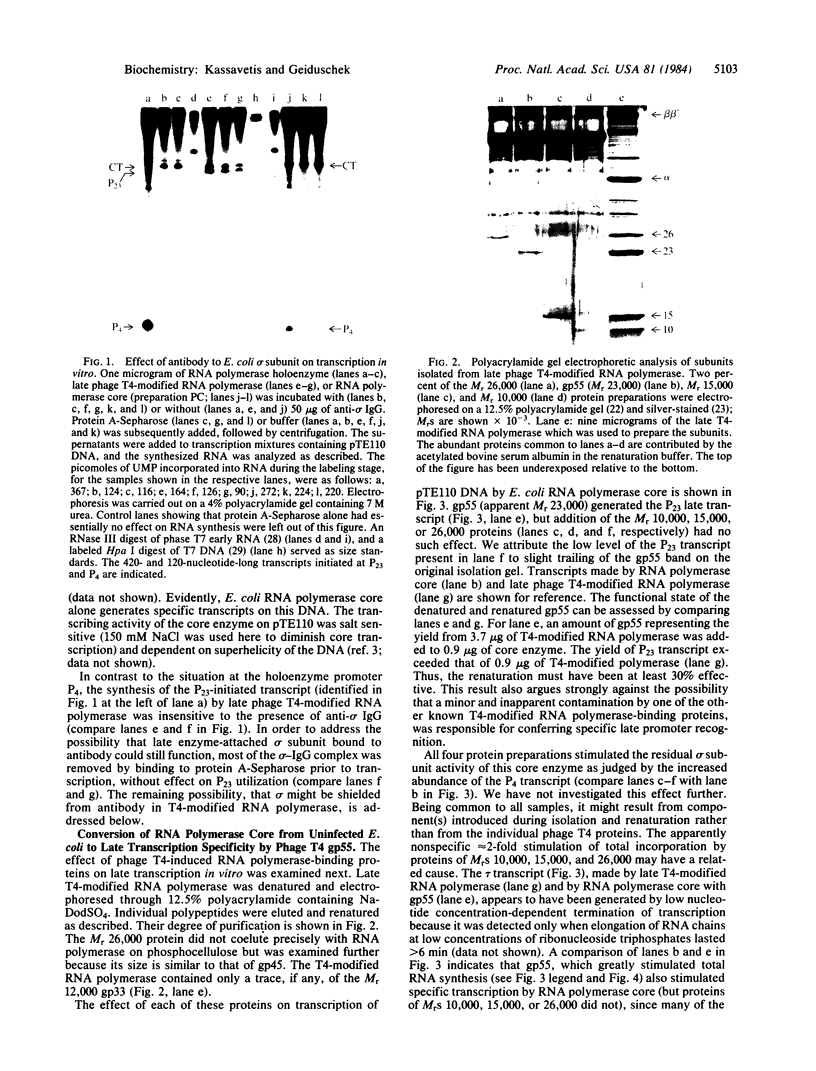
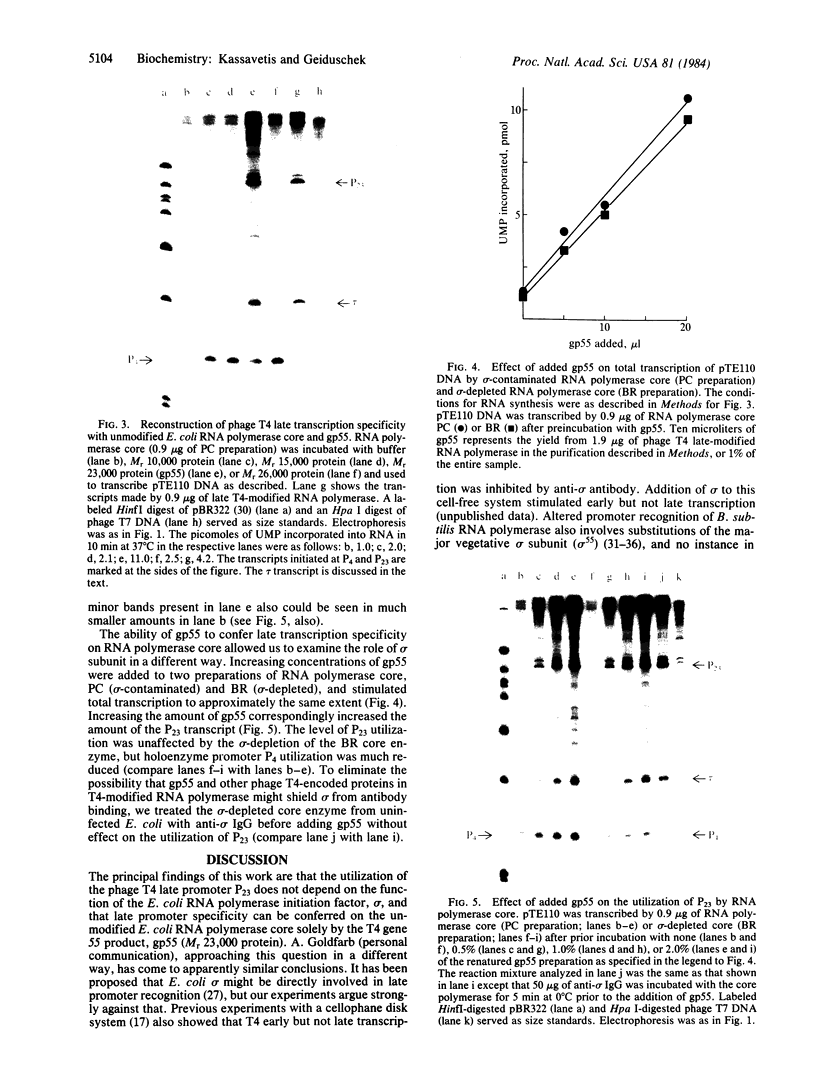
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D. Identification of phage SP01 proteins coded by regulatory genes 33 and 34. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):748–753. doi: 10.1038/262748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D., Losick R., Pero J. Regulatory gene 28 of bacteriophage SPO1 codes for a phage-induced subunit of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Chamberlin M. J. Developmental and genetic regulation of Bacillus subtilis genes transcribed by sigma 28-RNA polymerase. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb A. Changes in the promoter range of RNA polymerase resulting from bacteriophage T4-induced modification of core enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3454–3458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez N., Wiggs J., Chamberlin M. J. A simple procedure for resolution of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme from core polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Lang N., Losick R. A sporulation-induced sigma-like regulatory protein from B. subtilis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. Novel RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle D. C., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. I. The role of sigma subunit in site selection. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):157–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90531-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and termination of transcription within the early region of bacteriophage T7 DNA in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2777–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Elliott T., Rabussay D. P., Geiduschek E. P. Initiation of transcription at phage T4 late promoters with purified RNA polymerase. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutter E. M., Bradley D., Schenck R., Guttman B. S., Laiken R. Bacteriophage T4 alc gene product: general inhibitor of transcription from cytosine-containing DNA. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):822–829. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.822-829.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Pero J. Cascades of Sigma factors. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):582–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson T., Richardson J., Goodin D. Mutant of bacteriophage T4D affecting expression of many early genes. Nature. 1974 Jul 5;250(461):48–50. doi: 10.1038/250048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson T., Van Houwe G., Bolle A., Selzer G., Epstein R. Genetic identification of cloned fragments of bacteriophage T4 DNA and complementation by some clones containing early T4 genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Sep 9;154(3):319–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00571289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkley E. G., Pribnow D. Transcription of the early region of bacteriophage T7: selective initiation with dinucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;77(2):255–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulitzer J. F., Coppo A., Caruso M. Host--virus interactions in the control of T4 prereplicative transcription. II. Interaction between tabC (rho) mutants and T4 mot mutants. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 25;135(4):979–997. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabussay D., Geiduschek E. P. Phage T4-modified RNA polymerase transcribes T4 late genes in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5305–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner D. The interaction bacterial and phage proteins with immobilized Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90488-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L., Gold L., Kutter E. A gene of bacteriophage T4 whose product prevents true late transcription on cytosine-containing T4 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3098–3102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Bujard H. Organization of transcriptional signals in plasmids pBR322 and pACYC184. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. DNA-binding proteins. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1020–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.6308768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tijan R., Pero J. Bacteriophage SP01 regulatory proteins directing late gene transcription in vitro. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):753–757. doi: 10.1038/262753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Leautey J., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Brody E. Identification and biosynthesis of the bacteriophage T4 mot regulatory protein. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1207–1212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zograff Y. N. On the role of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase sigma factor in T4 phage development. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(3):557–558. doi: 10.1007/BF00268782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Franciscis V., Favre R., Uzan M., Leautey J., Brody E. In vitro system for middle T4 RNA. II. Studies with T4-modified RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4097–4101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]