Abstract
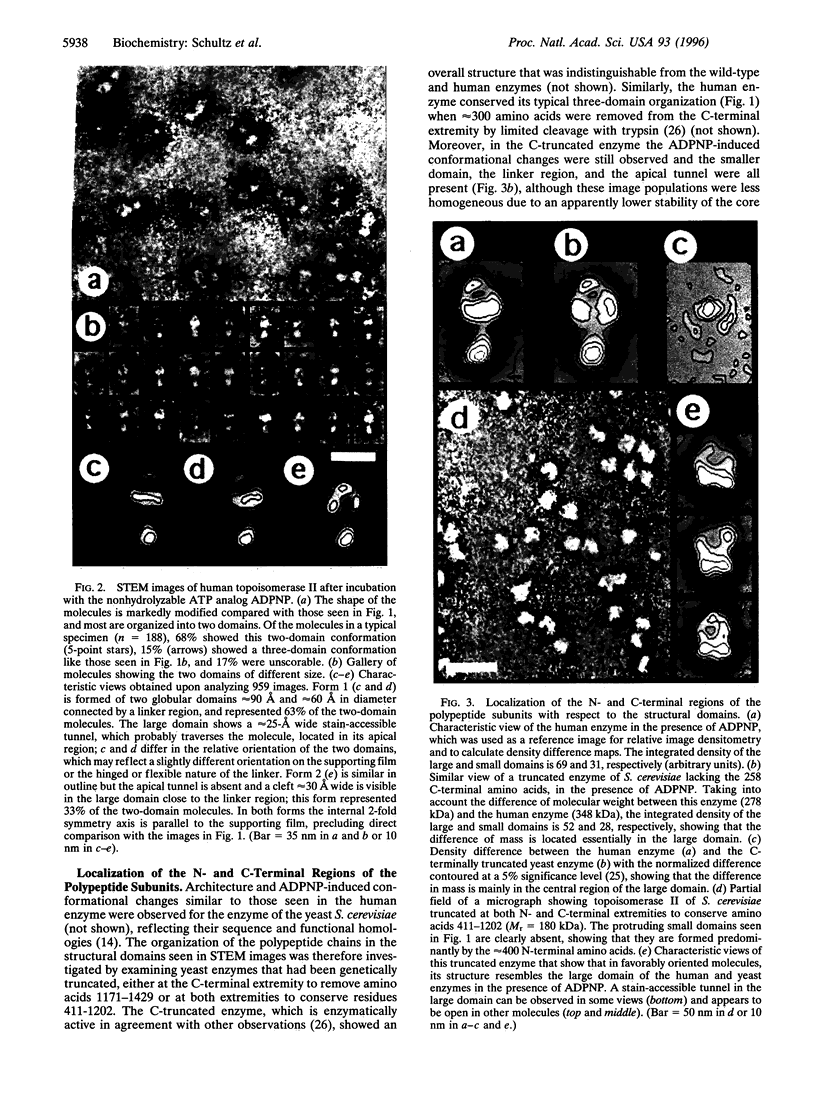
Type II DNA topoisomerases, which create a transient gate in duplex DNA and transfer a second duplex DNA through this gate, are essential for topological transformations of DNA in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and are of interest not only from a mechanistic perspective but also because they are targets of agents for anticancer and antimicrobial chemotherapy. Here we describe the structure of the molecule of human topoisomerase II [DNA topoisomerase (ATP-hydrolyzing), EC 5.99.1.3] as seen by scanning transmission electron microscopy. A globular approximately 90-angstrom diameter core is connected by linkers to two approximately 50-angstrom domains, which were shown by comparison with genetically truncated Saccharomyces cerevisiae topoisomerase II to contain the N-terminal region of the approximately 170-kDa subunits and that are seen in different orientations. When the ATP-binding site is occupied by a nonhydrolyzable ATP analog, a quite different structure is seen that results from a major conformational change and consists of two domains approximately 90 angstrom and approximately 60 angstrom in diameter connected by a linker, and in which the N-terminal domains have interacted. About two-thirds of the molecules show an approximately 25 A tunnel in the apical part of the large domain, and the remainder contain an internal cavity approximately 30 A wide in the large domain close to the linker region. We propose that structural rearrangements lead to this displacement of an internal tunnel. The tunnel is likely to represent the channel through which one DNA duplex, after capture in the clamp formed by the N-terminal domains, is transferred across the interface between the enzyme's subunits. These images are consistent with biochemical observations and provide a structural basis for understanding the reaction of topoisomerase II.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger J. M., Gamblin S. J., Harrison S. C., Wang J. C. Structure and mechanism of DNA topoisomerase II. Nature. 1996 Jan 18;379(6562):225–232. doi: 10.1038/379225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron P. R., Watt P., Wang J. C. The C-terminal domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA topoisomerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3197–3207. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M., Hancock R. DNA topoisomerase II is required for formation of mitotic chromosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cells: studies using the inhibitor 4'-demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-(4,6-O-thenylidene-beta-D-glucopyranoside). Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9531–9537. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake F. H., Zimmerman J. P., McCabe F. L., Bartus H. F., Per S. R., Sullivan D. M., Ross W. E., Mattern M. R., Johnson R. K., Crooke S. T. Purification of topoisomerase II from amsacrine-resistant P388 leukemia cells. Evidence for two forms of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16739–16747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida R., Miki T., Narita T., Yui R., Sato M., Utsumi K. R., Tanabe K., Andoh T. Inhibition of intracellular topoisomerase II by antitumor bis(2,6-dioxopiperazine) derivatives: mode of cell growth inhibition distinct from that of cleavable complex-forming type inhibitors. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18):4909–4916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhausen T., Wang J. C., Harrison S. C. DNA gyrase and its complexes with DNA: direct observation by electron microscopy. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley J. E., Wang J. C. Proteolysis patterns of epitopically labeled yeast DNA topoisomerase II suggest an allosteric transition in the enzyme induced by ATP binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10485–10489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitiss J. L. Roles of DNA topoisomerases in chromosomal replication and segregation. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;29A:103–134. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60542-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Corbett A. H., Robinson M. J. Mechanism of action of topoisomerase II-targeted antineoplastic drugs. Adv Pharmacol. 1994;29B:105–126. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)61134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):335–375. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Wang J. C. DNA transport by a type II DNA topoisomerase: evidence in favor of a two-gate mechanism. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):609–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Wang J. C. The capture of a DNA double helix by an ATP-dependent protein clamp: a key step in DNA transport by type II DNA topoisomerases. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):833–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90558-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Thomas W., Holm C. Segregation of recombined chromosomes in meiosis I requires DNA topoisomerase II. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1009–1017. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90349-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P., Nobelis P., Colin P., Louys M., Huet J., Sentenac A., Oudet P. Electron microscopic study of yeast RNA polymerase A: analysis of single molecular images. Chromosoma. 1990 Jul;99(3):196–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01731130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. A functional 125-kDa core polypeptide of fission yeast DNA topoisomerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6093–6102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. R., Drlica K. Bacterial chromosome segregation: evidence for DNA gyrase involvement in decatenation. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassetzky Y. S., Dang Q., Benedetti P., Gasser S. M. Topoisomerase II forms multimers in vitro: effects of metals, beta-glycerophosphate, and phosphorylation of its C-terminal domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6962–6974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigley D. B., Davies G. J., Dodson E. J., Maxwell A., Dodson G. Crystal structure of an N-terminal fragment of the DNA gyrase B protein. Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):624–629. doi: 10.1038/351624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worland S. T., Wang J. C. Inducible overexpression, purification, and active site mapping of DNA topoisomerase II from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4412–4416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J., Liu L. F. Roles of DNA topoisomerases in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]