Abstract
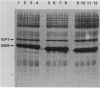
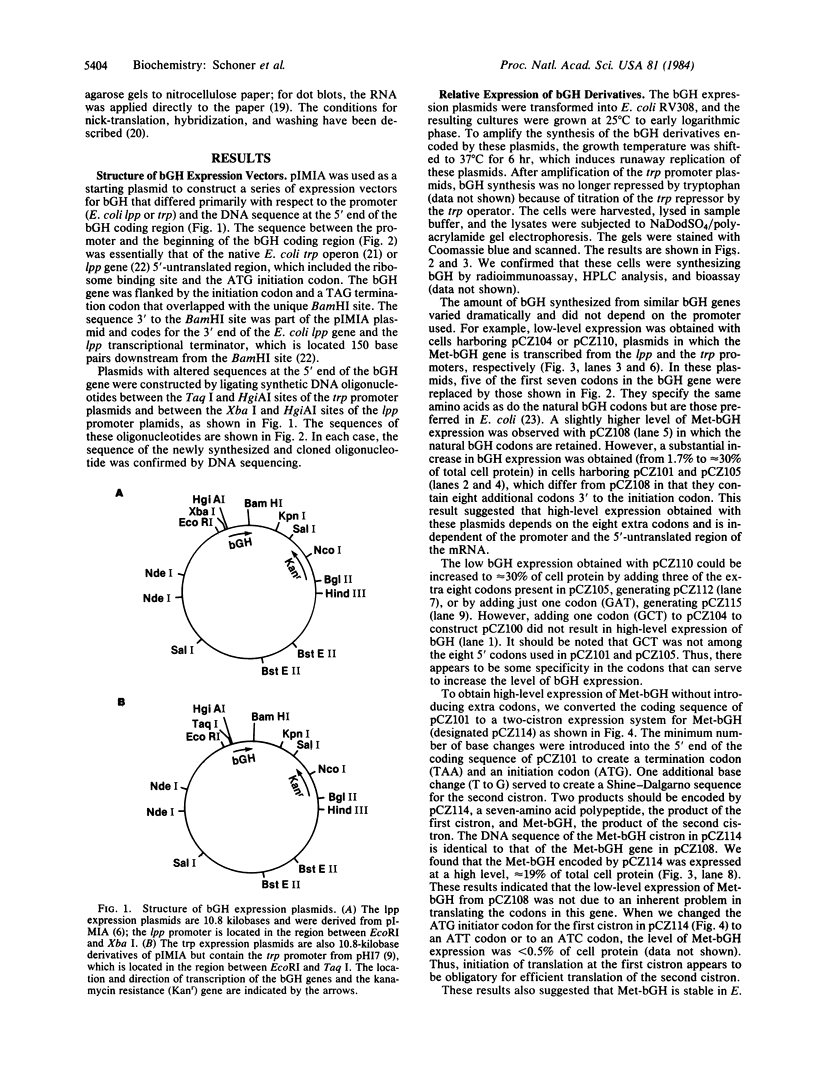
The conditions necessary for high-level expression of methionyl bovine growth hormone (Met-bGH) in Escherichia coli were investigated. Plasmids were constructed that contain a thermoinducible runaway replicon and either the E. coli tryptophan or lipoprotein promoter and ribosome binding sites, which served as transcriptional and translational initiation sites for the expression of the bGH gene. The expression of Met-bGH was low with either system. However, expression levels of up to 30% of total cell protein were obtained after the introduction of additional codons 3' to the initiating AUG codon, thus altering the NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of bGH. To obtain high-level expression of Met-bGH a two-cistron system was constructed in which the codons that enhanced the expression of bGH were incorporated into the first cistron, and the coding region for Met-bGH was incorporated into the second cistron. This approach may be generally applicable to achieving high-level expression of a gene that contains NH2-terminal sequences that do not allow for its efficient expression. Analyses of the stabilities of the bGH derivatives and their transcripts in vivo suggested that the variations in the level of expression were due to variations in the efficiency of mRNA translation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. L., Belagaje R., Ryan M. J., Khorana H. G. Chemical synthesis and cloning of a tyrosine tRNA gene. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:109–151. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D. B. Recovery of DNA fragments from gels by transfer to DEAE-paper in an electrophoresis chamber. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;125(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Urbanowski J., Weissbach H., Nestor J., Yanofsky C. In vitro synthesis of the tryptophan operon leader peptides of Escherichia coli, Serratia marcescens, and Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2879–2883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., Iserentant D., Derom C., Fiers W. Systematic alteration of the nucleotide sequence preceding the translation initiation codon and the effects on bacterial expression of the cloned SV40 small-t antigen gene. Gene. 1982 Jan;17(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Débarbouillé M., Schwartz M. A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):616–618. doi: 10.1038/295616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., Hayflick J., Dinkelspiel K., de Boer H. A. Mutagenesis of the three bases preceding the start codon of the beta-galactosidase mRNA and its effect on translation in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):623–629. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iserentant D., Fiers W. Secondary structure of mRNA and efficiency of translation initiation. Gene. 1980 Apr;9(1-2):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg W., Godson G. N. Evidence for use of rare codons in the dnaG gene and other regulatory genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):687–691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R., Meyer B., Ptashne M. Gene regulation at the right operator (OR) bacteriophage lambda. I. OR3 and autogenous negative control by repressor. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):147–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90302-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. Molecular cloning of DNA complementary to bovine growth hormone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7521–7524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Inouye M. DNA sequence of the gene for the outer membrane lipoprotein of E. coli: an extremely AT-rich promoter. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1109–1117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narang S. A., Hsiung H. M., Brousseau R. Improved phosphotriester method for the synthesis of gene fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:90–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton C. R., Greene A. R., Heathcliffe G. R., Atkinson T. C., Holland D., Markham A. F., Edge M. D. Ion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography of oligodeoxyribonucleotides using formamide. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Rosenberg M. Differential translation efficiency explains discoordinate expression of the galactose operon. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosteck P. R., Jr, Hershberger C. L. Selective retention of recombinant plasmids coding for human insulin. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner B., Schoner R. G. Distribution of IS5 in bacteria. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Roa M., Débarbouillé M. Mutations that affect lamB gene expression at a posttranscriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Sias S., Adelman J., de Boer H. A., Hayflick J., Jhurani P., Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L. Efficient bacterial expression of bovine and porcine growth hormones. DNA. 1983;2(1):37–45. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1983.2.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard H. M., Yelverton E., Goeddel D. V. Increased synthesis in E. coli of fibroblast and leukocyte interferons through alterations in ribosome binding sites. DNA. 1982;1(2):125–131. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Molin S., Gustafsson P., Nordström K. Plasmids with temperature-dependent copy number for amplification of cloned genes and their products. Gene. 1979 Jun;6(2):91–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Finnegan D. J., Donelson J. E., Hogness D. S. A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Platt T., Crawford I. P., Nichols B. P., Christie G. E., Horowitz H., VanCleemput M., Wu A. M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6647–6668. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. S., Furano A. V. Regulation of the synthesis of E. coli elongation factor Tu. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Hui A., Comstock L. J., Wong E., Vasser M. Portable Shine-Dalgarno regions: a system for a systematic study of defined alterations of nucleotide sequences within E. coli ribosome binding sites. DNA. 1983;2(3):231–235. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]