Abstract
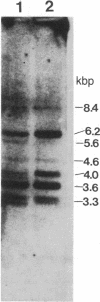
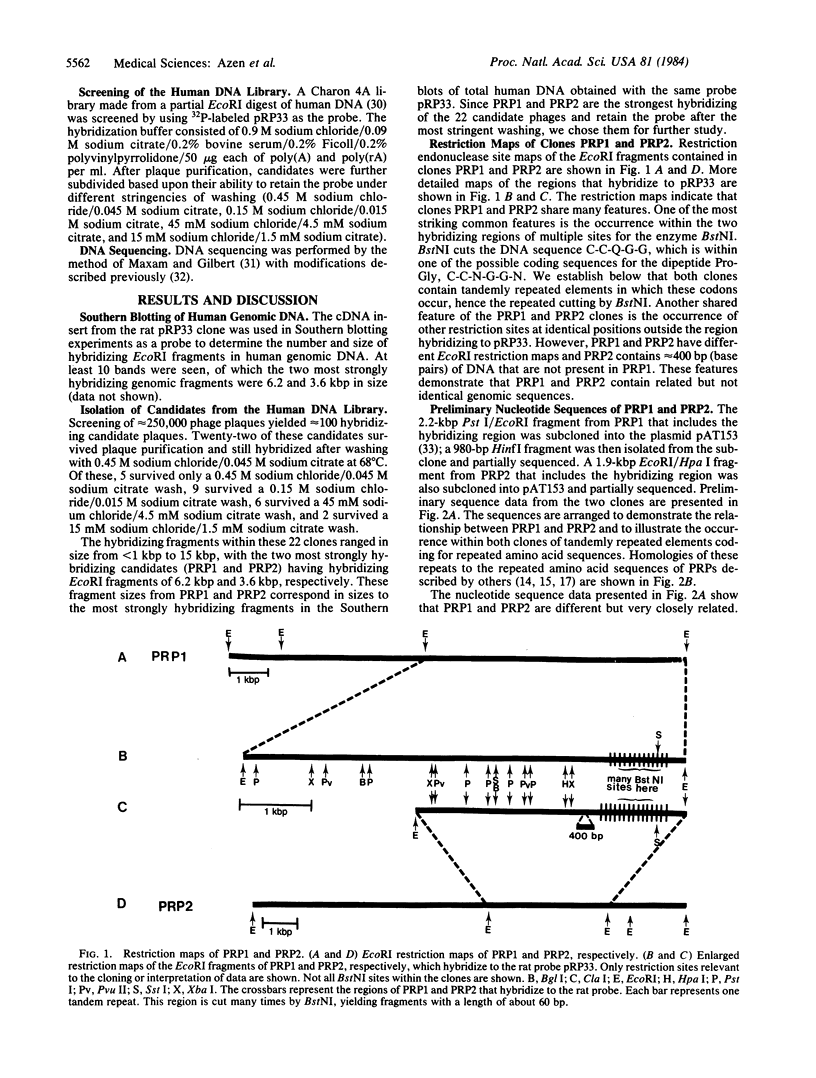
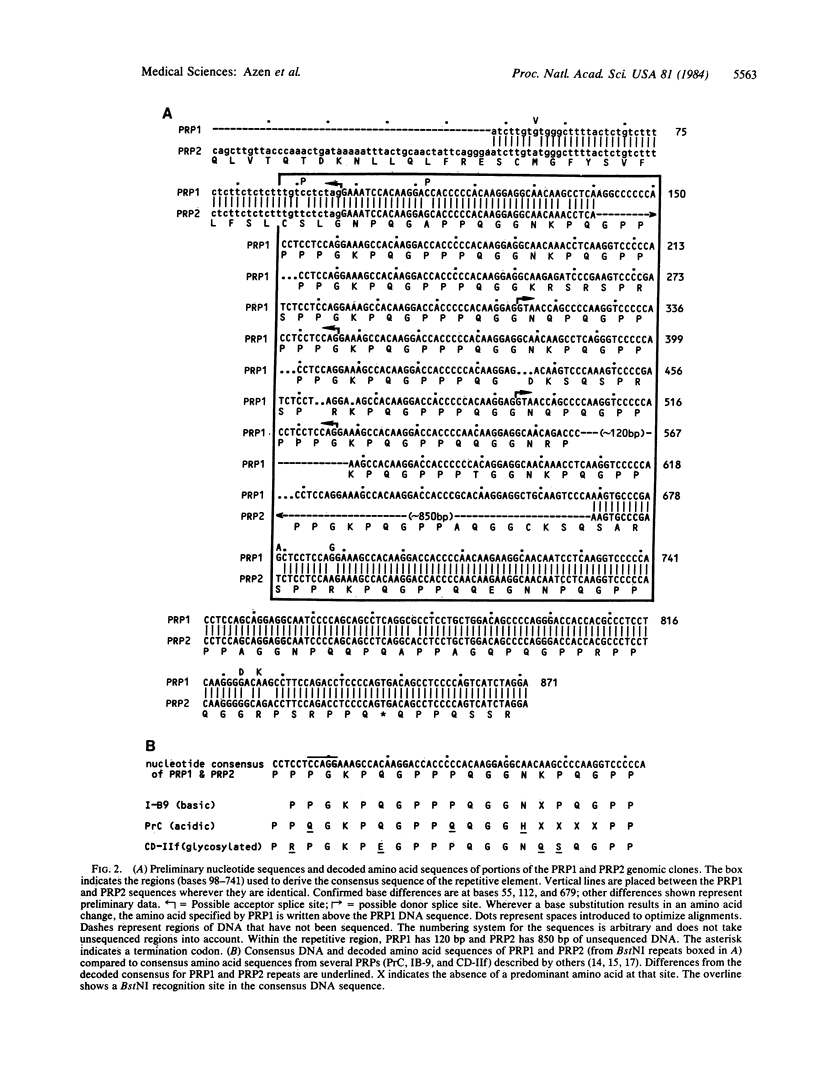
The salivary protein gene complex consists of a series of loci coding for related but distinct proline-rich proteins (PRPs) found chiefly in saliva. We have screened a library of human genomic DNA fragments in bacteriophage lambda Charon 4A with a PRP cDNA synthesized and cloned from rat parotid gland mRNA. Two phages (PRP1 and PRP2) hybridizing to the rat probe under moderately stringent conditions contain related but not identical DNAs. Preliminary nucleotide sequence data indicate that both DNAs include regions comprised of nearly identical tandemly repeated sequences, each able to code for about 21 amino acids. The decoded consensus repeat sequence is homologous to the repeating amino acid units found by others in human PRPs. This and other features demonstrate that these two clones are members of the PRP gene family. Polymorphic differences between the DNAs of different individuals were observed after probing digests of human genomic DNA with a HinfI fragment from PRP1. These DNA polymorphisms reflect size differences, possibly caused by frequent unequal crossing-over between the repeated units in the PRP genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azen E. A., Denniston C. Genetic polymorphism of PIF (parotid isoelectric focusing variant) proteins with linkage to the PPP (parotid proline-rich protein) gene complex. Biochem Genet. 1981 Jun;19(5-6):475–485. doi: 10.1007/BF00484620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azen E. A., Yu P. L. Genetic polymorphism of CON 1 and CON 2 salivary proteins detected by immunologic and concanavalin A reactions on nitrocellulose with linkage of CON 1 and CON 2 genes to the SPC (salivary protein gene complex). Biochem Genet. 1984 Feb;22(1-2):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00499283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. Chemical and physical characteristics of a phosphoprotein from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):557–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1450557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. Chemical and physical characterization of a phosphoprotein, Protein C, from human saliva and comparison with a related protein A. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):229–239. doi: 10.1042/bj1630229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A., Connell G. E. Purification and partial characterization of four proteins from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):455–464. doi: 10.1042/bj1230455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. D., Merritt A. D. Partial purification and characterization of a polymorphic protein (Pa) in human parotid saliva. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 May;27(3):304–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I., Oppenheim F. G. The isolation from human parotid saliva of a further group of proline-rich proteins. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Aug;19(8):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman D. L., Keller P. J. The basic proline-rich proteins in human parotid saliva from a single subject. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(4):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman D. L., Keller P. J. The basic proline-rich proteins in human parotid saliva from a single subject. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(4):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman D., Wong R., Bennick A., Keller P. Basic proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva: complete covalent structure of protein IB-9 and partial structure of protein IB-6, members of a polymorphic pair. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6558–6562. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Ellison S. A., Bahl O. P. The isolation from human parotid saliva and partial characterization of the protein core of a major parotid glycoprotein. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Jul;18(7):827–837. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel I. D., Thompson R. H., Jr, Ellison S. A. Studies on the mucoproteins of human parotid saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1965 May-Jun;10(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(65)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning R. F., Gage L. P. Internal structure of the silk fibroin gene of Bombyx mori. II. Remarkable polymorphism of the organization of crystalline and amorphous coding sequences. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9451–9457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenzer J., Bildstein C., Gleason M., Carlson D. M. Properties of proline-rich proteins from parotid glands of isoproterenol-treated rats. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5629–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenzer J., Bildstein C., Gleason M., Carlson D. M. Purification of proline-rich proteins from parotid glands of isoproterenol-treated rats. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5623–5628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. An expandable gene that encodes a Drosophila glue protein is not expressed in variants lacking remote upstream sequences. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1041–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim F. G., Hay D. I., Franzblau C. Proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva. I. Isolation and partial characterization. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov;10(23):4233–4238. doi: 10.1021/bi00799a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh E., Isemura S., Sanada K. Complete amino acid sequence of a basic proline-rich peptide, P-F, from human parotid saliva. J Biochem. 1983 Mar;93(3):883–888. doi: 10.1093/jb/93.3.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura H., Kanai Y., Sanada K. Amino acid sequences of glycopeptides obtained from basic proline-rich glycoprotein of human parotid saliva. J Biochem. 1983 Mar;93(3):857–863. doi: 10.1093/jb/93.3.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Henthorn P. S., Kioussis D., Grosveld F., Smithies O. Unexpected relationships between four large deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viotti A., Abildsten D., Pogna N., Sala E., Pirrotta V. Multiplicity and diversity of cloned zein cDNA sequences and their chromosomal localisation. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):53–58. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R., Lamm L. U. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 6. Oslo Conference (1981): Sixth International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;32(1-4):130–143. doi: 10.1159/000131693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. S., Bennick A. The primary structure of a salivary calcium-binding proline-rich phosphoprotein (protein C), a possible precursor of a related salivary protein A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5943–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. S., Hofmann T., Bennick A. The complete primary structure of a proline-rich phosphoprotein from human saliva. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4800–4808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu P. L., Karn R. C., Merritt A. D., Azen E. A., Conneally P. M. Linkage relationships and multipoint mapping of the human parotid salivary proteins (Pr, Pa, Db). Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Jul;32(4):555–563. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]