Abstract
Net reclassification indices have recently become popular statistics for measuring the prediction increment of new biomarkers. We review the various types of net reclassification indices and their correct interpretations. We evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of quantifying the prediction increment with these indices. For pre-defined risk categories, we relate net reclassification indices to existing measures of the prediction increment. We also consider statistical methodology for constructing confidence intervals for net reclassification indices and evaluate the merits of hypothesis testing based on such indices. We recommend that investigators using net reclassification indices should report them separately for events (cases) and nonevents (controls). When there are two risk categories, the components of net reclassification indices are the same as the changes in the true-positive and false-positive rates. We advocate use of true- and false-positive rates and suggest it is more useful for investigators to retain the existing, descriptive terms. When there are three or more risk categories, we recommend against net reclassification indices because they do not adequately account for clinically important differences in shifts among risk categories. The category-free net reclassification index is a new descriptive device designed to avoid pre-defined risk categories. However, it suffers from many of the same problems as other measures such as the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. In addition, the category-free index can mislead investigators by overstating the incremental value of a biomarker, even in independent validation data. When investigators want to test a null hypothesis of no prediction increment, the well-established tests for coefficients in the regression model are superior to the net reclassification index. If investigators want to use net reclassification indices, confidence intervals should be calculated using bootstrap methods rather than published variance formulas. The preferred single-number summary of the prediction increment is the improvement in net benefit.
Risk prediction is an important component of medical care and public health. Examples of models currently used for risk prediction are the Framingham model1 in cardiovascular disease and the Gail model2 in breast cancer. Accurate risk prediction enables clinicians to match the intensity of treatment to the level of risk.3 For many conditions, clinicians have a limited ability to accurately identify high-risk patients, and research efforts continue to be devoted to improving risk prediction models. In cardiovascular disease, many epidemiologic publications have evaluated whether new predictors can improve on the risk predictions from the Framingham model,1 which includes the established risk factors age, sex, systolic blood pressure, lipids and smoking. The goal of such investigations is to evaluate new biomarkers for the predictive capacity they offer above and beyond established predictors. The improvement in risk prediction is called the incremental value or prediction increment of the biomarker.
In 2008, Pencina and colleagues4 introduced a new measure of incremental value called the net reclassification index. They expanded the definition of this index in 2011.5 Variants have recently become popular in some areas of medical research, especially cardiovascular epidemiology. There are approximately 500 papers that contain “ net reclassification index” and cite the original paper. 4
Although net reclassification indices have become popular, there are common mistakes in interpretation. Further, since there are now multiple net reclassification indices to choose from, investigators may be unsure which, if any, to use. In addition, statistical methods pertaining to these indices are not yet well-developed. The goals of this review are to clarify the interpretation of net reclassification indices; to relate net reclassification indices to more traditional measures; to provide guidance on choice of net reclassification indices; to highlight problems with current methods for calculating confidence intervals and p-values for net reclassification indices; and to recommend methods for confidence intervals.
Net reclassification indices and other measures of the prediction increment
We provide basic definitions and introduce data on cardiovascular disease risk that we will use for illustration. In the next section we describe issues with the interpretation and application of both categorical and category-free net reclassification indices. Following that, we describe statistical issues in applying net reclassification indices. We then apply these findings to data from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis, and conclude with a summary and recommendations.
The context here is risk prediction. The specific goal is to improve risk prediction by adding a new predictor to an existing set of predictors. A traditional way to evaluate the prediction increment of a new biomarker is to consider the improvement in the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for the expanded risk model compared to the baseline risk model (ΔAUC). However, promising new markers have failed to produce large increases in the area under the curve. 4 There have been explicit calls for ways to evaluate new markers other than ΔAUC.6 Responding to these calls, Pencina and colleagues4 proposed new metrics, “integrated discrimination improvement” and “net reclassification improvement” (or “index”) for quantifying the prediction increment of a new marker. The net reclassification indices have become widely used and are the topic of this review.
The net reclassification index, as originally proposed, seeks to quantify whether a new marker provides clinically relevant improvements in prediction. In the definition of “ net reclassification indices,” the risk prediction model with established predictors is called the “old” model. The model that adds the new marker is the “new” model. “Events” are cases — persons who have or will have the disease or outcome in the absence of intervention. “Nonevents” are controls. The formula defining the net reclassification index (NRI) is4
| (1) |
“Up” means that the new risk model places a person into a higher risk category than the old model. Similarly, “down” means the new model places a person into a lower risk category. For example,NRI0.2 means a two-category index with cut-off at 0.20 defining low and high risk. NRI0.1,0.2 is a three-category index with cut-offs at 0.10 and 0.20 defining low-, medium-, and high-risk categories. Any set of risk thresholds can be used to define a net reclassification index.
The definition of the net reclassification index in Equation (1), based originally on discrete pre-defined risk categories, generalizes to any upward or downward movement in predicted risks.5 The “category-free net reclassification index” (also called “continuous net reclassification index”) interprets definition (1) this way. We use NRI>0 to denote the category-free index.
The idea behind the net reclassification index is that a valuable new biomarker will tend to increase predicted risks or risk categories for events and decrease predicted risks or risk categories for nonevents. P(up|event) and P(down|nonevent) form the positive components of the net reclassification index in definition (1). On the other hand, events that move down and nonevents that move up are mistakes introduced by the new marker — these are the negative components of definition (1).
A net reclassification index is the sum of the “event NRI” and the “nonevent NRI”:
| (2) |
| (3) |
For example, and .
For the two-category setting, Pencina et al.5 generalized the net reclassification index to consider the savings s1 from identifying an event as high risk and s2 from identifying a nonevent as low risk. s1 is meant to capture the adverse events that are avoided by labeling a person destined to have an event as high risk. s2 should capture all the savings (adverse events, money) from allowing a nonevent to avoid unnecessary treatment. The “weighted net reclassification index” (wNRI) is the average savings per person.
| (4) |
Two established measures of the prediction increment include: ΔAUC (mentioned above) and ΔNB, which refers to the change in net benefit associated with the use of the new marker.7 For example, if the risk model is used to classify persons as “high-risk” or “low-risk” and high-risk entails an intervention, the Net Benefit is
| (5) |
where B is the average benefit of the intervention among those who otherwise would have an event and C is the cost of intervention (including side effects) to nonevents. For old and new risk models, the change in net benefit (ΔNB) is a measure of the prediction increment of the new marker.
Example: Coronary Artery Calcification and Predicting Coronary Events
Polonsky et al.8 examined the prediction increment of the coronary artery calcium score for predicting coronary heart disease (CHD) among 5878 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Median follow-up was 5.8 years, and 209 CHD events were observed. The cohort was 54% female, and the mean age was 62 years with a standard deviation of 10 years. The “old” risk model included the risk factors from the Framingham risk model plus race; the “new” model added the arterial calcium score. We use these data to illustrate metrics and methods. We estimate risks using Cox models; for simplicity we otherwise ignore censoring in the data, following Polonsky et al.8 We refer readers to the original paper8 for more details.
Interpreting net reclassification indices
Net reclassification index is not a proportion
A common mistake is to interpret the net reclassification index as a proportion.9 For example, it is incorrect to interpret the index as “the proportion of patients reclassified to a more appropriate risk category,”10 as this is P(up and event)+P(down and nonevent). The net reclassification index combines four proportions but is not itself a proportion.9 The maximum value of the net reclassification index is 2.
NRIe and NRIne are easier to interpret than the net reclassification index because they are differences in proportions. NRIe is the net proportion of events assigned a higher risk or risk category. NRIne is the net proportion of nonevents assigned a lower risk or risk category. The word “net” here is crucial for correct interpretation.
Issues with combining event and nonevent net reclassification indices
Given the interpretations of NRIe and NRIne, it is not clear why one would want to take a simple sum (or unweighted average) to produce the net reclassification index. One logical alternative is to weight by the prevalence of events. This weighting extends the interpretations of NRIe and NRIne to the whole population. We define the “population-weighted net reclassification index” as ρNRIe+(1–ρ)NRIne, where ρ is the prevalence of the condition or outcome. The population-weighted net reclassification index can be interpreted as the net change in the proportion of subjects assigned a more appropriate risk or risk category under the new model.
Data from the CHD study illustrate another problem with the unweighted sum of NRIe and NRIne. Using 5-year risks, NRI0.1=0.164. Looking at the components, we see that but the nonevent index is negative, . Among nonevents, the arterial calcium score introduces many more errors than corrections at the 10% risk threshold. Since there are many more nonevents than events (a common situation), the new risk model introduces far more errors than corrections overall. The positive value for NRI0.1masks the population-level results. Estimating the prevalence of CHD in this population as 3.6%, the population-weighted NRI0.1 is −0.020. That is, the net proportion of subjects assigned to a more appropriate risk category using the 0.1 threshold is −0.02.
The population-weighted net reclassification index illustrates one problem with this index. However, we do not advocate use of the population-weighted index because there is no compelling advantage in collapsing NRIe and NRIne into a single number. NRIe and NRIne provide information on how the new risk model (potentially) improves prediction for events and, separately, for nonevents. The two types of improvements have different implications. Important information is lost when these two summaries are combined.11
Large and small values for NRI>0 are undefined
Ideally, a measure of incremental value can be interpreted in terms of the clinical or public health benefit of incorporating the new marker. Pencina et al.12 remark that “further research is needed to determine meaningful or sufficient degree of improvement” in NRI>0”. NRI>0 has no interpretation that translates to the clinical benefit of the new marker.13 If it did, then the magnitude of the index would be directly applicable to the clinical setting, and a marker's sufficiency for improving prediction would be apparent. Other metrics, including ΔAUC, share this problem of lacking a clinically meaningful interpretation. However, an additional problem with NRI>0 is that its scale is unfamiliar.
Pencina et al.12 give a mathematical example of a new marker described as having “strong effect size.” The eAppendix section C describes the structure of the data considered by Pencina et al.12 Here and throughout this review, X represents the established predictor or set of predictors, and Y is the candidate new predictor. In the example,12 the new marker Y yields NRI>0=0.622. Is 0.622 large? Consider Figures 1 and 2. In all four examples in the figures, Y has the same distribution, and the odds ratio for Y given the baseline marker X is constant. The four examples differ only in the strength of the old risk model, i.e., the predictive capacity of X. At one extreme, the old risk model is uninformative, with AUC=0.5. At the other extreme, the old risk model is highly predictive with AUC=0.99. The figures suggest that the prediction increment for Y diminishes as the strength of the old model increases, even though NRI>0=0.622 in all four cases. Clearly there are important aspects of prediction not captured by NRI>0.12
Figure 1.
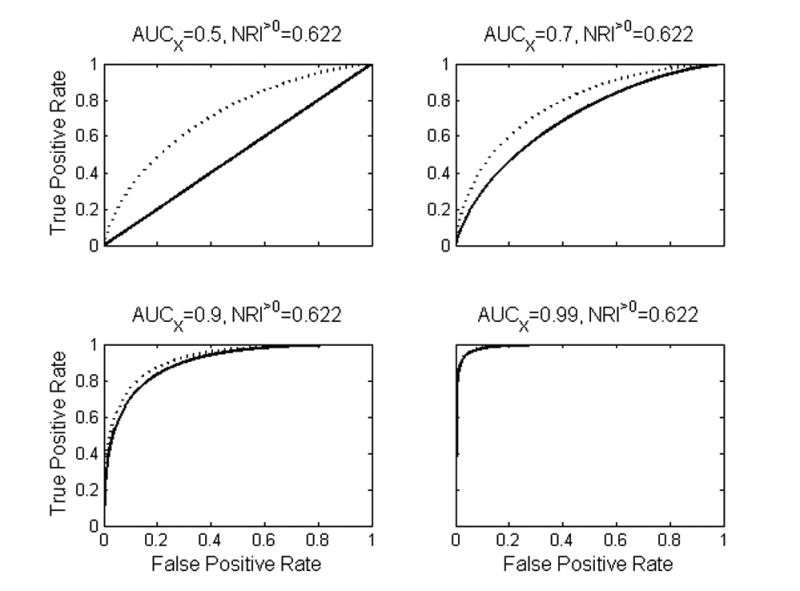
In each plot the solid line is the ROC curve for the “old” marker and the dotted line is the ROC curve for the “new” risk model that incorporates the new marker. The new marker has identical distribution in all four cases. NRI>0=0.622 in all cases, despite the fact that the prediction increment of the new marker decreases as the strength of the old model increases.
Figure 2.
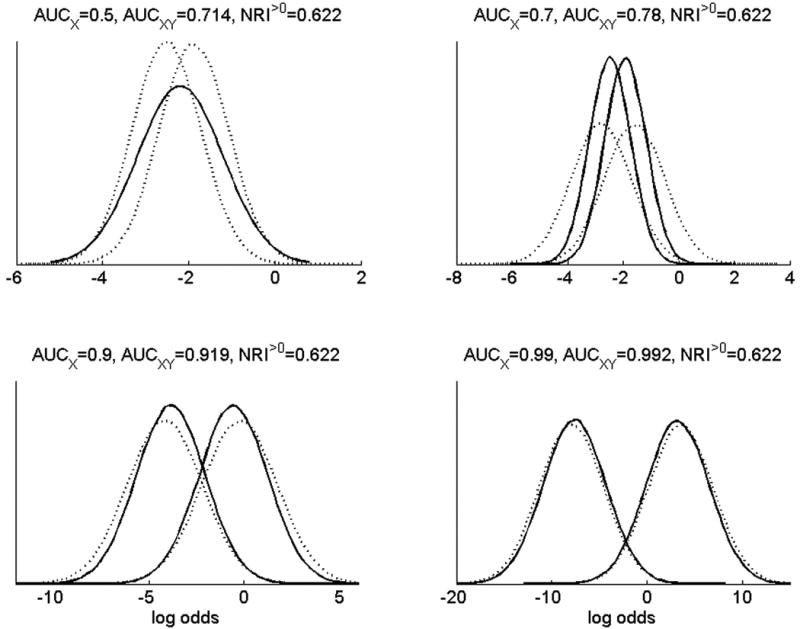
The same data as Figure 1 are shown here in terms of the distributions of risks for old and new risk models. Risk distributions are shown on the log odds scale. Solid lines are the risks using the established predictors X, with nonevents tending to have lower risks than events. Dotted lines are risks using the new marker Y together with X.
NRI>0 does not contrast the performance of the new risk model with the performance of the old risk model
Most measures of incremental value are constructed by summarizing the performance of the old risk model, summarizing the performance of the new risk model, and comparing the two summaries. (ΔAUC and ΔNB are examples.) NRI>0 is fundamentally different. This index is not a difference of two performance measures for the two risk models but rather a comparison of the old and new risk values for each person. However, within-person changes in risk do not necessarily translate into improved performance on a population level. For example, Figure 2 (bottom row) shows examples with many changes in individual predicted risks (NRI>0=0.622), but the distribution of predicted risks in the population remains almost exactly the same.
When assessing a new biomarker, the ultimate question is whether clinicians should continue using the old risk model or switch to the new, expanded risk model. To answer this question we need to assess and compare the performances of each of the risk models. NRI>0 measures the difference between the old and new risk models within individual patients, but without providing information about the performances of the models.
NRI>0incorporates irrelevant information
NRI>0, like ΔAUC, does not rely on risk thresholds.Greenland14 points out that “cutpoint free” indices incorporate irrelevant information, diminishing their potential for clinical relevance. For example, area under the curve summarizes the entire receiver operating charateristic curve, including parts of the curve describing sensitivity for unacceptably poor specificity. There are two ways in which NRI>0 incorporates irrelevant information. First, NRI>0 does not account for the size of changes in a predicted risk. Infinitesimally small changes “count” even though they are clinically irrelevant. Second, NRI>0 does not account for an individual patient's position on the risk distribution. An event at the high end of the risk distribution who moves to an even higher risk reflects positively on NRI>0. Such movement likely has little effect on treatment decisions. A new marker is beneficial if it improves treatment decisions, which often means the marker can discriminate between events and nonevents in the middle of the risk distribution.
For the CVD data, and . 21% of events have a new 5-year risk within 1% of the old risk. Among nonevents the proportion is 53%. Therefore, a sizeable proportion of changes summarized by and especially by are small (and likely inconsequential) changes.
NRI>0 can make uninformative new markers appear predictive
Hilden and Gerds15 and Pepe and colleagues16 report a problematic feature of NRI>0. Suppose an old risk model (risk(X)) and a new risk model (risk(X,Y)) are fit to a training dataset. Suppose further that the new marker Y is completely uninformative. To avoid “optimistic bias” caused by using the same data to fit and evaluate model performance, a standard strategy is to use an independent dataset to assess the models' performances. However, NRI>0 tends to be positive for uninformative Y even when NRI>0 is computed on a large, independent validation dataset.16 This problem is likely to arise in settings where the risk models are not well calibrated ‐ a common phenomenon in practice. In contrast to NRI>0, more standard measures such as ΔAUC do not suffer this problem. These results show that NRI>0 can mislead researchers to believe that an uninformative marker improves prediction.
For 3+ categories NRI weights reclassifications indiscriminately
The purpose of risk categorization is to guide appropriate treatment decisions. For cardiovascular disease, suppose low risk indicates no intervention, medium risk indicates lifestyle changes, and high risk indicates both lifestyle changes and pharmaceutical intervention. When categories correspond to treatment decisions, the nature of reclassification matters, not just the direction. For example, changing an event from high risk to low risk is a more serious error than changing from high risk to medium risk.
When there are three or more risk categories, one should consider all the ways a new biomarker can move persons among risk categories. For three risk categories there are three ways to move “up”: low risk to medium risk; medium to high; and low to high. The 3-category NRIe gives each of these equal weight; in particular, moving up two risk categories counts the same as moving up one. Section B of the eAppendix describes how an appropriate weighting could be incorporated into a statistic. Weighting the different types of reclassification is extremely challenging, but that challenge does not justify using equal weights. As an alternative to assigning weights and providing a single numerical summary, one can instead examine the different types of reclassification in a reclassification table as shown below.
Polonsky et al.8 considered 3-category net reclassification indices with thresholds at 0.03 and 0.1 defining low, medium, and high 5-year risk. NRI0.03, 0.1=0.25. The value is driven by events and , even though most of the population count as nonevents. NRI0.03, 0.1=0.25 is a very coarse summary and almost impossible to interpret. Table 1 shows that the new risk model tends to place nonevents in the low and high risk categories, placing fewer nonevents in the medium risk category than the old risk model. If the harm of moving a nonevent from medium to high risk is greater than the benefit of moving a nonevent from medium risk to low risk, then the harms of the new risk model outweigh the benefits among nonevents. The single numerical summary, , does not reflect this.
Table 1.
Percentage of subjects in low-, medium-, and high-risk categories in the cardiovascular disease study data, presented separately for events (those with coronary heart disease) and nonevents (those without coronary heart disease) and for the old and new risk models.
| Risk Category | Old model | New modela | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonevent (n=5669) % |
Event (n=209) % |
Nonevent (n=5669) % |
Event (n=209) % |
|
| 0-3% | 67.1 | 27.3 | 70.6 | 24.4 |
| 3–10% | 30.6 | 55.0 | 22.3 | 38.8 |
| >10% | 4.4 | 17.7 | 7.1 | 36.8 |
|
| ||||
| Total | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
With coronary artery calcium score.
Table 2 shows the reclassifications of nonevents and, separately, events between the old and new risk models in the cardiovascular disease study data. Such tables are interesting and potentially instructive. However, it is easiest and most informative to simply look at how a risk model assigns nonevents and events to risk categories. This information appears on the margins of Table 2, and more succinctly in Table 1. Net reclassification indices statistics do not capture this important information.
Table 2.
Reclassification table for nonevents and events in the cardiovascular disease study data. Each interior cell contains the number of persons in the corresponding risk categories under the old and new risk models. The percentages in interior cells are among nonevents or events. The rows and columns labeled “Total” show the distributions of nonevents and events in the three risk categories under the old and new risk models – the same data are found in Table 1
| Old Model | New Modela | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-3% | 3-10% | >10% | Column Total | ||||
|
| |||||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | % | |
| Nonevents (n=5669) | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| 0–3% | 3276 | 58 | 408 | 7 | 5 | 1 | |
| 65 | |||||||
| 3–10% | 697 | 12 | 791 | 14 | 244 | 4 | |
| 31 | |||||||
| >10% | 30 | 1 | 63 | 1 | 155 | 3 | |
| 4 | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| Row Total (%) | 71 | 22 | 7 | ||||
| Events (n=209) | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| 0–3% | 34 | 16 | 22 | 11 | 1 | 0 | |
| 27 | |||||||
| 3–10% | 15 | 7 | 52 | 25 | 48 | 23 | |
| 55 | |||||||
| >10% | 2 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 28 | 13 | |
| 18 | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| Row Total (%) | 24 | 39 | 37 | ||||
With coronary artery calcium score.
Two-category NRIs: new names for existing measures
When there are two risk categories, low and high, NRIe is the change in the proportion of events assigned to the high risk category, i.e., the change in the true positive rate (ΔTPR). NRIne is the change in the proportion of nonevents designated low risk. In other words, NRIne = –ΔFPR, where ΔFPR is the change in the false positive rate. For 2 risk categories, the population-weighted NRI is the change in the misclassification rate.
Furthermore, the weighted net reclassification index is the same as the change in net benefit between the old and new risk models (eAppendix section A or Van Calster et al17). In other words, wNRI=ΔNB.
Data Analysis with NRI
Common practice is as follows. Investigators have a dataset that includes established risk factors (X) for a condition of interest and a potentially useful new marker (Y). They fit two regression models: an “old” model that uses only X, and a “new” model that uses both X and Y. The risk models are typically logistic regression models, or Cox models if data are censored. The prediction increment of Y is then assessed, typically using the same data that were used to fit the models.
NRI should not be used for testing
A researcher may consider testing the null hypothesis H0 : NRI=0. Pencina et al.4 provide a z-statistic for net reclassification index -based testing. However, the test based on this z-statistic has never been validated. The next section, and eAppendix sections D and E, discuss problems with the variance formula on which this z-statistic is based.18
Interestingly for the category-free index, NRI>0, hypothesis testing is unnecessary. Pepe et al.19 show that rejecting the null hypothesis H0 : NRI>0=0 is implied by rejecting the null hypothesis about the novel marker being a risk factor. In other words, once a test on the coefficient of the new marker is performed, it is redundant to perform a test based on NRI>0.
For the two-category or where t is the risk threshold, one cannot reject and on the basis of Y being a risk factor. Good tests are not yet established for these null hypotheses.
We favor inference about the nature and size of the prediction increment rather than testing a null hypothesis of no improvement. Such inference is challenging. At the early stages of model development it might be unclear how a risk model will be used, yet understanding how a risk model will be used is important for appropriately evaluating incremental value. Setting aside these larger considerations, the next section considers methods for constructing confidence intervals for net reclassification indices.
NRI Confidence Intervals
We conducted a simulation study to evaluate methods for constructed NRI confidence intervals. Based on the section above, we considered only category-free and 2-category event and non-event net reclassification indices. Results indicate that the most reliable confidence intervals use a bootstrap estimate of the variance of the statistic. Such confidence intervals outperformed confidence intervals constructed using the estimator proposed by Pencina et al.4 and other types of bootstrap confidence intervals. Sections C and D of the eAppendix describe the simulation study and its results in detail.
NRI inference in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis data
In the cardiovascular disease study data, we used 5-year risk thresholds 0.03 and 0.1following Polonsky et al.8 Table 3 compares confidence intervals for category-free and various 2-category event and nonevent net reclassification indices. Confidence intervals computed with bootstrapping are usually, but not always, wider than confidence intervals computed using . For the 2-category indices with threshold 0.03 for 5-year risk, the changes in the true- and false-positive rates are modest, with an estimated 6% reduction in the false-positive rate and 3% increase in the true-positive rate. For the 0.1 risk threshold, adding the coronary artery calcium score to risk prediction increases the true-positive rate substantially (19%), but also increases the false-positive rate by 3%.
Table 3.
Confidence intervals for select event and nonevent net reclassification indices in the cardiovascular disease study data. Intervals based on bootstrap estimates of the standard error, which we recommend, tend to be wider than intervals based on the formula for the variance of the estimated NRI statistic.. Recall that for a threshold t delineating high risk, and .
|
|
|
|||
|
| ||||
| formula | (0.252 to 0.503) | (0.294 to 0.344) | ||
| bootstrap | (0.275 to 0.481) | (0.257 to 0.382) | ||
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|||
|
| ||||
| formula | (−0.030 to 0.088) | (0.044 to 0.067) | ||
| bootstrap | (−0.039 to 0.097) | (0.026 to 0.084) | ||
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|||
|
| ||||
| formula | (0.125 to 0.258) | (−0.034 to −0.021) | ||
| bootstrap | (0.097 to 0.286) | (−0.039 to −0.016) | ||
Although the reclassification table (Table 2) and summary statistics (Table 3) are interesting, we find the risk distributions (Table 1) most useful. Table 1 shows that adding the arterial calcium score to prediction increases the proportion of events labeled as high risk. Unfortunately, it also increases the proportion of nonevents labeled as high risk. Since nonevents vastly outnumber events, Table 1 identifies an important problem with adding the calcium score to the risk model.
Discussion
The recent literature on measures of incremental value has developed as follows. Dissatisfaction with ΔAUC led to proposals for measures based on risk categories and reclassification.20 The category-based net reclassification index soon followed to address issues with those new measures.4 A preference to avoid arbitrary or weakly-justified risk thresholds led to the proposal for NRI>0.5 Unfortunately, NRI>0 has many of the same problems as ΔAUC. Neither measure is clinically meaningful; both measures are broad summaries of changes in risk models; and both measures incorporate irrelevant information. In these respects, things have come full circle. It is difficult to understand whether a value of NRI>0 is large or small, and this is due only partly to lack of experience with the index. Furthermore, without proper attention to model fit, NRI>0 can mislead researchers to believe that an uninformative marker improves prediction.15-16 We are skeptical that NRI>0 will help investigators develop biomarkers or improve risk models, and we are concerned about the potential for NRI>0 to mislead.
The net reclassification index statistics that are most useful are re-named versions of existing measures. Specifically, event and nonevent 2-category net reclassification indices are the changes in the true- and false-positive rates; and the weighted 2-category net reclassification index is the change in net benefit. In both cases, we prefer the established, descriptive terminology.
We recommend the bootstrap method for estimating the variance of net reclassification index estimates and constructing confidence intervals. However, methodology that works well for markers with small prediction increment is needed.21
The issues described above for NRI>0 also apply to net reclassification indices for 3+ categories. However, the overriding issue for 3+ categories is that the net reclassification indices do not discriminate between different types of reclassification — all upward movements in risk categories count the same, as do all downward movements. We thus recommend against net reclassification indices for 3 or more categories. As in the 2-category case, if the benefits and costs of different types of classification can be specified, these can be used as weights in a weighted net reclassification index, which would be the same as the change in net benefit. This is a challenging approach and, to the best of our knowledge, has not yet been done in practice. A practical alternative is to examine how the old and new risk models place events and nonevents into the risk categories (e.g. Table 1). A reclassification table (e.g. Table 2) may also be informative, as it presents the classification achieved with the new marker within strata defined by the baseline risk model. Depending on the application, select 2-category summary statistics may be appropriate, particularly for risk thresholds that indicate expensive or invasive treatment.
NRI>0 should not be used in hypothesis testing. Better tests are available and validated for the regression setting. However, we emphasize the limited value of hypothesis testing in assessing biomarkers. We recommend that investigators focus on describing the operating characteristics of risk models. Ideally, then, the prediction increment of a new marker is described in terms of how it improves risk model operating characteristics.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Financial Support: The MESA study was supported by contracts N01-HC-95159 through N01-HC-95169 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. This work was also supported by grant NIH GM054438 to MSP, grant NIH R01 CA152089 to HJ, and a subcontract to the University of Washington from NIH grant HL085757-07 to KFK.
Footnotes
SDC Supplemental digital content is available through direct URL citations in the HTML and PDF versions of this article (www.epidem.com). This content is not peer-reviewed or copy-edited; it is the sole responsibility of the author.
Contributor Information
Kathleen F. Kerr, Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington
Zheyu Wang, Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington.
Holly Janes, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington.
Robyn L. McClelland, Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington
Bruce M. Psaty, Cardiovascular Health Research Unit, Departments of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Health Services, University of Washington, Group Health Research Institute, Group Health Cooperative
Margaret S. Pepe, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Department of Biostatistics, University of Washington
References
- 1.Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Levy D, Belanger AM, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB. Prediction of coronary heart disease using risk factor categories. Circulation. 1998;97(18):1837–1847. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.97.18.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gail MH, Brinton LA, Byar DP, Corle DK, Green SB, Schairer C, Mulvihill JJ. Projecting individualized probabilities of developing breast cancer for white females who are being examined annually. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1989;81(24):1879–86. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.24.1879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.27th Bethesda Conference: Matching the intensity of risk factor management with the hazard for coronary disease events. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 1996;27(5):957–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB, Sr, D'Agostino RB, Jr, Vasan RS. Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: from area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Statistics in Medicine. 2008;27:157–172. doi: 10.1002/sim.2929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB, Sr, Steyerberg EW. Extensions of net reclassification improvement calculations to measure usefulness of new biomarkers. Statistics in Medicine. 2011;30:11–21. doi: 10.1002/sim.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Greenland P, O'Malley PG. When Is a New Prediction Marker Useful? A Consideration of Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 and C-Reactive Protein for Stroke Risk. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2005;165(21):2454–2456. doi: 10.1001/archinte.165.21.2454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Peirce CS. The Numerical Measure of the Success of Prediction. Science. 1884;4:453–454. doi: 10.1126/science.ns-4.93.453-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Polonsky T, McClelland R, Jorgensen N, Bild D, Burke G, Guerci A, Greenland P. Coronary artery calcium score and risk classification for coronary heart disease prediction. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2010;303(16):1610–1616. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Leening MJG, Steyerberg EW. Fibrosis and mortality in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2013;309(24):2547–2549. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.6470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pickering JW, Endre ZH. New metrics for assessing diagnostic potential of candidate biomarkers. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2012;7:1–10. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09590911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pepe MS. Problems with risk reclassification methods for evaluating prediction models. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2011;173(11):1327–1335. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwr013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB, Sr, Pencina K, Janssens A, Greenland P. Interpreting incremental value of markers added to risk prediction models. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2012;176:473–481. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kerr KF, Bansal A, Pepe MS. Further insight into the incremental value of new markers: the interpretation of performance measures and the importance of clinical context. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2012;176:482–487. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Greenland S. The need for reorientation toward cost-effective prediction: Comments on ‘Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: From area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond’ by MJ Pencina et al. Statistics in Medicine. 2008;27(2):199–206. doi: 10.1002/sim.2995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hilden J, Gerds TA. Evaluating the impact of novel biomarkers: Do not rely on integrated discrimination improvement and net reclassification index. Statistics in Medicine. 2013 doi: 10.1002/sim.5804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pepe M, Fang J, Feng Z, Gerds T, Hilden J. The Net Reclassification Index (NRI): a Misleading Measure of Prediction Improvement with Miscalibrated or Overfit Models. UW Department of Biostatistics Working Paper Series. 2013 Paper 392. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Van Calster B, Vickers AJ, Pencina MJ, Baker SG, Timmerman D, Steyerberg EW. Evaluation of Markers and Risk Prediction Models: Overview of Relationships between NRI and Decision-Analytic Measures. Medical Decision Making. 2013;33:490. doi: 10.1177/0272989X12470757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pepe MS, Feng Z, Gu JW. Comments on ‘Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: From area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond’ by Pencina et al. Statistics in Medicine. 2008;27:173–181. doi: 10.1002/sim.2991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pepe MS, Kerr KF, Longton G, Wang Z. Testing for improvement in prediction model performance. Statistics in Medicine. 2013;32(9):1467–1482. doi: 10.1002/sim.5727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cook NR. Use and misuse of the receiver operating characteristic curve in risk prediction. Circulation. 2007;115(7):928–935. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.672402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Uno H, Tian L, Cai T, Kohane IS, Wei LJ. A unified inference procedure for a class of measures to assess improvement in risk prediction systems with survival data. Statistics in Medicine. 2013;32(14):2430–2442. doi: 10.1002/sim.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


