Abstract
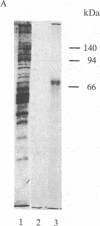
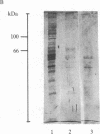
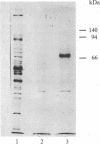
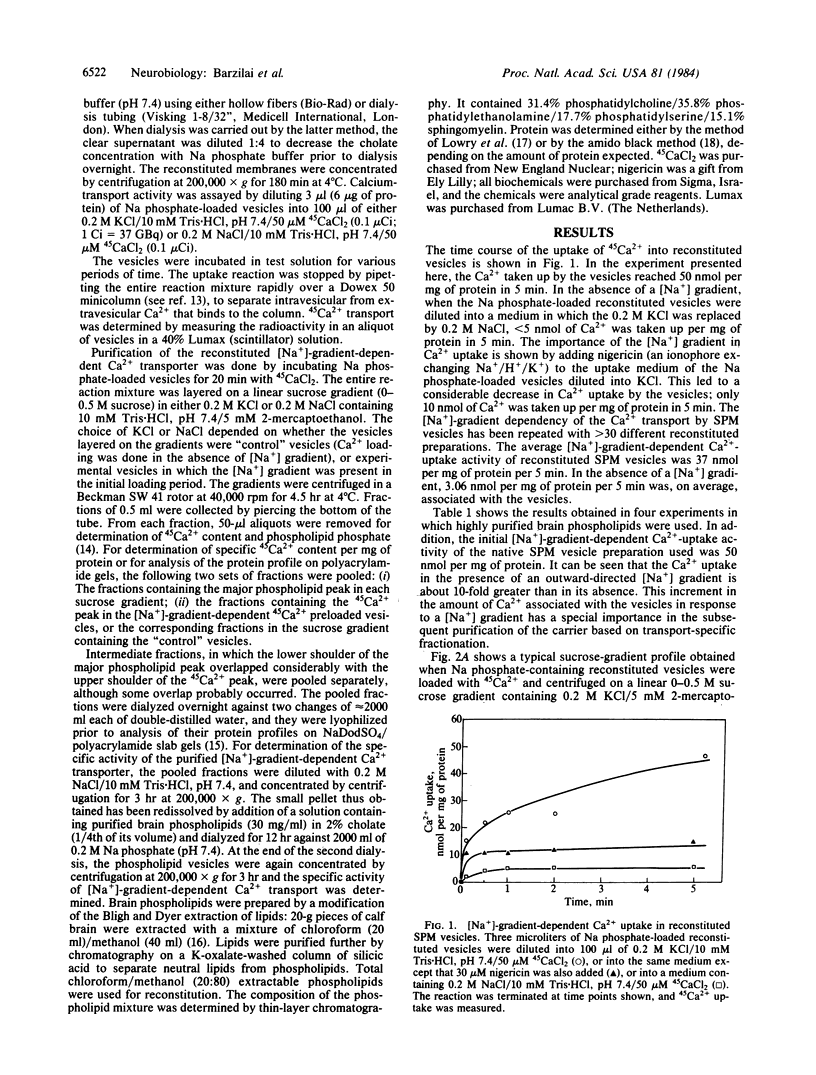
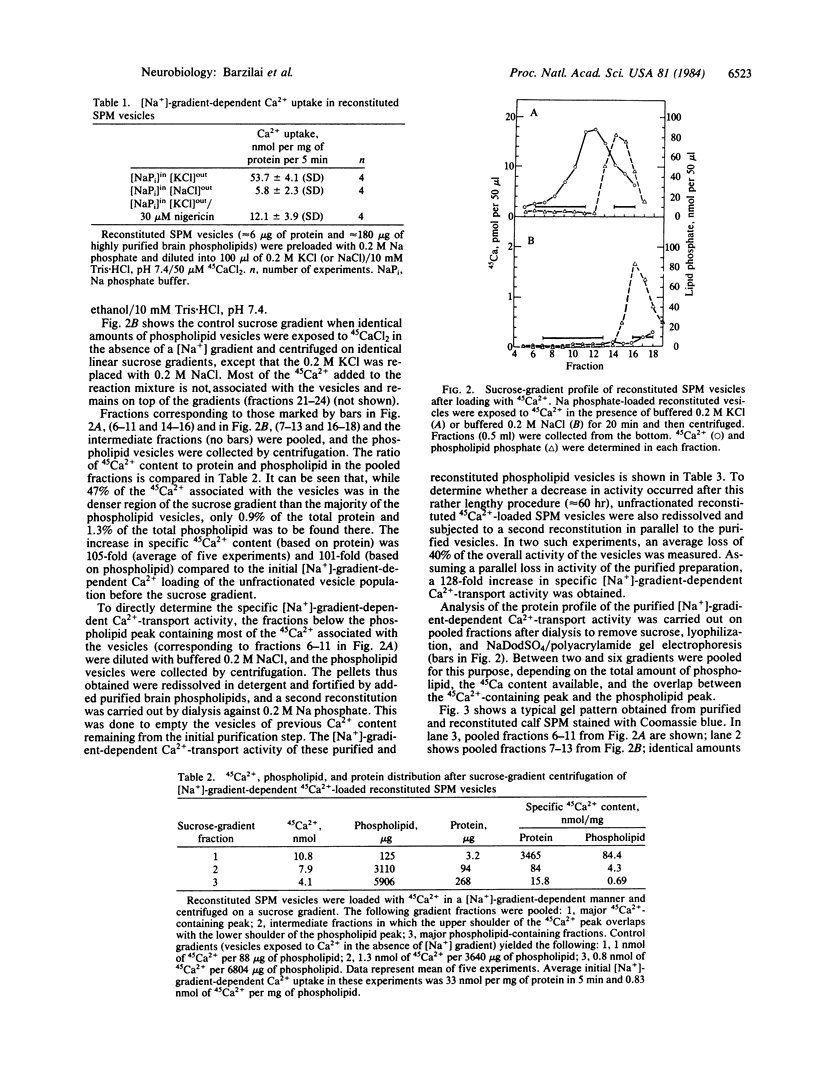
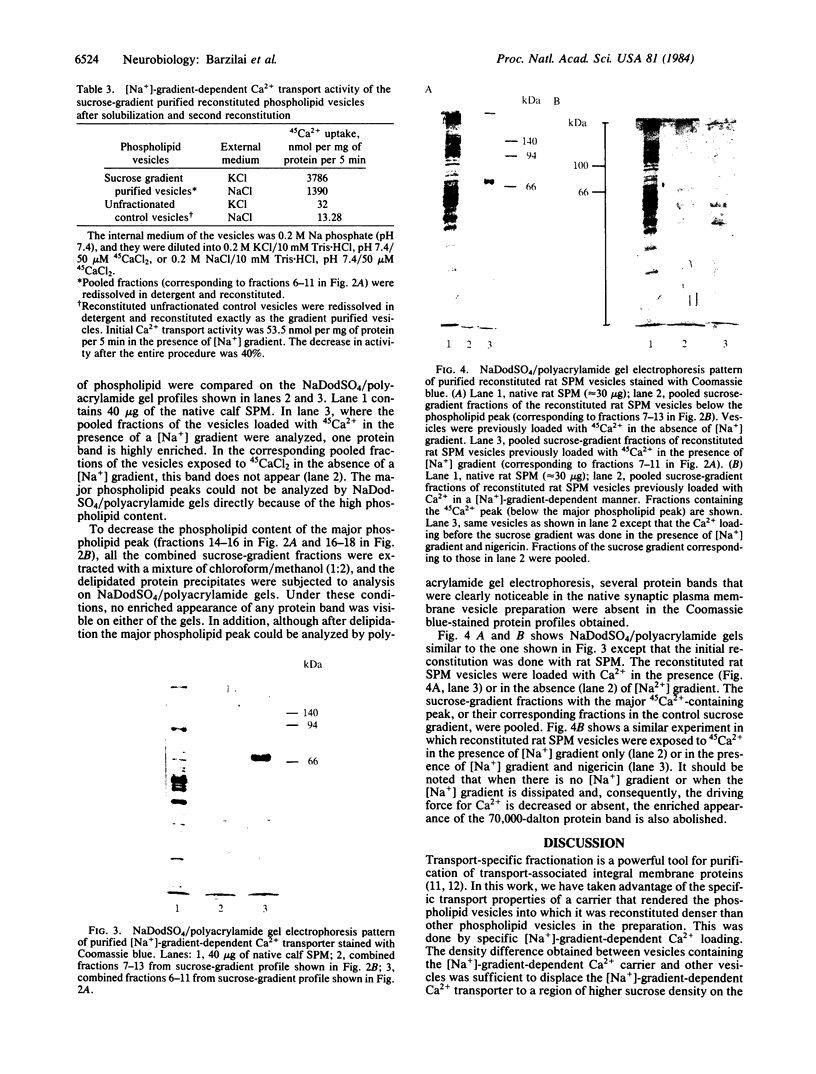
A [Na+]-gradient-dependent Ca2+ transporter from brain synaptic plasma membranes has been isolated, purified, and reconstituted into brain phospholipid vesicles. The purification was achieved by sucrose-gradient centrifugation after solubilization of the synaptic membranes in cholate in the presence of a 30-fold excess (by weight) of added brain phospholipids and [Na+]-gradient-dependent Ca2+ loading of the reconstituted vesicles. A 128-fold increase in specific activity of [Na+]-gradient-dependent Ca2+ uptake per mg of protein has been obtained. The purified and reconstituted vesicles took up Ca2+ only in response to an outward-oriented [Na+] gradient. The Ca2+ uptake could be inhibited by dissipation of the [Na+] gradient with nigericin. Successful purification was based on the initial [Na+]-gradient dependency of the Ca2+-transport process, the magnitude of the [Na+]-gradient-dependent uptake, and the presence of purified brain phospholipids. Analysis of the sucrose-gradient-purified reconstituted vesicles on NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels showed that the activity coincided with enriched appearance of a 70,000-Da protein.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L., Steinhardt R. A. The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):431–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ector A. C. Carrier-mediated sodium-dependent and calcium-dependent calcium efflux from pinched-off presynaptic nerve terminals (synaptosomes) in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. Y., Hess E. J., Rahamimoff H., Goldin S. M. Purification and immunological characterization of a calcium pump from bovine brain synaptosomal vesicles. J Neurosci. 1984 Jun;4(6):1468–1478. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-06-01468.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasko O. D., Knowles A. F., Shertzer H. G., Suolinna E. M., Racker E. The use of ion-exchange resins for studying ion transport in biological systems. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:57–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90506-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin S. M., Rhoden V. Reconstitution and "transport specificity fractionation" of the human erythrocyte glucose transport system. A new approach for identification and isolation of membrane transport proteins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2575–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUTTGAU H. C., NIEDERGERKE R. The antagonism between Ca and Na ions on the frog's heart. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):486–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto H., Racker E. Solubilization and partial purification of the Ca2+/Na+ antiporter from the plasma membrane of bovine heart. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2656–2658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J. The generation of electric currents in cardiac fibers by Na/Ca exchange. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C103–C110. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D., Rahamimoff H., Goldin S. M. Reconstitution and purification by "transport specificity fractionation" of an ATP-dependent calcium transport component from synaptosome-derived vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3708–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff H., Spanier R. Sodium-dependent calcium uptake in membrane vesicles derived from rat brain synaptosomes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Seitz N. The dependence of calcium efflux from cardiac muscle on temperature and external ion composition. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Swanson P. D. Solubilization and reconstitution of membranes containing the Na+ -Ca2+ exchange carrier from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 25;690(1):133–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Goshima K. Partial purification of Na+-Ca2+ antiporter from plasma membrane of chick heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 8;693(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90478-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]