Abstract
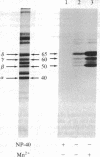
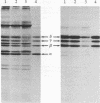
Postsynaptic membranes from the electric organ of Torpedo californica, rich in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, were shown to contain an endogenous tyrosine protein kinase. This endogenous kinase phosphorylated three major proteins with molecular masses corresponding to 50 kDa, 60 kDa, and 65 kDa. The phosphorylation of these three proteins occurred exclusively on tyrosine residues under the experimental conditions used and was abolished by 0.1% Nonidet P-40 and stimulated by Mn2+. The 50-kDa, and 60-kDa, and 65-kDa phosphoproteins were demonstrated to be the beta, gamma, and delta subunits, respectively, of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by purification of the phosphorylated receptor using affinity chromatography. The endogenous tyrosine kinase specifically phosphorylated the beta, gamma, and delta subunits rapidly to a final stoichiometry of approximately equal to 0.5 mol of phosphate per mol of sub-unit. Two-dimensional phosphopeptide mapping of the phosphorylated beta, gamma, and delta subunits, after limit proteolysis with trypsin or thermolysin, indicated that each subunit was phosphorylated on a single site. Locations are proposed for the amino acid residues phosphorylated on the receptor by the tyrosine-specific protein kinase and by two other protein kinases (cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C) which phosphorylate the receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony D. T., Schuetze S. M., Rubin L. L. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus prevents acetylcholine receptor clustering on cultured chicken muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2265–2269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Huang T. S. Decomposition of phosphoserine and phosphothreonine during acid hydrolysis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jun;73(2):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Ballivet M., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., McLaughlin M., Karlin A. Bromoacetylcholine as an affinity label of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):845–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91661-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Gordon A. S., Diamond I. Specificity and localization of the acetylcholine receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Giraudat J., Bentaboulet M., Changeux J. P. Complete mRNA coding sequence of the acetylcholine binding alpha-subunit of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor: a model for the transmembrane organization of the polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Davis C. G., Milfay D., Diamond I. Phosphorylation of acetylcholine receptor by endogenous membrane protein kinase in receptor-enriched membranes of Torpedo californica. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):539–540. doi: 10.1038/267539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Milfay D., Davis C. G., Diamond I. Protein phosphatase activity in acetylcholine receptor-enriched membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):876–883. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ek B., Rönnstrand L. Characterization of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor on human fibroblasts. Demonstration of an intimate relationship with a 185,000-Dalton substrate for the platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10054–10061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Greengard P. cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Racker E. Properties of proteoliposomes reconstituted with acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9372–9378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Blithe D. L., Kahn C. R. Tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity is associated with the purified insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blith D. L., Karlsson F. A., Häring H. U., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphorylation of the beta subunit of the insulin receptor. Formation of both phosphoserine and phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9891–9894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J. M., Whitehouse S., Walsh D. A. Possibility of shape conformers of the protein inhibitor of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4835–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation in the brain. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):583–588. doi: 10.1038/305583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Hirose T., Asai M., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Primary structures of beta- and delta-subunit precursors of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):251–255. doi: 10.1038/301251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Esch F. S., Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the sequence of amino acids surrounding sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):973–977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R., Krebs E. G. Characterization of platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation in cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9383–9390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Changeux J. P. Change in state of phosphorylation of acetylcholine receptor during maturation of the electromotor synapse in Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. A simple assay for the study of solubilized acetylcholine receptors. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smilowitz H., Hadjian R. A., Dwyer J., Feinstein M. B. Regulation of acetylcholine receptor phosphorylation by calcium and calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4708–4712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Weber M., Changeux J. P. Large-scale purification of the acetylcholine-receptor protein in its membrane-bound and detergent-extracted forms from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):215–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., Nambi P., Shorr R. G., Sawyer D. F., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Catecholamine-induced desensitization of turkey erythrocyte adenylate cyclase is associated with phosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3173–3177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tank D. W., Huganir R. L., Greengard P., Webb W. W. Patch-recorded single-channel currents of the purified and reconstituted Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5129–5133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Sobel A., Changeux J. P. In vitro phosphorylation of the acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):540–542. doi: 10.1038/267540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandlen R. L., Wu W. C., Eisenach J. C., Raftery M. A. Studies of the composition of purified Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor and of its subunits. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1845–1854. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. W., Goldberg A. R. In vitro phosphorylation of angiotensin analogs by tyrosyl protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1022–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor beta subunit activates the receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5277–5286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Comerci C., Subers E., Egan J. J., Huang C. K., Feinstein M. B., Smilowitz H. cAMP, not Ca2+/calmodulin, regulates the phosphorylation of acetylcholine receptor in Torpedo californica electroplax. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Mar 14;770(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]