Abstract
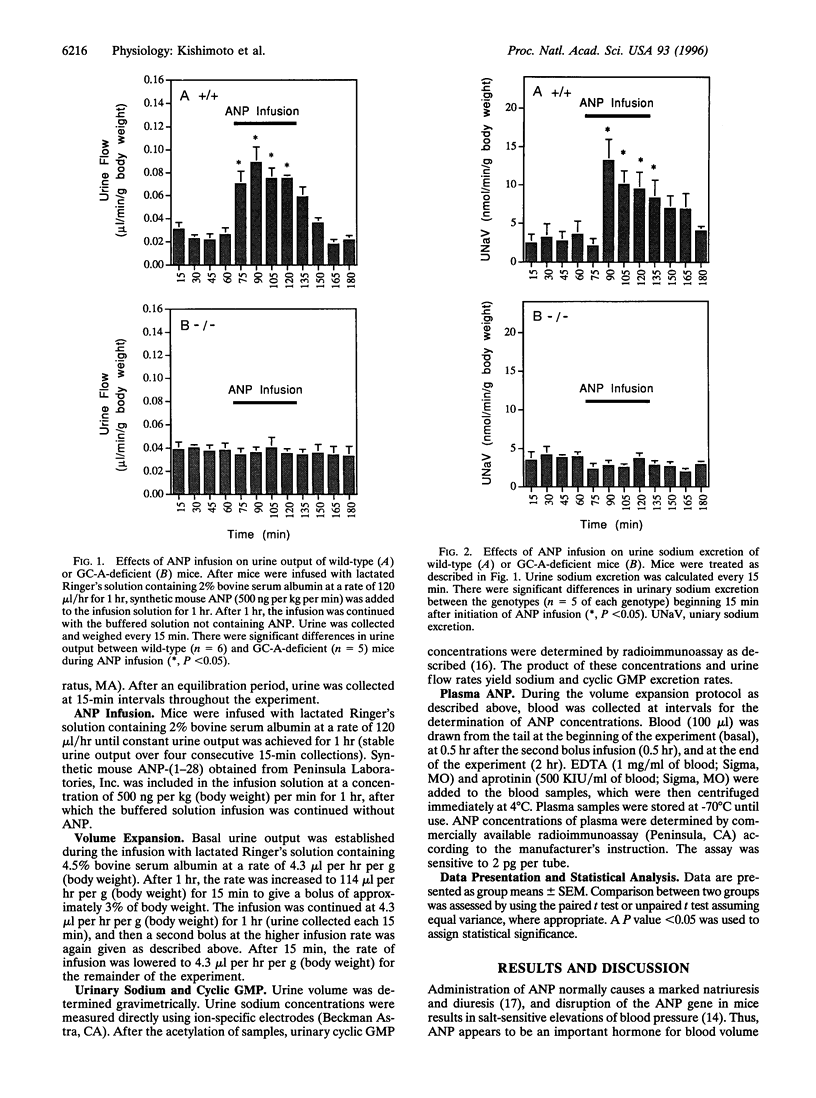
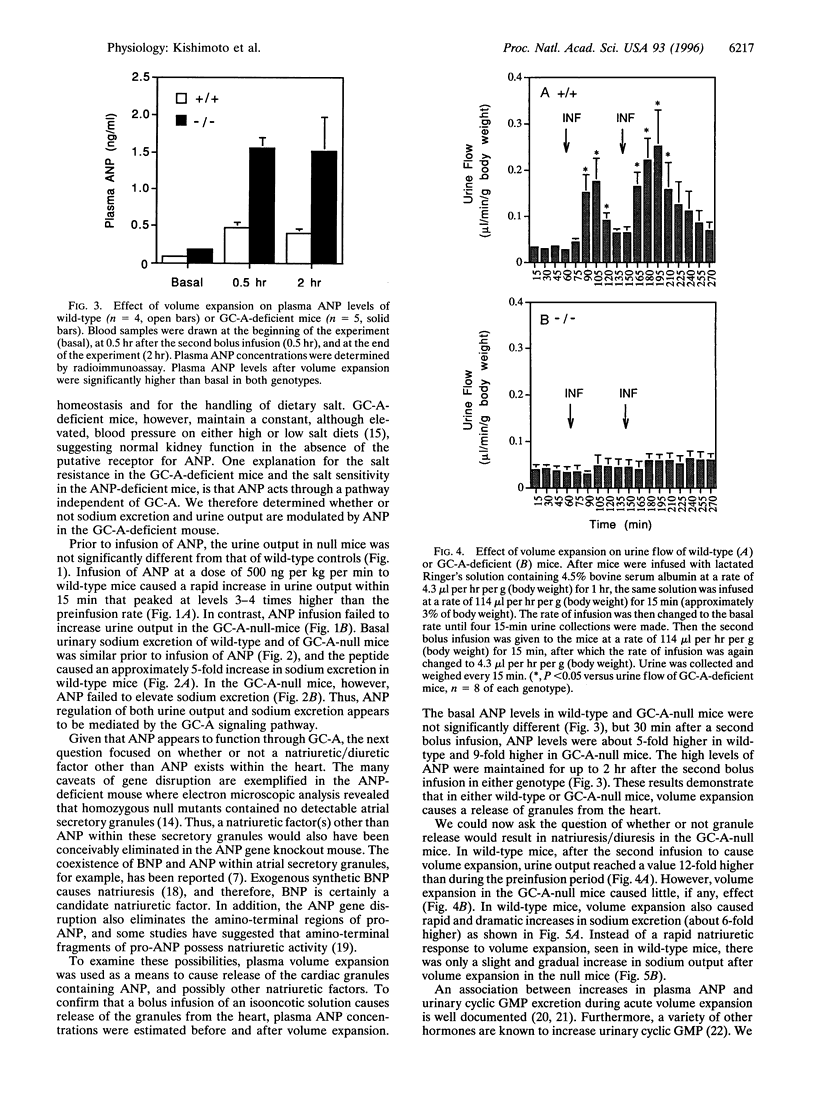
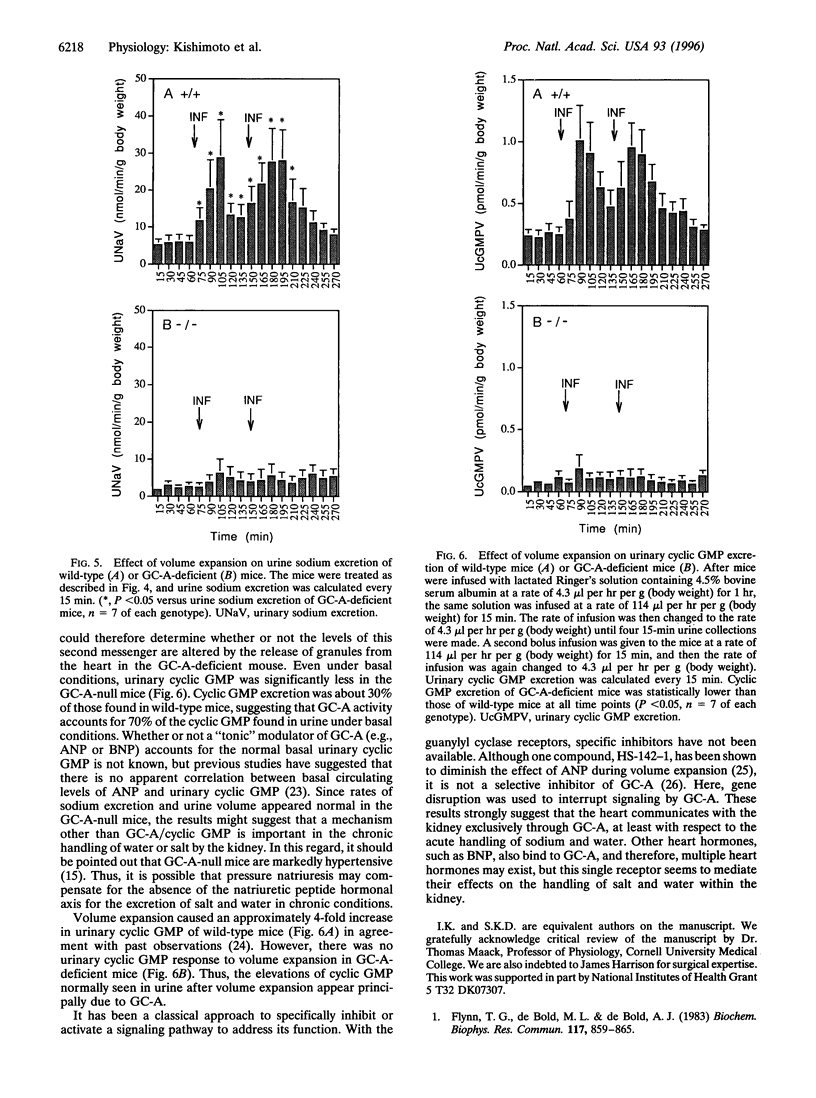
Disruption of guanylyl cyclase-A (GC-A) results in mice displaying an elevated blood pressure, which is not altered by high or low dietary salt. However, atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), a proposed ligand for GC-A, has been suggested as critical for the maintenance of normal blood pressure during high salt intake. In this report, we show that infusion of ANP results in substantial natriuresis and diuresis in wild-type mice but fails to cause significant changes in sodium excretion or urine output in GC-A-deficient mice. ANP, therefore, appears to signal through GC-A in the kidney. Other natriuretic/diuretic factors could be released from the heart. Therefore, acute volume expansion was used as a means to cause release of granules from the atrium of the heart. That granule release occurred was confirmed by measurements of plasma ANP concentrations, which were markedly elevated in both wild-type and GC-A-null mice. After volume expansion, urine output as well as urinary sodium and cyclic GMP excretion increased rapidly and markedly in wild-type mice, but the rapid increases were abolished in GC-A-deficient animals. These results strongly suggest that natriuretic/diuretic factors released from the heart function exclusively through GC-A.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand-Srivastava M. B., Sairam M. R., Cantin M. Ring-deleted analogs of atrial natriuretic factor inhibit adenylate cyclase/cAMP system. Possible coupling of clearance atrial natriuretic factor receptors to adenylate cyclase/cAMP signal transduction system. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8566–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker G., Harper J. F., Terasaki W. L., Moylan R. D. Radioimmunoassay of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. G., de Bold M. L., de Bold A. J. The amino acid sequence of an atrial peptide with potent diuretic and natriuretic properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):859–865. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91675-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Porter J. G., Arfsten A. E., Miller J., Schilling J. W., Scarborough R. M., Lewicki J. A., Schenk D. B. Atrial natriuretic peptide clearance receptor. Complete sequence and functional expression of cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9395–9401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbers D. L. Guanylyl cyclase receptors and their endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine ligands. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90258-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., Haddox M. K. Cyclic GMP metabolism and involvement in biological regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:823–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S. W., Krege J. H., Oliver P. M., Hagaman J. R., Hodgin J. B., Pang S. C., Flynn T. G., Smithies O. Genetic decreases in atrial natriuretic peptide and salt-sensitive hypertension. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):679–681. doi: 10.1126/science.7839143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. E., Thölken H., Ganten D., Luft F. C., Ruskoaho H., Unger T. Atrial natriuretic factor--a circulating hormone stimulated by volume loading. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):264–266. doi: 10.1038/314264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis H. M., Wilkins M. R., Selwyn B. M., Yelland U. J., Griffith M. E., Bhoola K. D. Urinary guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate but not tissue kallikrein follows the plasma atrial natriuretic factor response to acute volume expansion with saline. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Nov;75(5):489–494. doi: 10.1042/cs0750489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez M. J., Wong S. K., Kishimoto I., Dubois S., Mach V., Friesen J., Garbers D. L., Beuve A. Salt-resistant hypertension in mice lacking the guanylyl cyclase-A receptor for atrial natriuretic peptide. Nature. 1995 Nov 2;378(6552):65–68. doi: 10.1038/378065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T., Suzuki M., Almeida F. A., Nussenzveig D., Scarborough R. M., McEnroe G. A., Lewicki J. A. Physiological role of silent receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.2823385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Naruse M., Naruse K., Kawana M., Nishikawa T., Hosoda S., Tanaka I., Yoshimi T., Yoshihara I., Inagami T. Atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide coexist in the secretory granules of human cardiac myocytes. Am J Hypertens. 1991 Nov;4(11):909–912. doi: 10.1093/ajh/4.11.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzveig D. R., Lewicki J. A., Maack T. Cellular mechanisms of the clearance function of type C receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20952–20958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama Y., Miyamoto K., Morishita Y., Matsuda Y., Saito Y., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Stable expression of natriuretic peptide receptors: effects of HS-142-1, a non-peptide ANP antagonist. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):336–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91563-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagnella G. A., Markandu N. D., Buckley M. G., Singer D. R., MacGregor G. A. Atrial natriuretic peptide-cyclic GMP relationships in normal humans: effects of dietary sodium intake. Clin Sci (Lond) 1993 Jul;85(1):13–17. doi: 10.1042/cs0850013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano T., Morishita Y., Yamada K., Matsuda Y. Effects of HS-142-1, a novel non-peptide ANP antagonist, on diuresis and natriuresis induced by acute volume expansion in anesthetized rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):824–829. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91806-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suga S., Nakao K., Hosoda K., Mukoyama M., Ogawa Y., Shirakami G., Arai H., Saito Y., Kambayashi Y., Inouye K. Receptor selectivity of natriuretic peptide family, atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, and C-type natriuretic peptide. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):229–239. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1309330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin J. P., Qiu C., Muldowney W. P., Ying W. Z., Gardner D. G., Humphreys M. H. Cellular basis for blunted volume expansion natriuresis in experimental nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1302–1312. doi: 10.1172/JCI115995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesely D. L., Douglass M. A., Dietz J. R., Gower W. R., Jr, McCormick M. T., Rodriguez-Paz G., Schocken D. D. Three peptides from the atrial natriuretic factor prohormone amino terminus lower blood pressure and produce diuresis, natriuresis, and/or kaliuresis in humans. Circulation. 1994 Sep;90(3):1129–1140. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.3.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widecka K., Celibała R., Goździk J., Syrenicz A., Ciechanowski K., Czekalski S. Exaggerated natriuresis induced by sodium chloride infusion in essential hypertension is accompanied by an exaggerated urinary 3' 5' guanosine monophosphate excretion. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1993;8(8):711–715. doi: 10.1093/ndt/8.8.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Yasue H., Morita E., Sakaino N., Jougasaki M., Kurose M., Mukoyama M., Saito Y., Nakao K., Imura H. Hemodynamic, renal, and hormonal responses to brain natriuretic peptide infusion in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1991 Oct;84(4):1581–1588. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.4.1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J. Atrial natriuretic factor: a hormone produced by the heart. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2932797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


