Abstract
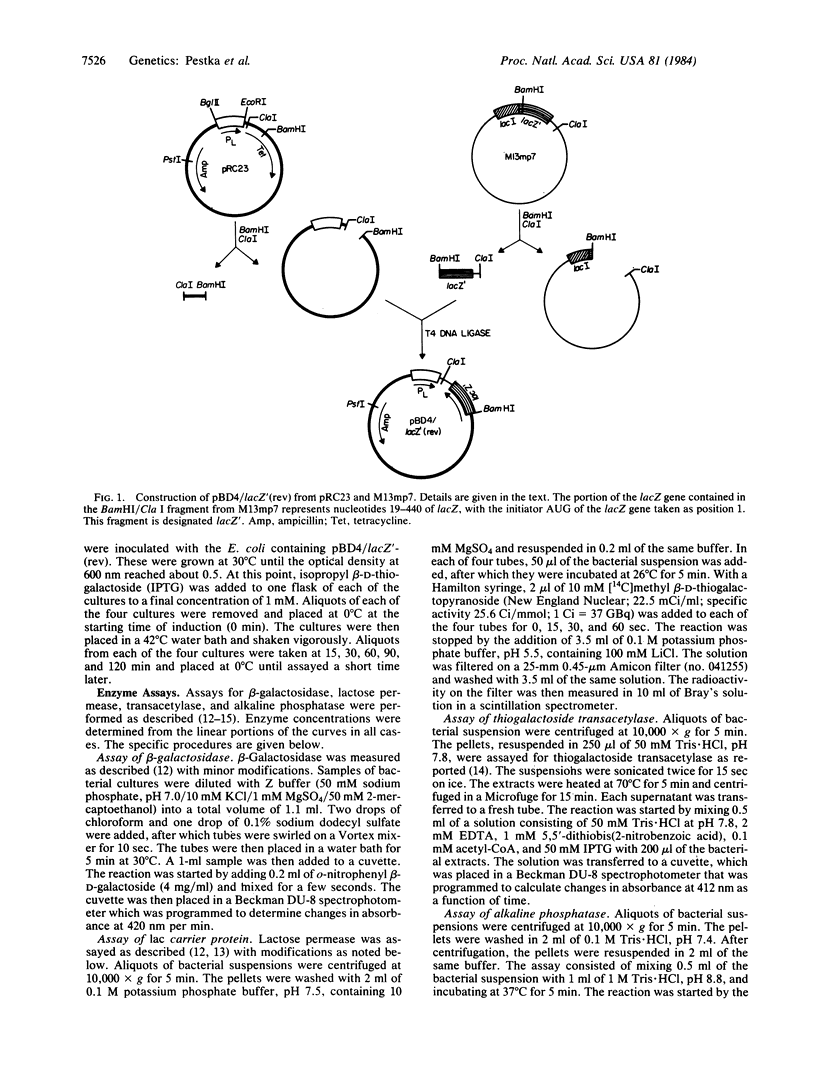
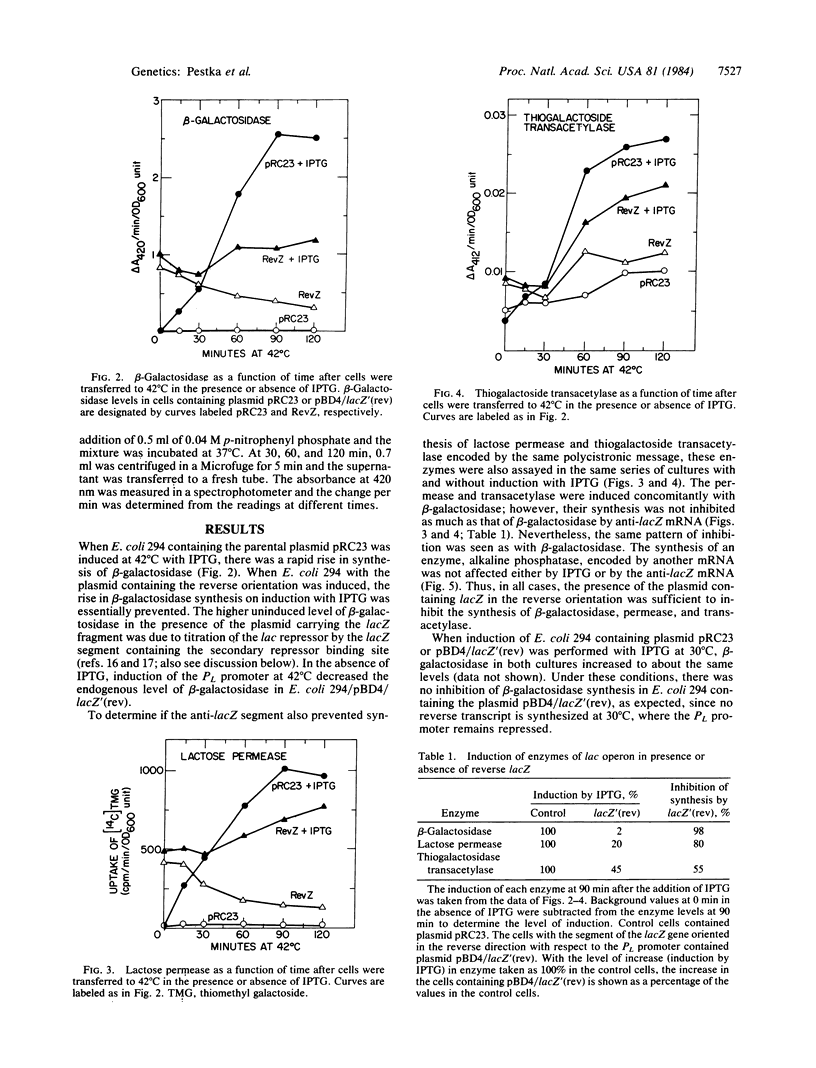
A plasmid was constructed to generate RNA complementary to the beta-galactosidase mRNA under control of the phage lambda PL promoter. When this anti-mRNA was produced, synthesis of beta-galactosidase was dramatically inhibited (98%). Syntheses of galactoside permease and transacetylase, whose coding sequences are downstream of the beta-galactosidase coding region, are inhibited to a lesser degree, 80% and 55%, respectively. The generation of anti-mRNA that can be targeted to inhibit a single species of mRNA molecule within cells provides a potent mechanism by which specific transcripts can be translationally inactivated. This can be used to determine the function of proteins as well as to select cloned genes in a single rapid and convenient step.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALPERS D. H., APPEL S. H., TOMKINS G. M. A SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC ASSAY FOR THIOGALACTOSIDE TRANSACETYLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:10–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich M. A., Venetianer P., Goldberger R. F. Alternative modes of derepression of the histidine operon observed in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4426–4433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Helinski D. R. Use of the lambda phage promoter PL to promote gene expression in hybrid plasmid cloning vehicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:482–492. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Held W. A. Analysis of mRNA populations by cDNA.mRNA hybrid-mediated inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene expression by anti-sense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic analysis. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb M. Studies of heat-inducible lambda bacteriophage. I. Order of genetic sites and properties of mutant prophages. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A unique mechanism regulating gene expression: translational inhibition by a complementary RNA transcript (micRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1966–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Kuff E. L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Winter R. B., Hurley C. K. The location of the repressor binding sites in the lac operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2314–2318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER M. F., JONES O. W., NIRENBERG M. W. The effect of secondary structure of the template activity of polyribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Mar 15;49:392–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.3.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumble W. R., Viitanen P. V., Sarkar H. K., Poonian M. S., Kaback H. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of cys148 in the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 30;119(3):860–867. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90853-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


