Abstract
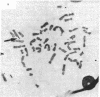
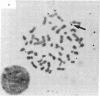
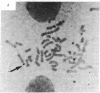
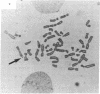
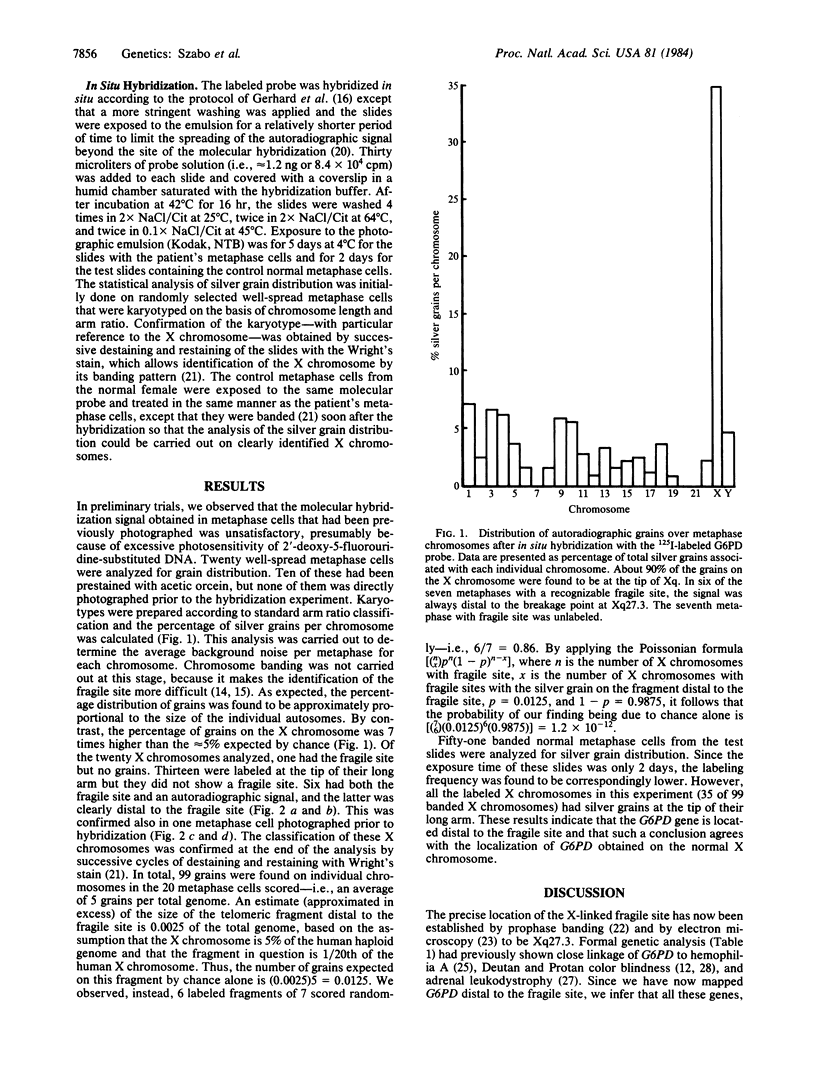
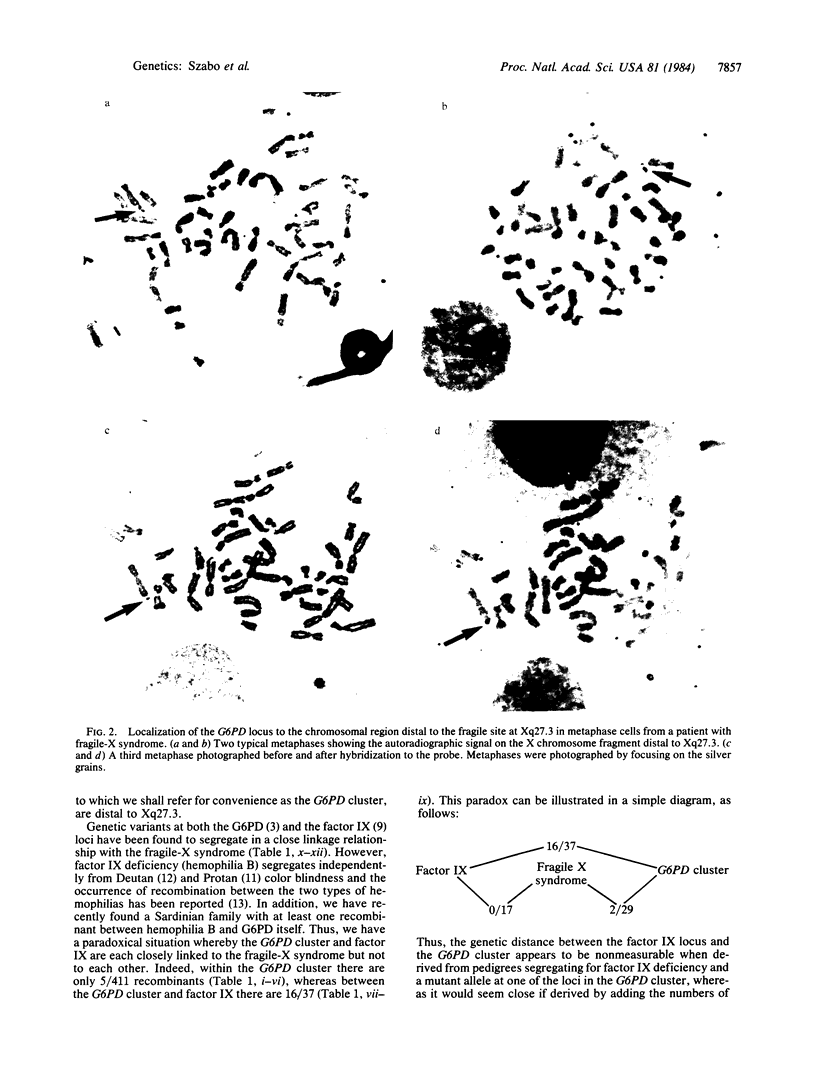
The human gene for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) has been subregionally mapped to band Xq28 by segregation analysis in rodent-human somatic cell hybrids [Pai, G. S., Sprinkel, J. A., Do, T. T., Mareni, C. E. & Migeon, B. R. (1980) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 2810-2813]. We have previously reported a common type of X-linked mental retardation associated with an inducible fragile site at Xq27-Xq28 segregates in a close linkage relationship with a G6PD variant, but the relative position of G6PD with respect to the fragile site has not yet been established. This fragile-X syndrome has been shown to be closely linked also to a Taq I restriction fragment length polymorphism detected by a cDNA probe for factor IX, and the latter locus has been mapped to the subtelomeric region Xq26-Xq28 [Camerino, G., Mattei, M. G., Mattei, G. F., Jaye, B. & Mandel, J. L. (1983) Nature (London) 306, 701-704]. The in situ hybridization studies reported here provide strong evidence that G6PD is located on the Xq telomeric fragment distal to the fragile site. These observations and the well-established knowledge that the genes for Deutan and Protan colorblindness are closely linked to G6PD, but segregate independently of factor IX deficiency, suggest that the fragile site associated with this type of X-linked mental retardation occurs in a region prone to high frequency of meiotic recombination.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd Y., Buckle V. J., Munro E. A., Choo K. H., Migeon B. R., Craig I. W. Assignment of the haemophilia B (factor IX) locus to the q26-qter region of the X chromosome. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 May;48(Pt 2):145–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb01009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookwell R., Turner G. High resolution banding and the locus of the Xq fragile site. Hum Genet. 1983;63(1):77–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00285404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Jaye M., Mandel J. L. Close linkage of fragile X-mental retardation syndrome to haemophilia B and transmission through a normal male. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):701–704. doi: 10.1038/306701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M. E., Yunis J. J. A high resolution in situ hybridization technique for the direct visualization of labeled G-banded early metaphase and prophase chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):352–356. doi: 10.1159/000130970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Gould K. G., Rees D. J., Brownlee G. G. Molecular cloning of the gene for human anti-haemophilic factor IX. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):178–180. doi: 10.1038/299178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi G., Mannucci P. M., Coppola R., Farris A., Rinaldi A., Siniscalco M. Studies on hemophilia A in Sardinia bearing on the problems of multiple allelism, carrier detection, and differential mutation rate in the two sexes. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):44–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi G., Rinaldi A., Archidiacono N., Rocchi M., Balazs I., Siniscalco M. Brief report: linkage between G6PD and fragile-X syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1983 May;15(1):113–119. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320150115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard D. S., Kawasaki E. S., Bancroft F. C., Szabo P. Localization of a unique gene by direct hybridization in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3755–3759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Winship P. R., Ferrari N., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Characterisation and use of an intragenic polymorphic marker for detection of carriers of haemophilia B (factor IX deficiency). Lancet. 1984 Feb 4;1(8371):239–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Boyd Y., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Gene deletions in patients with haemophilia B and anti-factor IX antibodies. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):181–182. doi: 10.1038/303181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover T. W. FUdR induction of the X chromosome fragile site: evidence for the mechanism of folic acid and thymidine inhibition. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Mar;33(2):234–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON J. F. HAEMOPHILIA, CHRISTMAS DISEASE AND THE XG BLOOD GROUPS. OBSERVATIONS BASED ON THE HAEMOPHILIACS OF BIRMINGHAM. Br J Haematol. 1964 Jan;10:115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison C. J., Jack E. M., Allen T. D., Harris R. The fragile X: a scanning electron microscope study. J Med Genet. 1983 Aug;20(4):280–285. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.4.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., de la Salle H., Schamber F., Balland A., Kohli V., Findeli A., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. Isolation of a human anti-haemophilic factor IX cDNA clone using a unique 52-base synthetic oligonucleotide probe deduced from the amino acid sequence of bovine factor IX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2325–2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leversha M. A., Webb G. C., Pavey S. M. Chromosome banding required for studies on X-linked mental retardation. Lancet. 1981 Jan 3;1(8210):49–49. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Moser H. W., Moser A. B., Axelman J., Sillence D., Norum R. A. Adrenoleukodystrophy: evidence for X linkage, inactivation, and selection favoring the mutant allele in heterozygous cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Drayna D., Goodfellow P. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):176–204. doi: 10.1159/000132009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai G. S., Sprenkle J. A., Do T. T., Mareni C. E., Migeon B. R. Localization of loci for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and biochemical evidence of nonrandom X chromosome expression from studies of a human X-autosome translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2810–2813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Toniolo D., Nobile C., D'Urso M., Luzzatto L. cDNA sequences of human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase cloned in pBR322. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):778–780. doi: 10.1038/294778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensky W. The radioiodination of RNA and DNA to high specific activities. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:121–152. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61800-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. H., TRUEMAN R. G. COMBINED HEMOPHILIA AND CHRISTMAS DISEASE. Blood. 1964 Sep;24:281–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi A., Velivasakis M., Latte B., Filippi G., Siniscalco M. Triplo-X constitution of mother explains apparent occurrence of two recombinants in sibship segregating at two closely X-linked loci (G6PD and deutan). Am J Hum Genet. 1978 Jul;30(4):339–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi A., Velivasakis M., Latte B., Filippi G., Siniscalco M. Triplo-X constitution of mother explains apparent occurrence of two recombinants in sibship segregating at two closely X-linked loci (G6PD and deutan). Am J Hum Genet. 1978 Jul;30(4):339–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER D. L., COPELAND D. L., GRAHAM J. B. Linkage of color blindness to hemophilias A and B. Am J Hum Genet. 1962 Jun;14:149–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. L., McConnell J., Moore D., Macpherson C. R., Marson A. Christmas disease, color-blindness and blood group Xga. Am J Med. 1967 Aug;43(2):214–226. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]