Abstract
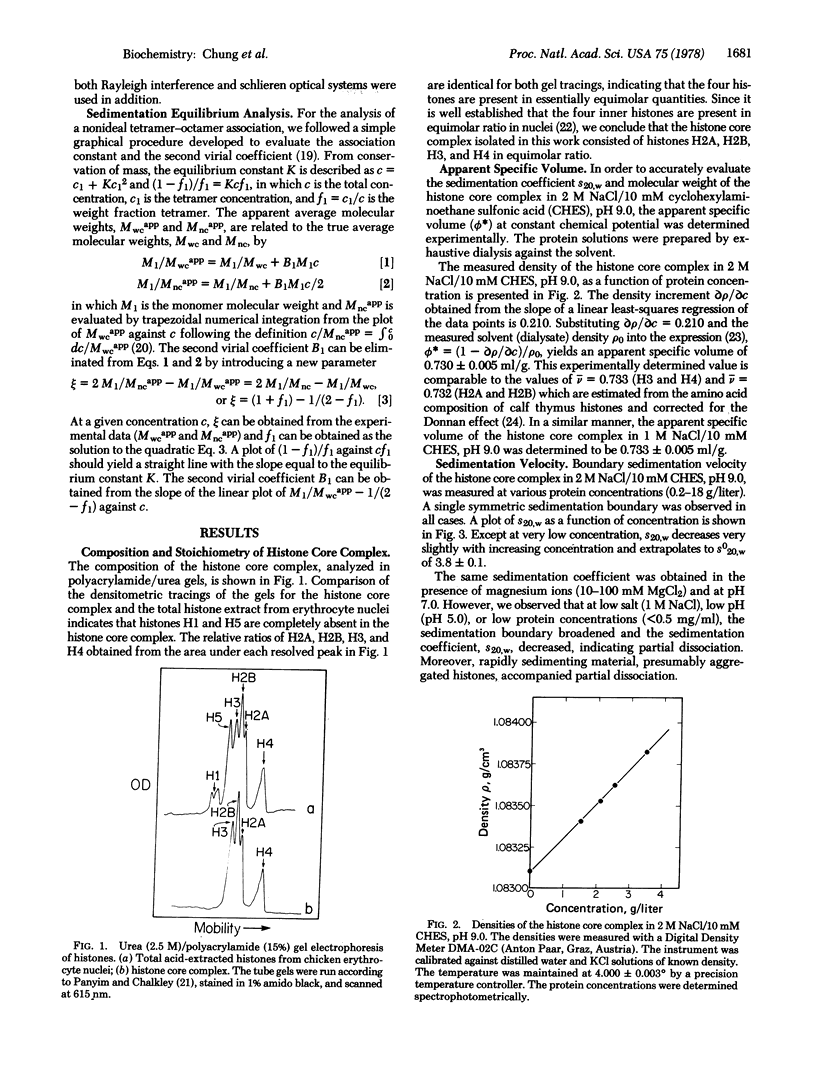
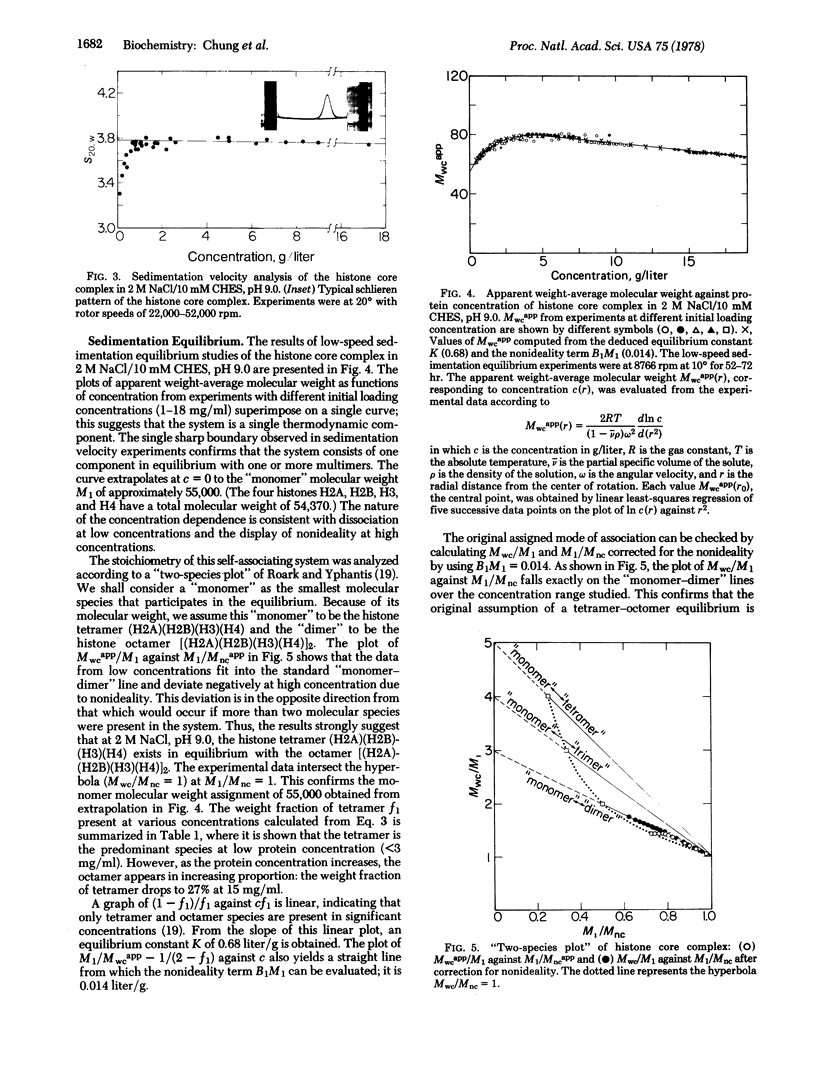
A stable histone core complex containing equimolar ratios of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 has been isolated from chicken erythrocyte chromatin in high salt. This complex has been characterized by sedimentation and chemical cross-linking studies. In velocity ultracentrifugation, only one single sharp sedimentation boundary has been observed with sedimentation coefficient S020,w = 3.8 +/- 0.1. The molecular weight of the histone core complex has been investigated by low-speed sedimentation equilibrium studies over a wide range of protein concentration. Analysis of the apparent weight-average molecular weight as a function of concentration indicates that the histone core complex in 2 M NaCl, pH 9.0, is in equilibrium between a tetramer (H2A)(H2B)(H3)(H4) and an octamer [(H2A)(H2B)(H3)(H4)]2 species with a tetramer molecular weight of 55,000. The equilibrium constant K is approximately 1.2 X 10(-5) liter per mol at 10 degrees. Evidence of such a tetramer-octamer equilibrium in solution is also supported by the results of our chemical crosslinking experiments on the histone core complex.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams E. T., Jr Sedimentation equilibrium in reacting systems. 3. Evaluation of the number average (Mn(c)) molecular weight, equilibrium constants, and nonideal effects. Biochemistry. 1965 Aug;4(8):1646–1654. doi: 10.1021/bi00884a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenburger W., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Nuclease cleavage of chromatin at 100-nucleotide pair intervals. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):517–522. doi: 10.1038/264517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Pollard H. B. The presence of F3-F2a1 dimers and F1 oligomers in chromatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):282–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. M., Cotter R. I. The molecular weight of nucleosome protein by laser light scattering. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80759-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Jr, Isenberg I. A histone cross-complexing pattern. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 19;13(24):4992–4997. doi: 10.1021/bi00721a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Jr, Isenberg I. Interaction of renatured histones f3 and f2al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90572-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joffe J., Keene M., Weintraub H. Histones H2a, H2b, H3, and H4 are present in equimolar amounts in chick erythroblasts. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1236–1238. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure; oligomers of the histones. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):865–868. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmore J. P., Wooley J. C. Chromatin architecture: investigation of a subunit of chromatin by dark field electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffak I. M., Grainger R., Weintraub H. Conservative assembly and segregation of nucleosomal histones. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson H. G., McCarthy B. J. Histone-histone interactions within chromatin. Preliminary characterization of presumptive H2B-H2A and H2B-H4 binding. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):4126–4131. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Differences and similarities in chromatin structure of Neurospora crassa and higher eucaryotes. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon J. F., Worcester D. L., Wooley J. C., Cotter R. I., Lilley D. M., Richards R. M. The structure of the chromatin core particle in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3199–3214. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon J. F., Worcester D. L., Wooley J. C., Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E., Richards B. M. Low-angle neutron scattering from chromatin subunit particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Nov;2(11):2163–2176. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.11.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Geoghegan T. E., Keller G. H. A two-subunit histone complex from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):542–547. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Geoghegan T. E., Keller G. H., Matter K. V., Engle R. L. Histone interactions in solution and susceptibility to denaturation. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):3019–3025. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Yphantis D. A. Studies of self-associating systems by equilibrium ultracentrifugation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Nov 7;164(1):245–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb14043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw B. R., Herman T. M., Kovacic R. T., Beaudreau G. S., Van Holde K. E. Analysis of subunit organization in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Whitlock J. P. Mapping DNAase l-susceptible sites in nucleosomes labeled at the 5' ends. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E. Reconstitution of chromatin core particles. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5295–5303. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Palter K., Van Lente F. Histones H2a, H2b, H3, and H4 form a tetrameric complex in solutions of high salt. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):85–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]