Abstract
Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are the major factors implicated in Parkinson’s disease (PD) pathogenesis. The maintenance of healthy mitochondria is a very complex process coordinated bi-genomically. Here, we review association studies on mitochondrial haplogroups and subhaplogroups, discussing the underlying molecular mechanisms. We also focus on variation in the nuclear genes (NDUFV2, PGC-1alpha, HSPA9, LRPPRC, MTIF3, POLG1, and TFAM encoding NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) flavoprotein 2, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, mortalin, leucine-rich pentatricopeptide repeat containing protein, translation initiation factor 3, mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma, and mitochondrial transcription factor A, respectively) primarily linked to regulation of mitochondrial functioning that recently have been associated with PD risk. Possible interactions between mitochondrial and nuclear genetic variants and related proteins are discussed.
Keywords: Association studies, Mitochondrial dysfunction, mtDNA haplogroups, Nuclear genes, Parkinson’s disease, Polymorphism.
1. INTRODUCTION
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common progressive neurodegenerative disorder, clinically defined by cardinal motor features: tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability [1]. The symptoms appear upon the loss of approximately 50% of substantia nigra (SN) dopaminergic (DA) neurons resulting in a depletion of striatal dopamine by about 70-80%, indicative of compensatory mechanisms enabling “normal” functioning despite the ongoing deterioration [2, 3]. Also other neuronal populations in the brain stem and subcortical and cortical regions are affected in PD [4]. Additionally, PD is associated with non-motor symptoms that can co-occur or precede the motor manifestations by many years [5]. They comprise cognitive and psychiatric problems, impaired olfaction, sleep disturbances, and autonomic insufficiency [6, 7]. PD is clinically heterogeneous, with two major subtypes associated with different prognoses: the tremor- prevalent and the “postural imbalance and gait disorder” (PIGD) form, the latter aggravating more rapidly [8]. The pathological hallmark of PD are proteinaceous aggregates in neuronal perikarya (Lewy bodies, LBs) and processes (Lewy neurites, LNs) containing mainly misfolded α-synuclein (SNCA) [4]. They are observed in most PD cases with the exception of some genetically caused ones (e.g. PARK2 mutations).
Despite their apparently different causative factors and possibly also the course of pathogenesis, most of the sporadic PD forms are difficult to be distinguished from the genetic ones at the clinical level [8, 9]. Only about 10% of PD cases arise due to mutations in known genes. Mutations in PARK2 (coding for parkin), PARK6 (coding for PTEN induced kinase 1, PINK1), and PARK7 (coding for DJ-1) are responsible for autosomal recessive PD forms, while PARK1 (coding for α-synuclein, (-SNCA) and PARK8 (coding for leucine-rich repeat kinase 2, LRRK2) mutations cause autosomal dominant PD. The remaining cases are idiopathic, however, currently unknown genetic background could not be ruled out in those cases.
PD pathogenesis involves complex interactions between individual inherited genetic background, physiological aging, and the environment. At present aging is considered the most important PD risk factor connected with a decline in the efficiency of numerous cellular processes and aggravated by possible environmental insults, e.g., exposure to mitochondrial toxins. Additionally, male gender seems to predispose to PD [10].
Analysis of sporadic and genetically caused PD in humans, in animal and in vitro PD models enabled identification of major molecular mechanisms involved in PD pathogenesis, namely, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, impairment of cellular degradation systems, (including micro- and macroautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy, and the ubiquitine-proteasome system), defective protein folding, and cellular transport abnormalities. These processes are interdependent, which makes it difficult to determine the primary cause of the neurodegeneration.
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in both sporadic and genetically caused PD, in patients as well as in numerous PD models; reviewed in [11-13]. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) encodes 13 proteins of oxidative phosphorylation, two rRNAs and 22 tRNAs. The remaining ETC subunits and approximately 1000-1500 other mitochondrial proteins are encoded by nuclear DNA (nDNA) [22]. Therefore, proper mitochondrial functioning requires a coordinated interplay among factors encoded by both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA.
The products of genes involved in the pathogenesis of rare genetic PD cases have turned out to be involved in the maintenance of mitochondrial function, reviewed in [12-15]. To date, parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1 have been implicated in mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy), where they likely operate in a network of reciprocally regulated pathways [16, 17]. Moreover, parkin and PINK1 seem to be crucial for mitochondrial biogenesis, transport, and dynamics [12-14, 18, 19]. Also LRRK2 and SNCA take part in mitochondrial dynamics and homeostasis [20, 21]. All these processes are engaged in the maintenance of healthy mitochondria, which seems especially important in stress conditions.
Here, we focus on common variation of mtDNA and nDNA as a potential source of functional changes that could affect mitochondrial performance and thus influence PD risk. We also discuss possible interactions between the two genomes and their potential significance for future design of PD association studies.
The genes coding for the mammalian mitochondrial proteome consisting of about 1000–1500 distinct proteins [22, 23] are all potentially plausible candidates for PD association studies. For this reason our report is limited to those encoding the main mitochondrial biogenesis/maintenance factors (NDUFV2, PGC-1alpha, HSPA9, LRPPRC, MTIF3, POLG1, TFAM, TFB1M, TFB2M) and for which association studies/mutational screening have been performed. These genes only recently have been linked to PD pathogenesis and thus have not been deeply studied. We have searched extensively the public databases, including NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) and PDGene (a database of Parkinson’s disease association studies) [24]. The role of genetic variation in PARK genes and of their products (parkin, PINK1, DJ-1, SNCA, LRRK2) in mitochondrial physiology and PD pathogenesis have been reviewed extensively elsewhere [12-14, 25, 26] and is not the subject of this review.
2. WHAT CAUSES THE SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY OF PD-AFFECTED NEURONS TO MITOCHONDRIAL DYSFUNCTION AND OXIDATIVE STRESS?
A common denominator of neurons degenerating in PD are long, thin axons with little or no myelination [27]. Gene expression profiling studies indicate that substantia nigra A9 DA neurons are more metabolically active, with up-regulation of genes involved in energy metabolism, electron transport and those coding for mitochondrial proteins, than the A10 DA neurons of ventral tegmental area (VTA) that are relatively well preserved in PD [28-30]. These characteristics make the SN DA neurons highly dependent on properly regulated mitochondrial function: efficient oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) providing ATP, mitochondrial fusion and fission, transport between cell bodies and long axon terminals, biogenesis and mitophagy. In addition, the selective vulnerability of the SN DA neurons preferentially affected in PD could also stem from:
1). sustained cytosolic and mitochondrial Ca2+ overload driven by unique to substantia nigra voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ channels contributing to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation [31, 32];
2). higher oxidative stress caused by prooxidative dopamine metabolism, in addition to the OXPHOS-derived ROS [33]. ROS are generated during dopamine autooxidation while H2O2 is produced during physiological activity of tyrosine hydroxylase and monoamine oxidase – enzymes of dopamine biosynthesis and degradation pathways;
4). the highest frequency of mtDNA deletions relative to other brain regions, possibly as a result of oxidative damage induced by ROS derived from OXPHOS, dopamine metabolism, and Ca2+ overload [34].
3. MITOCHONDRIAL DYSFUNCTION IN PD PATHOGENESIS
Mitochondria are crucial in energy generation, ROS production, Ca2+ cellular homeostasis, apoptosis, and numerous metabolic pathways including steroid and heme biosynthesis, and β-oxidation of fatty acids. Thus, it is not surprising that mitochondrial failure is implicated in a wide variety of diseases, generally involving organs with a high-energy demand such as brain, heart and skeletal muscles [35, 36].
One of the earliest pieces of evidence of mitochondrial dysfunction in PD was the discovery that the complex I (CI) NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity was decreased in platelets from patients with sporadic PD [37]. Those results were confirmed in midbrain substantia nigra, frontal cortex, skeletal muscles, and platelets of PD patients and in cybrid models of PD [38-47]. Moreover, analysis of cybrids obtained by fusion of rho0 cells lacking mtDNA and platelets from sporadic PD patients showed that mitochondria from the PD platelets are sufficient to reproduce parkinsonian-like changes at the cellular level, including the PD hallmarks such as LBs - like proteinaceous inclusions containing α-synuclein, ubiquitin, parkin and synphilin-1 [48]. Furthermore, since Langston et al. described acute PD development in drug addicts after exposure to a complex I inhibitor, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), in the early 1980s [49], administration of complex I inhibitors (MPTP, rotenone, paraquat, maneb, etc.) has become a standard approach in animal and cellular PD models reproducing PD pathology to different extents [50-55]. The rotenone-based animal PD model is still among the most faithful ones, recapitulating Lewy body-like cytoplasmic inclusions, increased oxidative stress, microglia activation, and behavioral symptoms, such as bradykinesia, stiffness and tremor-like movements [51]. Rotenone crosses the blood-brain barrier (unlike MPTP which is selectively taken up by dopamine receptors) causing systemic inhibition of complex I and degeneration of SN DA neurons. A role of endogenous neurotoxins (dopamine metabolites - tetrahydroisoquinolines and their derivatives with neurochemical characteristics similar to MPTP) has been also proposed in PD pathogenesis, reviewed in [56]. Moreover, numerous epidemiological studies have shown an association between PD and exposure to complex I inhibitors, used as pesticides/insecticides in agriculture [57].
However, the hypothesis that mitochondrial CI deficiency is a causal factor of PD has been challenged recently. Selective inactivation of the nucleus-encoded CI subunit of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase, iron-sulfur protein 4 (Ndufs4), in neurons and glia of knockout mice affected primarily non-DA neurons of the olfactory bulb, cerebellum, and vestibular nuclei, without substantia nigra degeneration [58, 59]. The Ndufs4 loss in mice led to fatal encephalomyopathy with growth retardation, ataxia, unsteady gait, and blindness, recapitulating some features of Leigh syndrome [58, 60]. As subsequently demonstrated a conditional Ndufs4 knockout in DA neurons in mice resulted in only a small decrease in DA neurons, with striatal innervation preserved. Although the DA release was impaired and the level of DA metabolites increased, no symptoms of parkinsonism were observed. In addition, the knockout mice were more vulnerable to the neurotoxin MPTP [61].
Nonetheless, it is worth noting that induced mitochondrial dysfunction in DA neurons of transgenic mice, results, in most cases, in parkinsonian-like phenotypes. For instance, a conditional SN-specific deletion of both mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) alleles in mice leads to progressive motor dysfunction with adult onset, formation of intraneuronal inclusions, striatal dopamine depletion, death of DA neurons, abnormal mitochondrial morphology, reduced mtDNA expression, and respiratory chain deficiency [62-64]. In another model, selective overexpression of a mitochondria-targeted restriction enzyme PstI introducing DNA double-strand breaks in DA neurons resulted in mtDNA depletion, a progressive neurodegeneration of the SN DA neurons, striatal dopamine depletion, and a motor phenotype responsive to L-DOPA treatment [65]. Finally, overexpression of mutant twinkle, a helicase essential for mtDNA maintenance and replication, in DA neurons in mouse, causes mtDNA deletions, degeneration of SN DA neurons, and some PD-like behavioral deficits [66].
The differences in the outcome between the targeted disruption of TFAM or twinkle versus Ndufs4 in DA neurons could be explained by the different molecular mechanisms and the compensatory potential related to the different causes of the mitochondrial dysfunction. In the case of TFAM or twinkle, mtDNA damage seems to be the primary source of mitochondrial dysfunction. In contrast, upon the Ndufs4 gene disruption, the cause of the mitochondrial impairment is CI deficiency, possibly due to CI assembly failure and instability [58]. Ndufs4 is one out of at least 45 different subunits forming CI, the largest respiratory chain complex encoded both by nuclear and mitochondrial DNA. As it has turned out subsequently, CI activity is only partially compromised in vivo in the Ndufs4 knockouts, due to compensatory formation of respiratory supercomplexes with mitochondrial complex III [61, 67]. Thus, it could be speculated that the Ndufs4-related mitochondrial dysfunction is easier to compensate than TFAM or twinkle-related impairment.
4. MITOCHONDRIAL HAPLOGROUPS AND PD RISK
The mtDNA is inherited exclusively maternally as a haplotype. Based on phylogenetic relationships, the mtDNA haplotypes can be classified into subhaplogroups, haplogroups and haplogroup clusters characterized by a set of specific polymorphisms. An analysis of mtDNA haplotypes has enabled creation of a human migration map and trace the human origins to Africa, where the most ancient and variable lineages occur: L0, L1, L2 and L3 [68]. They evolved into macrohaplogroups M and N, that subsequently left Africa to colonize Eurasia. In Europe, nine mtDNA lineages prevail: H, I, J, K, T, U, V, W and X, forming four clusters: HV, UK, WIX and TJ. Haplogroup H is the most common one, in spite of being relatively young in evolution [69-73]. The haplogroup distribution on Earth shows highly specific regional variation that, according to some researchers, cannot be explained merely by the founder effect [68, 74-77].
An exclusively maternal mode of inheritance has been observed in few PD pedigrees [78, 79]. Only cybrids carrying mtDNA from the maternal descendants of PD patients (asymptomatic or manifesting PD) had a lower activity of complex I, increased ROS levels and activities of ROS scavenging enzymes, and altered mitochondrial morphology [78]. In contrast, a recent large case-control study of 168 multiplex PD families found no evidence of maternal inheritance in familial PD [80].
Importantly, no inherited causative mtDNA mutations have been identified through mtDNA sequencing in PD patients [81-83]. Thus, it was proposed that common mitochondrial DNA variation, comprising inherited and somatic mutations, could influence the OXPHOS efficiency, mitochondrial functioning, and thereby modify the PD risk. Numerous association studies have addressed this issue producing ambiguous results [84-93]. In parallel, in vitro and in silico studies allowed the formation of a hypothesis that facilitated interpretation of discordant outcomes of the association studies.
4.1. Do “Partially Uncoupling” mtDNA Lineages Decrease PD Risk?
The hypothesis posits that the JTKU cluster and its specific sublineages (U4, U5a1, K, J1c and J2) could exert a protective effect in PD and other diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), diabetes, and aging due to the presence of sub/haplogroup-specific polymorphisms that decrease the mitochondrial coupling. In such conditions, ATP but also ROS production is decreased, while more energy dissipates as heat [68, 94-97], (Fig. 1). To date, Montiel-Sosa et al. have found that, within the UK cluster, sperm carrying subhaplogroups U4, K and U5a1 exhibit lower viability and motility (parameters directly related to OXPHOS coupling efficiency and ATP generation) than the U5b sperm [94, 97]. In silico studies pinpointed potentially “partially uncoupling” polymorphisms within subhaplogroups J1c and J2 [95, 97]. These results underline functional heterogeneity even within a given haplogroup that could account for the discrepant results obtained in association studies and underscore the need to stratify haplogroups into subhaplogroups [93]. Interestingly, it has also been found that lineages carrying “partially uncoupling” mtDNA variants (U5a and U4) are enriched in Northern Europe, and could have played a role in the adaptation to cold climates by more efficient heat generation [97]. In addition, cytochrome b gene has been shown to have a higher ratio of non-synonymous vs. synonymous (NS/S) variants in European than African mtDNAs. Although purifying selection is regarded the major driving force in the human mtDNA evolution [95, 98], the above results suggest that the role of adaptive selection increased upon human migration from Africa to the moderate and arctic climates of Eurasia [95]. They also explain the specific geographic pattern of haplogroups [68].
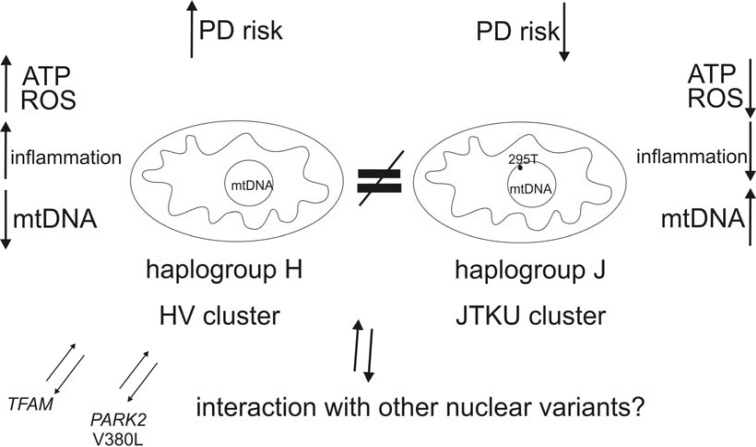
Fig. (1).
mtDNA common variation and PD risk.
JTKU cluster and specific sublineages within it (U4, U5a1, K, J1c and J2) are postulated to decrease PD risk due to the presence of sub/haplogroup-specific polymorphisms that lead to a less efficient coupling efficiency. In such conditions, ATP but also ROS production is decreased, while relatively more energy dissipates as heat. Also the influence of non-coding SNPs (such as 295T within the TFAM binding site) should be taken into account (see paragraph 4.5). On the other hand, the most common European haplogroup H (present in about 40% of Caucasians) has been demonstrated to increase PD risk in the recent meta-analysis. It has been associated with higher levels of inflammation biomarkers than haplogroup U. It is plausible that mtDNA background interacts with nuclear variants. For example, PARK2 and TFAM SNPs seem to increase PD risk on the HV cluster background (see paragraph 5.5).
The discussed hypothesis, however, has been challenged by other researchers [98-101]. For instance, Sun et al. did not find differences in the NS/S ratio between haplogroups from three distinct climatic regions, proposing instead that the specific haplogroup distribution on Earth should be attributed to genetic drift and purifying selection [98], while Kivisild et al. found gene-specific differences in the NS/S ratio between mtDNA haplotypes even in the same geographic region [101]. Moreover, no functional respiratory differences between Arctic- and African-specific mtDNA lineages, expected from the hypothesis in question, were found in a cybrid model, with even better OXPHOS coupling observed in cybrids carrying the arctic ones [99].
4.2. Haplogroup J – Less ROS, More Protection?
Despite the controversy regarding the hypothesis discussed above, some studies have found an association between the JTKU cluster or particular haplogroups within it and a decreased PD risk [87-90, 93] or reported such a trend for haplogroup J [92]. In particular, we and others have found that sublineages U4, U5a1, K, J1c, J2 (collectively) proposed to be partially uncoupling are associated with a decreased PD and AD risk in Polish and Russian Tatar cohorts [90, 93, 102].
In addition, haplogrup J has been associated with longevity [103-106]. It has also been shown to protect from osteoarthrithis, where oxidative damage is strongly implied in the pathogenesis [107, 108]. As demonstrated by a growing number of functional studies, the beneficial effect of haplogroup J seems to arise from a lower systemic oxidative and nitrosative stress due to less efficient ATP generation in comparison with other haplogroups [109-111], (Fig. 1). Consistent with this notion, various cybrid models using different lines of rho0 cells have demonstrated lower ATP production and ROS levels for haplogroup J cybrids in comparison to non-J or haplogroup H cybrids [112, 113]. Interestingly, haplogroup J cybrids grew faster than H cybrids, which could be related to higher lactate levels indicating enhanced glycolysis rate in those cybrids [113].
Similar observations have been made for human-derived tissues, despite potentially confounding variation of the nuclear genome [110]. Martinez-Redondo et al. have shown lower maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max) rates and lower oxidative damage in individuals carrying haplogroup J [110]. In addition, Fernandez-Moreno et al. have reported that subjects harboring haplogroup J have decreased mRNA levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), lower production of nitric oxide (NO) in cultured chondrocytes, and longer telomeres in leukocytes, independently of age and gender [111]. Although oxidative stress has been suggested as a causative factor of telomere shortening, telomere length analyses in PD patients are inconclusive [114-118].
Recently, mitochondrial haplogroups have been reported to modulate global DNA methylation levels, found higher in peripheral blood DNA of J - carriers in comparison with non-J ones [112]. The significance of the latter finding remains to be clarified.
In some specific disorders, however, haplogroup J has detrimental effects, as it increases the penetration of mild mtDNA complex I mutations associated with Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) [119, 120]. The partially uncoupling OXPHOS variants have therefore been proposed to act synergistically with mild mtDNA complex I mutations, lowering the ATP level below the physiological threshold and thus leading to energetic deficit and blindness manifestation [96].
4.3. Haplogroup H – A Pro-oxidative Haplogroup?
On the other hand, the most common European haplogroup H and the HV cluster have been proposed to predispose to certain neurodegenerative diseases, such as PD and AD due to the most efficient OXPHOS coupling among the European haplogroups, and the consequent increased ATP and ROS production [96], (Fig. 1). For this reason, haplogroup H is thought to be advantageous for organs with a high ATP demand such as brain, liver, and heart [121] and has been shown to exert a protective effect in temporarily compromised OXPHOS as occurs in sepsis and stroke [122, 123]. Indeed, functional studies have demonstrated that haplogroup H carriers have a higher VO2max and increased ATP and oxidative stress levels in comparison with haplogroup J carriers [109, 110, 112, 113]. Also patients with Huntington’s disease carrying haplogroup H display higher ATP levels than non-H individuals [121]. The association studies supporting haplogroup H-related increased PD risk have low statistical power [55, 90], with the exception of a recent one including meta-analysis [124]. Similar evidence has been also provided for AD [125, 126].
Despite the elegance of the hypothesis on beneficial/detrimental effects of “partially uncoupling vs. efficiently coupling” haplogroups (respectively) in neurodegenerative diseases, consistent evidence is lacking. Some studies found no association of mitochondrial haplogroups with the risk of PD [80, 91]. Likewise, some functional studies failed to corroborate the postulated bioenergetic differences between the “partially uncoupling” and “efficiently coupling” haplogroups such as J, T, K and H [127-129], while others do not match the hypothesis [73]. For example, K cybrids show higher ATP production than haplogroup H cybrids and comparable ROS levels [73].
Contradictory functional results have also been obtained for cybrids carrying Asian mitochondrial haplogroups, many of which had been previously associated with the risk of various disorders including PD, AD and diabetes [130-135]. One study on Taiwanese population-derived cybrids reported that haplogroup B4b cybrids had a significantly lower oxygen consumption rate and higher mitochondrial membrane potential compared to F1a, B5, D5a, D4a, and N9a cybrids, but at the same time they were more susceptible to H2O2-induced oxidative stress than F1a, D4a, or N9a cybrids [135]. A N9a cybrid had a higher oxygen consumption and H2O2-challenged viability compared to B4b, F1a, B5, D5a, and D4a [135]. On the other hand, a Korean study did not detect any differences in ATP and ROS levels, mitochondrial membrane potential, and viability among analyzed cybrids [134]. However, microarray gene expression profiling showed that haplogroups N9a, D5 and F did influence the expression pattern of both mitochondrial and nuclear genes involved in cellular energetics [134]. For example, haplogroup N9a cybrids featured up-regulation of the oxidative phosphorylation pathway and down-regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis signaling, as compared to haplogroup F ones [134], suggesting that variations in mtDNA can affect the expression of nuclear genes regulating mitochondrial functioning or cellular energetics.
4.4. Changes of mtDNA Levels in PD
Although some data indicate that the amount of mtDNA decreases during aging in humans and animal models, they are generally inconclusive [136-143]. No systematic effort to correlate the mtDNA level with PD pathogenesis and progression has been undertaken to date. Cybrids containing mtDNA from sporadic PD patients demonstrated decreased mtDNA and mtRNA levels [144, 145]. Interestingly, the MPP(+) ion (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium), apart from complex I inhibition, has also been proposed to destabilize mtDNA D-loop structure, inhibit mtDNA replication and decrease its content in cultured cells [146, 147]. Also early onset (EOPD) patients carrying PARK2 mutations display a 22% decrease in mtDNA level [19]. Moreover, in substantia nigra of elderly people up to 80% of mtDNA molecules carry deletions [34, 148], suggesting that mtDNA and the mitochondrial network can be damaged more promptly there than in other brain regions, possibly due to prooxidative dopamine metabolism.
The mtDNA copy number has been proposed to be regulated by ROS levels. Low-level chronic oxidative stress has been shown to increase the copy number in vitro and in vivo, and in mice cybrids [149-151]. Thus, the “partially uncoupling” sublineages within the UKTJ cluster could be expected to display higher mtDNA levels in comparison with the prooxidative haplogroup H [152]. However, the results obtained so far are inconsistent. The amount of mtDNA has been reported either lower for K cybrids or higher/unchanged for J cybrids in comparison with haplogroup H cybrids [73, 113, 152].
4.5. Do Control Region Variants Contribute to Haplogroup-related PD Risk?
The studies on the role of mtDNA variation in PD focused mainly on the coding-sequence polymorphisms potentially influencing encoded RNA or protein products. Recently the attention has turned to, so far neglected, non-coding SNPs, occurring within the control region, which comprises mtDNA promoters and origins of replication – the binding sites for the mtDNA replication and transcription machineries [153, 154]. For instance, the mtSNP 295T unique to haplogrup J is localized within the mitochondrial transcription factor A binding site. Haplogroup J cybrids had higher mtDNA level, increased TFAM binding and mtDNA transcription level in vitro in comparison with haplogrup H cybrids [152]. mtSNP 295T could be potentially responsible for these phenomenon. However, no differences were found in mitochondrial RNA (mtRNA) levels between cybrids with the haplogroups J and H [152]. It is plausible that compensatory normalization of mitochondrial gene expression in response to changed mtDNA levels could account for this observation [145]. It is also known that increased mtDNA level is not necessarily coupled with increased mRNA level [152]. Interestingly, lower levels of mtRNA transcripts have been observed in K cybrids in comparison with H cybrids [73, 152].
The above results indicate that a dysfunction of mtDNA replication and/or transcription may be a common feature in both sporadic and genetic PD forms. It is conceivable that the higher mtDNA level and possibly also transcription efficiency in haplogroup J carriers (if confirmed in future studies) could favor a more efficient compensatory mechanism when mitochondrial functioning is compromised in the course of PD and therefore slow down PD progress, shifting the threshold towards functional mitochondria (Fig. 1).
The inconsistent outcomes of studies addressing physiological differences among mtDNA sub/haplogroups indicate that a) some mtDNA lineages may be functionally significant while others not, or/and b) the nuclear genome may compensate for subtle functional differences between mtDNA lineages [134]. All in all, there is a need of an integrative approach combining well-designed association studies with functional ones, simultaneously analyzing the mtDNA haplotype and its physiological properties in human subjects/animal/in vitro models, in conditions related to health and disease.
4.6. mtDNA Somatic Mutations
Mitochondrial dysfunction can also result from accumulation of somatic mtDNA mutations throughout the lifespan, particularly detrimental for post-mitotic cells such as neurons. The burden of somatic point mutations in the mtDNA control region is increased in PD brain samples [35], although it is not known whether it is accompanied by compromised mtDNA replication and transcription, similarly to what has been shown for AD brains [155]. Other studies reported insignificantly higher levels of somatic point mutations in the frontal cortex and substantia nigra of PD patients, in the ND4 gene of complex I [156], and in the ND5 gene in muscle biopsies, in comparison to healthy controls [157]. This trend has not been replicated in all studies [158]. Also mtDNA deletions seem to play a role in PD pathogenesis [34, 159]. Substantia nigra has the highest frequency of mtDNA deletions among all tissues, possibly due to the pro-oxidative dopamine metabolism mentioned earlier [34]. They reach a very high level (up to 50%) in PD patients and in healthy elderly subjects, which correlates with decreased cytochrome c activity, although the deletion level is only slightly higher in PD patients than in age-matched controls [34]. However, in patients with early stage PD and those with incidental Lewy body disease (ILBD) the burden of somatic mutations in SN neurons is significantly higher than in a control group [160].
5. POLYMORPHISMS IN NUCLEAR GENES INVOLVED IN MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTIONING AND BIOGENESIS AFFECT PD RISK
Mitochondrial biogenesis is coordinated by three PGC-1 family proteins, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1alpha) [161], PGC-1beta and PGC-1-related coactivator (PRC) [162]. PGC-1alpha integrates the activity of a wide range of transcription factors responsible for mitochondrial biogenesis [163]. All PGC-1 family members are able to co-activate nuclear respiratory factors (NRF1, NRF2) and trans-activate NRFs-responsive genes directly and indirectly involved in mitochondrial biogenesis. The NRFs regulate the majority of nuclear genes encoding subunits of five respiratory complexes [162]. They also act on genes whose products conduct mtDNA transcription and replication (TFAM; mitochondrial transcription factor B1, TFB1M; mitochondrial transcription factor B2, TFB2M; mitochondrial RNA polymerase, POLRMT; mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma, POLG1; RNA component of mitochondrial RNA processing endoribonuclease, RMRP) and those encoding components of the mitochondrial translation apparatus (ribosomal proteins, tRNA synthetases), mitochondrial protein import and assembly machinery (translocases of the outer mitochondrial membrane, TOM20, TOM70), and heme biosynthesis enzymes [153, 164], see also (Fig. 2).
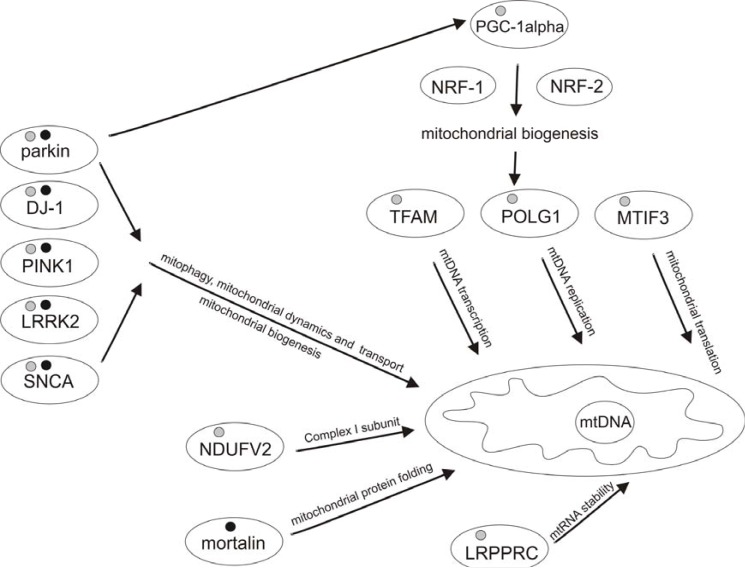
Fig. (2).
Genes related to mitochondrial function and implicated in PD pathogenesis.
About 10% of PD cases arise due to mutations in PARK genes. PARK2 (parkin), PARK6 (PINK1), and PARK7 (DJ-1), are responsible for autosomal recessive PD forms, while PARK1 (α-SNCA) and PARK8 (LRRK2) mutations cause autosomal dominant PD. The influence of polymorphisms in PARK genes on PD risk has been extensively studied. Recent research have demonstrated that variation in other (than PARK) mitochondria-related genes may modulate PD risk. Parkin, PINK1, DJ-1, LRRK2 and α-SNCA are involved in regulation of mitochondrial function to different extent. Parkin regulates PGC-1alpha levels through PARIS. PGC-1alpha coordinates mitochondrial biogenesis through trans-activation of NRF1/2-responsive genes, such as NDUFV2, TFAM, POLG1, MTIF3. The function given above arrows is general. Black dots designate mutations. Grey dots designate polymorphisms.
There is a growing body of evidence that nucleus – encoded proteins participating at different stages in mitochondrial maintenance and biogenesis are important for PD pathogenesis.
5.1. Nucleus-encoded Respiratory Chain Subunits
Polymorphisms/mutations in nuclear genes encoding respiratory chain subunits seem obvious candidates for PD risk factors. However, according to the PDgene most of the obtained results, so far, are negative [24]. Only a single such gene has been implicated in PD pathogenesis that codes for a subunit of mitochondrial complex I - NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) flavoprotein 2 (NDUFV2). Homozygotes with a substitution Ala29Val in the mitochondrial targeting sequence have a 2.4-fold higher PD risk than a control group [165]. A screen of the entire NDUFV2 coding region in 33 familial and 238 sporadic PD patients of North African Arab-Berber ethnicity revealed two cases of a novel substitution p.K209R (c.626A>G), possibly with an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance [166], (Fig. 2).
5.2. PGC-1alpha
Of the PGC-1 family members only PGC-1alpha polymorphisms have been analyzed in the context of PD risk in a single study [167]. Interactions with a coding mtDNA SNP 10398G present in haplogroups J, K and I were found, however, only in subgroups comprising less than 200 patients [167]. The rs6821591 C/C genotype was associated with the risk of early onset PD, with age of PD onset, and with longevity (Fig. 2). The rs2970848 G/G allele was associated with the risk of late onset PD (p = 0.027). The PGC-1alpha rs8192678 (c.1444C>T, Gly482Ser) C/C genotype was associated with longevity (p = 0.019), but not with PD risk [167]. Functional studies demonstrated that c.1444C>T decreased the PGC-1alpha level [168] and that this variant of the protein co-activated downstream transcription factors less efficiently [169]. In silico analysis suggested that splicing of the T-allele could be defective [170]. Interestingly, the c.1444C >T allele was associated previously with type II diabetes [171] and hypertension [172], while carriers of at least one c.1444C>T allele had an almost two times higher risk of late onset AD (LOAD) than those with the C/C genotype, however, only among APOE4 carriers [102].
A meta-analysis of genome-wide expression studies has shown that PGC-1alpha and its target genes involved in cellular bioenergetics are downregulated in sporadic PD patients in comparison with control groups [173]. Also in parkin deficiency conditions the PGC-1alpha level is changed [174, 175], reviewed in [14]. Thus, PGC-1alpha has been proposed as a therapeutic target for PD treatment. However, there are some important concerns that should be stressed. It has recently been shown that sustained overexpression of PGC-1alpha in the rat nigrostriatal system leads to metabolic alterations followed by degeneration of DA neurons. This result indicates that maintaining physiological levels of therapeutic proteins is critical [176]. Moreover, the functional redundancy among the PGC-1 coactivator family members should be taken into account, as well, for review see [162].
5.3. Other Genes Involved in Mitochondrial Biogenesis: HSPA9, LRPPRC and TOMM40
Apart from the PGC-1 family co-activators, several other proteins involved in mitochondrial biogenesis have been implicated in PD pathogenesis, such as mortalin and LRPPRC.
Mortalin is a mitochondrial matrix chaperone of the heat shock protein 70 family encoded by the HSPA9 gene. Its levels are downregulated in PD brains, animal and cellular PD models [177-180] and correlate with disease progression in PD patients [179]. So far, four potentially pathogenic variants in the mortalin gene have been identified in PD patients from Spain (two missense R126W, P509S; one intron 8 insertion of 17 bp, predicted to affect RNA splicing) and Germany (A476T) but not in control groups [181, 182], Fig. 2.
The Translocase of Outer Mitochondrial Membrane 40 homolog (TOMM40) is essential for import of proteins into mitochondria [183]. Previously, a common polymorphic, deoxythymidine-tract in intron 6 of the TOMM40 gene (rs10524523) has been associated with Alzheimer's disease [184, 185]. However, we have found no association between this polymorphism and the risk of PD [186].
The LRPPRC protein (leucine rich PPR-motif containing protein, also known as LRP130) is one of the seven proteins of the pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) family that all localize to mitochondria [187]. It plays a role in the post-transcriptional regulation of all mtDNA-encoded mRNAs, increasing their stability [188, 189]. Sequencing of the LRPPRC gene in 46 atypical EOPD patients has revealed over 20 variants, some of potential significance for PD [190], (Fig. 2).
Above-mentioned data suggest that association studies of PGC-1 family, NRFs, LRPPRC, HSPA9 and other genes involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis ought to be performed.
5.4. Genes Encoding mtDNA Expression Machinery
Mitochondrial transcription factors A and two B isoforms (TFAM and TFB1M, TFB2M, respectively) and mitochondrial RNA polymerase (POLRMT) form the basal mtDNA transcription apparatus [187]. TFB1M and TFB2M are recruited to the transcription initiation complex through the TFAM’s C-terminal tail. TFAM is also implicated in packaging of mtDNA in a nucleoid-like structure, displaying both mtDNA promoter-specific and non sequence-specific mtDNA binding capacity [191, 192]. The use of TFAM in experimental PD therapy has been suggested since it protects from oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial respiratory functions in cellular and animal models [193, 194]. A molecular therapy based on transfection of either free or mtDNA-complexed recombinant TFAM led to a marked improvement of mitochondrial functioning in cybrids with mtDNA from PD patients, characterized by decreased mtDNA and mtRNA levels and impaired respiratory capacity [144]. Eleven weeks after single recombinant TFAM-mtDNA complex application, the mtDNA and mtRNA levels were restored, and the levels of PGC1alpha mRNA, TFAM and ETC proteins increased, indicative of an induction of mitochondrial biogenesis and also a feedback loop between TFAM and/or mtDNA levels and PGC1alpha. Control cybrids, as well as those exhibiting limited mitochondrial dysfunction, did not respond to the therapy, which suggested selectivity of the treatment without interference with normal mitochondrial functioning.
TFB1M and, to a lesser extent, TFB2M display also a 12S rRNA methyltransferase activity and thus contribute to the biogenesis of mitochondrial ribosomes and translation [187, 195]. This suggests that mitochondrial transcription and translation are regulated in a coordinated manner. TFB2M is more potent in promoting mtDNA transcription than TFB1M, while the latter one is primarily a 12S rRNA methyltransferase; reviewed in [187].
Mutational screening of TFAM, TFB1M and TFB2M has not revealed any potentially pathogenic mutations in PD patients [196, 197]. No TFB1M or TFB2M polymorphisms showed association with PD risk [197]. In the case of TFAM, only our previous study reported that the rs2306604 G/G genotype is an independent risk factor for PD (OR 1.789, 95% CI 1.162-2.755, p=0.008) [198], (Fig. 1). Other studies, including GWAS and a meta-analysis, have not found any association with PD risk [24, 196, 199-201]. Our data indicated that four of five haplotypes containing allele G had higher frequencies in the PD group, but without reaching statistical significance [198]. Earlier in silico analysis showed that the TFAM rs2306604G (IVS4 + 113 G) allele creates a putative new splice donor and a cryptic splice acceptor resulting in a truncated TFAM protein of 102 amino acids [202], although its presence is yet to be demonstrated in vivo.
As to the translation machinery, a polymorphism in one of the two mitochondrial translation initiation factors that operate in mammalian mitochondria - translation initiation factor 3 (MTIF3) - was recently associated with PD risk [203-205]. The protein is crucial for ribosome assembly and initiation of translation in mitochondria; reviewed in [187]. The rs7669 c.798C>T polymorphism of the MTIF3 gene showed allelic or genotype association with PD [203-205]. The rs7669 T/T-genotype is associated with a decreased MTIF3 mRNA expression in comparison to the C/C-genotype [205], (Fig. 2). A dearth of MTIF3 could impair the ability of mitochondria to respond rapidly and dynamically to stress or damage by limiting the pool of available mtDNA-encoded proteins, and thus the organelle biogenesis. An increased PD risk could be a consequence.
5.5. Genes Encoding mtDNA Replication Machinery
Defects of the mtDNA replication machinery (mutations in the DNA polymerase gamma 1, POLG1 and Twinkle genes) have been found to contribute to the parkinsonian phenotype [206-210].
Twinkle is a DNA helicase unwinding mtDNA at the replication fork, essential for mtDNA maintenance and copy number regulation in mammals [211, 212]. As previously mentioned, targeted overexpression of mutant twinkle in SN DA neurons recapitulated some of the cardinal features of Parkinson disease [66]. However, the role of twinkle variants in idiopathic PD remains to be addressed.
The POLG1 gene coding for the catalytic subunit of the heterotrimeric mitochondrial DNA polymerase is responsible for mtDNA replication (5'→3' polymerase activity) and repair (3'→5' exonuclease activity) in mammals [213, 214]. POLG1 contains at its N-terminus a variable poly-glutamine tract (poly-Q) encoded by exon 2 CAG repeat sequence crucial for the exonuclease activity and the proofreading of mtDNA. The most common STR variant has ten CAG repeats (10Q, frequency >80%), a moderately common allele 11Q has a frequency of 6-12%, while minor variants 6Q-9Q and 12Q-14Q each have frequencies not exceeding 4%. Rare poly-Q variants of POLG1 have been shown to increase sporadic PD risk in Finnish [215], North American Caucasians (non-10Q) [216], Swedish (non-10/11Q) [217], and Norwegian populations (non-10/11Q) [218], though it was not confirmed in all studies [219]. A recent meta-analysis of association studies corroborated the notion that rare non-10Q variants are significantly associated with PD risk (p=0.0017) [218], (Fig. 2). A bioinformatic analysis showed aberrant mRNA folding energy for non-10/11Q variants [217]. A recombinant POLG1 lacking the poly-glutamine tract (delta10Qs) overexpressed in a cellular model exhibited increased mRNA, protein level and polymerase activity in comparison with a control variant (10Qs) [220]. Those cells had a lower than normal mtDNA content. However, no changes in the composition, amount or assembly state of respiratory chain complexes and no up-regulation of TFAM or mtSSB expression have been found [220].
These results indicate that rare POLG1 STR variants could modulate the POLG1 functioning, but more detailed functional studies are necessary to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism.
5.6. Interplay Between Nuclear and Mitochondrial Genomes in PD Pathogenesis – Old Actors on New Stage
As mentioned earlier, proper mitochondrial activity requires a well-coordinated expression of mitochondrial and nuclear genomes.
We hypothesized that the impact of nuclear genes on PD risk could be modified by the mtDNA background (see also Fig. 1). Parkin has been shown to interact with TFAM and mtDNA in vitro and in vivo and to increase mtDNA transcription, replication and mitochondrial mass in a cellular model [18, 19]. Those results suggested that parkin and TFAM could operate in the same physiological pathway, prompting us to analyze the interaction between mitochondrial haplogroups/clusters and 1) PARK2 polymorphisms, and 2) TFAM variation. Our results indicated that genotypes G/G V380L of PARK2 and G/G rs2306604 of TFAM increased PD risk in combination with the prooxidative background of the most common mitochondrial HV cluster although the rs2306604 TFAM has been shown to be an independent PD risk factor [198, 221]. We have also found a significant interaction between the rs2306604 G/G genotype of TFAM and the V380L G/G genotype of PARK2, in subjects with the mitochondrial HV cluster. Those findings imply that simultaneous presence of G/G V380L PARK2 and G/G rs2306604 TFAM in the pro-oxidative HV cluster background is a PD risk factor with detrimental influence stronger than predicted by additive model [221], (Fig. 1).
Meta-analyses of PARK2 polymorphism studies indicate that allele C of V380L is protective against PD, but only when all ethnicities and studies with control groups violating Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are included [24]. Earlier reports showed either no association for V380L or pointed to the G/G V380L genotype as increasing the PD risk and/or allel C decreasing it [222, 223]. Among PD patients potentially exposed to pesticides (postulated to increase PD risk) those carrying allele C of V380L had a higher age at onset [224]. Interestingly, this allele also decreases the risk of familial and sporadic progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), a tauopathy that genetically, clinically and histopathologically partially overlaps PD [25]. The amino acid position 380 of parkin is located in the IBR (in between RING) domain. Structural analyses indicate that the domain is likely responsible for stabilizing the geometry and relative orientation of the two RING domains of parkin [24]. Thus, the V380L replacement could bring about a decreased interaction with E2 protein–ubiquitin conjugating enzymes and impaired ubiquitination of substrates [24].
A plethora of polymorphisms in other nuclear genes including PARK genes have been implicated in PD pathogenesis (Fig. 1). The results are available in the database for PD genetic association studies and feature also meta-analyses [24]. It can be speculated that the influence of nuclear genes (especially those tightly regulating mitochondrial functioning) could be modified by mtDNA background. Recent findings have demonstrated that the levels of inflammatory biomarkers related to air-pollution, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), are higher in subjects with mitochondrial haplogroup H (as compared to subjects with haplogroup U) [225] (Fig. 1), however, common genetic variation in IL-6 or TNF-alpha genes has not been associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson's disease.
6. CONCLUSION
Individual susceptibility to PD is a result of complex interactions between genetic factors, environment and physiological aging. Natural consequence of such complexity is the pathophysiological heterogeneity of PD. It seems plausible that different molecular pathways are compromised to a different extent in individual PD patients, possibly creating “molecular/genetic” subtypes of the disease. To date, mitochondrial dysfunction and/or increased oxidative stress are only found in a subset of sporadic PD patients (30%) [226]. Detailed understanding of this obvious heterogeneity is of great importance for the development of future individualized therapies, for example those targeting mitochondrial dysfunction and/or oxidative stress [9].
Although there is convincing evidence of mitochondrial dysfunction both in sporadic and familial PD cases, none of the genes discussed here (NDUFV2, PGC-1alpha, HSPA9, LRPPRC, MTIF3, POLG1, TFAM), have been highlighted in PD genome-wide association studies (GWAS). To date, PARK1 and PARK8 common variation (coding for SNCA and LRRK2, respectively), and TAU are fairly consistently reported in GWAS as risk factors for PD [24, 200, 227-236]. This can be partially due to the specificity of GWAS, which usually do not allow for the detection of rare variants or markers with small effects that are lost in the background noise.
The presented results of candidate-gene driven association studies and sequence analyses in case and control groups underscore the differences in the predisposition to develop PD related to common variation of nuclear and mitochondrial genomes. There is growing evidence from functional studies that common variants of mtDNA influence numerous biological parameters, such as ATP and oxidative stress levels, mtDNA transcription/replication rate, and nuclear gene expression pattern. The interactions between the two genomes in PD pathogenesis can be addressed through carefully designed association studies. The main challenge for the future is to secure sufficient statistical power allowing for reliable conclusions to be drawn (several thousands of participants). Ideally, the environmental PD risk factors should also be taken into account, such as caffeine intake, smoking or exposure to mitochondrial toxins, because they may constitute important confounding factors, leading to discrepant results of association studies [237]. It would be also important to verify whether clinical subtypes of PD (such as the previously mentioned tremor-prevalent and PIGD forms) are associated with different molecular mechanisms or different genetic background, a question not addressed so far in association studies.
An integrative approach combining detailed characterization of mitochondrial parameters (bioenergetics, ROS levels, biogenesis, mitophagy, mitochondrial dynamics) along with other highly related pathways (such as response to oxidative stress, cellular clearance pathways, etc.) in PD patients and healthy controls with well defined genetic background (mtDNA haplogroups, nuclear gene variants tightly regulating mitochondrial functioning and oxidative stress such as PGC1alpha, TFAM, POLG1, PARK2, HSPA9, etc.) would greatly advance the understanding of the impact of common genetic variants on PD risk. It remains to be established whether knowing of individual patient’s genotype could help to select them for a specific type of therapy, e.g. mitochondria-targeted one, or help to predict the response to treatment. The usefulness of genetic markers (such as individual PARK2 mutations) is already being tested along with clinical symptoms considered as predisposing to PD in so called enriched risk cohorts approach, reviewed by [238].
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank prof. Jan Fronk for critical reading of the manuscript.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author(s) confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Samii A, Nutt JG, Ransom BR. Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2004;363:1783–1793. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fearnley JM, Lees AJ. Ageing and Parkinson's disease substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain. 1991;114 (( Pt 5):2283–2301. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.5.2283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.van Nuenen BF, van Eimeren T, van der Vegt JP, Buhmann C, Klein C, Bloem BR, Siebner HR. Mapping preclinical compensation in Parkinson's disease: an imaging genomics approach. Mov. Disord. 2009;24(Suppl 2 ):S703–710. doi: 10.1002/mds.22635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2003;24:197–211. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hawkes CH. The prodromal phase of sporadic Parkinson's disease: does it exist and if so how long is it. Mov Disord. 2008;23:1799–1807. doi: 10.1002/mds.22242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jankovic J. Parkinson's disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2008;79:368–376. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2007.131045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Langston JW. The Parkinson's complex: parkinsonism is just the tip of the iceberg. Ann. Neurol. 2006;59:591–596. doi: 10.1002/ana.20834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Selikhova M, Williams DR, Kempster PA, Holton JL, Revesz T, Lees AJ. A clinico-pathological study of subtypes in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2009;132:2947–2957. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Goetz CG, Marin C, Kordower JH, Rodriguez M, Hirsch EC, Farrer M, Schapira AH, Halliday G. Missing pieces in the Parkinson's disease puzzle. Nat. Med. 2010;16:653–661. doi: 10.1038/nm.2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Elbaz A, Bower JH, Maraganore DM, McDonnell SK, Peterson BJ, Ahlskog JE, Schaid DJ, Rocca WA. Risk tables for parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2002;55:25–31. doi: 10.1016/s0895-4356(01)00425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Abou-Sleiman PM, Muqit MM, Wood NW. Expanding insights of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006;7:207–219. doi: 10.1038/nrn1868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Exner N, Lutz AK, Haass C, Winklhofer KF. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: molecular mechanisms and pathophysiological consequences. EMBO. J. 2012;31:3038–3062. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pilsl A, Winklhofer KF. Parkin, PINK1 and mitochondrial integrity: emerging concepts of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Acta. Neuropathol. 2012;123:173–188. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0902-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gaweda-Walerych K, Zekanowski C. Integrated pathways of parkin control over mitochondrial maintenance - relevance to Parkinson's disease pathogenesis. Acta. Neurobiol. Exp. (Wars) 2013;73:199–224. doi: 10.55782/ane-2013-1931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sai Y, Zou Z, Peng K, Dong Z. The Parkinson's disease-related genes act in mitochondrial homeostasis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012;36:2034–2043. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Thomas KJ, McCoy MK, Blackinton J, Beilina A, van der Brug M, Sandebring A, Miller D, Maric D, Cedazo-Minguez A, Cookson MR. DJ-1 acts in parallel to the PINK1/parkin pathway to control mitochondrial function and autophagy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011;20:40–50. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Joselin AP, Hewitt SJ, Callaghan SM, Kim RH, Chung YH, Mak TW, Shen J, Slack RS, Park DS. ROS-dependent regulation of Parkin and DJ-1 localization during oxidative stress in neurons. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012;21:4888–4903. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kuroda Y, Mitsui T, Kunishige M, Shono M, Akaike M, Azuma H, Matsumoto T. Parkin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis in proliferating cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006;15:883–895. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rothfuss O, Fischer H, Hasegawa T, Maisel M, Leitner P, Miesel F, Sharma M, Bornemann A, Berg D, Gasser T, Patenge N. Parkin protects mitochondrial genome integrity and supports mitochondrial DNA repair. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009;18:3832–3850. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rideout HJ, Stefanis L. The Neurobiology of LRRK2 and its Role in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2013 doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mullin S, Schapira A. Alpha-synuclein and mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013;47:587–597. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8394-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Calvo SE, Mootha VK. The mitochondrial proteome and human disease. Annu. Rev. Genomics. Hum. Genet. 2010;11:25–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-082509-141720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Meisinger C, Sickmann A, Pfanner N. The mitochondrial proteome: from inventory to function. Cell. 2008;134:22–24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lill CM, Roehr JT, McQueen MB, Kavvoura FK, Bagade S, Schjeide BM, Schjeide LM, Meissner E, Zauft U, Allen NC, Liu T, Schilling M, Anderson KJ, Beecham G, Berg D, Biernacka JM, Brice A, DeStefano AL, Do CB, Eriksson N, Factor SA, Farrer MJ, Foroud T, Gasser T, Hamza T, Hardy JA, Heutink P, Hill-Burns EM, Klein C, Latourelle JC, Maraganore DM, Martin ER, Martinez M, Myers RH, Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Payami H, Satake W, Scott WK, Sharma M, Singleton AB, Stefansson K, Toda T, Tung JY, Vance J, Wood NW, Zabetian CP, Young P, Tanzi RE, Khoury MJ, Zipp F, Lehrach H, Ioannidis JP, Bertram L. Comprehensive research synopsis and systematic meta-analyses in Parkinson's disease genetics: . The PDGene database http://www.dgene.org/. PLoS. Genet. 2012;8:e1002548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Warner TT, Schapira AH. Genetic and environmental factors in the cause of Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 2003;53(Suppl 3 S16-23 ): S23–15. doi: 10.1002/ana.10487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fujioka S, Wszolek ZK. Update on genetics of parkinsonism. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012;10:257–260. doi: 10.1159/000334285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Braak H, Del Tredici K. Poor and protracted myelination as a contributory factor to neurodegenerative disorders. Neurobiol. Aging. 2004;25:19–23. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chung CY, Seo H, Sonntag KC, Brooks A, Lin L, Isacson O. Cell type-specific gene expression of midbrain dopaminergic neurons reveals molecules involved in their vulnerability and protection. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005;14:1709–1725. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Greene JG, Dingledine R, Greenamyre JT. Gene expression profiling of rat midbrain dopamine neurons: implications for selective vulnerability in parkinsonism. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;18:19–31. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2004.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Grimm J, Mueller A, Hefti F, Rosenthal A. Molecular basis for catecholaminergic neuron diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2004;101:13891–13896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405340101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chan CS, Guzman JN, Ilijic E, Mercer JN, Rick C, Tkatch T, Meredith GE, Surmeier DJ. 'Rejuvenation' protects neurons in mouse models of Parkinson's disease. Nature. 2007;447:1081–1086. doi: 10.1038/nature05865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Guzman JN, Sanchez-Padilla J, Wokosin D, Kondapalli J, Ilijic E, Schumacker PT, Surmeier DJ. Oxidant stress evoked by pacemaking in dopaminergic neurons is attenuated by DJ-1. Nature. 2010;468:696–700. doi: 10.1038/nature09536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Drozak J, Bryla J. Dopamine: not just a neurotransmitter (in Polish). Postepy. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2005;59:405–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bender A, Krishnan KJ, Morris CM, Taylor GA, Reeve AK, Perry RH, Jaros E, Hersheson JS, Betts J, Klopstock T, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM. High levels of mitochondrial DNA deletions in substantia nigra neurons in aging and Parkinson disease. Nat. Genet. 2006 doi: 10.1038/ng1769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Coskun P, Wyrembak J, Schriner SE, Chen HW, Marciniack C, Laferla F, Wallace DC. A mitochondrial etiology of Alzheimer and Parkinson disease. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 2012;1820:553–564. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sangar V, Eddy JA, Simeonidis E, Price ND. Mechanistic modeling of aberrant energy metabolism in human disease. Front. Physiol. 2012;3:404. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Parker WD, Jr., Boyson SJ, Parks JK. Abnormalities of the electron transport chain in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Ann. Neurol. 1989;26:719–723. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schapira AH, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Clark JB, Jenner P, Marsden CD. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease. J. Neurochem. 1990;54:823–827. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gu M, Owen AD, Toffa SE, Cooper JM, Dexter DT, Jenner P, Marsden CD, Schapira AH. Mitochondrial function GSH and iron in neurodegeneration and Lewy body diseases. J. Neurol. Sci. 1998;158:24–29. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(98)00095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Parker WD, Jr., Parks JK, Swerdlow RH. Complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease frontal cortex. Brain Res. 2008;1189:215–218. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.10.061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Blin O, Desnuelle C, Rascol O, Borg M, Peyro Saint Paul H, Azulay JP, Bille F, Figarella D, Coulom F, Pellissier JF et al, et al. Mitochondrial respiratory failure in skeletal muscle from patients with Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. J. Neurol. Sci. 1994;125:95–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Haas RH, Nasirian F, Nakano K, Ward D, Pay M, Hill R, Shults CW. Low platelet mitochondrial complex I and complex II/III activity in early untreated Parkinson's disease. Ann. Neurol. 1995;37:714–722. doi: 10.1002/ana.410370604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Krige D, Carroll MT, Cooper JM, Marsden CD, Schapira AH. Platelet mitochondrial function in Parkinson's disease.The Royal Kings and Queens Parkinson Disease Research Group. Ann. Neurol. 1992;32:782–788. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gu M, Cooper JM, Taanman JW, Schapira AH. Mitochondrial DNA transmission of the mitochondrial defect in Parkinson's disease. Ann. Neurol. 1998;44:177–186. doi: 10.1002/ana.410440207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Swerdlow RH, Parks JK, Miller SW, Tuttle JB, Trimmer PA, Sheehan JP, Bennett JP, Jr., Davis RE, Parker WD Jr. Origin and functional consequences of the complex I defect in Parkinson's disease. Ann. Neurol. 1996;40:663–671. doi: 10.1002/ana.410400417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Winkler-Stuck K, Kirches E, Mawrin C, Dietzmann K, Lins H, Wallesch CW, Kunz WS, Wiedemann FR. Re-evaluation of the dysfunction of mitochondrial respiratory chain in skeletal muscle of patients with Parkinson's disease. J. Neural. Transm. 2005;112:499–518. doi: 10.1007/s00702-004-0195-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Esteves AR, Lu J, Rodova M, Onyango I, Lezi E, Dubinsky R, Lyons KE, Pahwa R, Burns JM, Cardoso SM, Swerdlow RH. Mitochondrial respiration and respiration-associated proteins in cell lines created through Parkinson's subject mitochondrial transfer. J. Neurochem. 2010;113:674–682. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Trimmer PA, Borland MK, Keeney PM, Bennett JP, Jr., Parker WD Jr. Parkinson's disease transgenic mitochondrial cybrids generate Lewy inclusion bodies. J. Neurochem. 2004;88:800–812. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Langston JW, Forno LS, Tetrud J, Reeves AG, Kaplan JA, Karluk D. Evidence of active nerve cell degeneration in the substantia nigra of humans years after 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1 2 3 6-tetrahydropyridine exposure. Ann. Neurol. 1999;46:598–605. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199910)46:4<598::aid-ana7>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bove J, Prou D, Perier C, Przedborski S. Toxin-induced models of Parkinson's disease. NeuroRx. 2005;2:484–494. doi: 10.1602/neurorx.2.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Betarbet R, Sherer TB, MacKenzie G, Garcia-Osuna M, Panov AV, Greenamyre JT. Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson's disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2000;3:1301–1306. doi: 10.1038/81834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Betarbet R, Sherer TB, Greenamyre JT. Animal models of Parkinson's disease. Bioessays. 2002;24:308–318. doi: 10.1002/bies.10067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Stout AK, Lund S, Baptista M, Panov AV, Cookson MR, Greenamyre JT. An in vitro model of Parkinson's disease: linking mitochondrial impairment to altered alpha-synuclein metabolism and oxi-dative damage. J. Neurosci. 2002;22:7006–7015. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-16-07006.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Betarbet R, Canet-Aviles RM, Sherer TB, Mastroberardino PG, McLendon C, Kim JH, Lund S, Na HM, Taylor G, Bence NF, Kopito R, Seo BB, Yagi T, Yagi A, Klinefelter G, Cookson MR, Greenamyre JT. Intersecting pathways to neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease: Effects of the pesticide rotenone on DJ-1 alpha-synuclein, and the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006;22(2):404–20. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shoffner JM, Brown MD, Torroni A, Lott MT, Cabell MF, Mirra SS, Beal MF, Yang CC, Gearing M, Salvo Ret al, et al. Mitochondrial DNA variants observed in Alzheimer disease and Parkinson disease patients. Genomics. 1993;17:171–184. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Surh YJ, Kim HJ. Neurotoxic effects of tetrahydroisoquinolines and underlying mechanisms. Exp. Neurobiol. 2010;19:63–70. doi: 10.5607/en.2010.19.2.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Landrigan PJ, Sonawane B, Butler RN, Trasande L, Callan R, Droller D. Early environmental origins of neurodegenerative disease in later life. Environ. Health. Perspect. 2005;113:1230–1233. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kruse SE, Watt WC, Marcinek DJ, Kapur RP, Schenkman KA, Palmiter RD. Mice with mitochondrial complex I deficiency develop a fatal encephalomyopathy. Cell. Metab. 2008;7:312–320. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Quintana A, Kruse SE, Kapur RP, Sanz E, Palmiter RD. Complex I deficiency due to loss of Ndufs4 in the brain results in progressive encephalopathy resembling Leigh syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2010;107:10996–11001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006214107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Leong DW, Komen JC, Hewitt CA, Arnaud E, McKenzie M, Phipson B, Bahlo M, Laskowski A, Kin-kel SA, Davey GM, Heath WR, Voss AK, Zahedi RP, Pitt JJ, Chrast R, Sickmann A, Ryan MT, Smyth GK, Thorburn DR, Scott HS. Proteomic and metabolomic analyses of mitochondrial complex I-deficient mouse model generated by spontaneous B2 short interspersed nuclear element (SINE) insertion into NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) Fe-S protein 4 (Ndufs4) gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2012;287:20652–20663. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.327601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sterky FH, Hoffman AF, Milenkovic D, Bao B, Paganelli A, Edgar D, Wibom R, Lupica CR, Olson L, Larsson NG. Altered dopamine metabolism and increased vulnerability to MPTP in mice with partial deficiency of mitochondrial complex I in dopamine neurons. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012;21:1078–1089. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Galter D, Pernold K, Yoshitake T, Lindqvist E, Hoffer B, Kehr J, Larsson NG, Olson L. MitoPark mice mirror the slow progression of key symptoms and L-DOPA response in Parkinson's disease. Genes. Brain. Behav. 2010;9:173–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2009.00542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ekstrand MI, Terzioglu M, Galter D, Zhu S, Hofstetter C, Lindqvist E, Thams S, Bergstrand A, Hansson FS, Trifunovic A, Hoffer B, Cullheim S, Mohammed AH, Olson L, Larsson NG. Progressive parkinsonism in mice with respiratory-chain-deficient dopamine neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2007;104:1325–1330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605208103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sterky FH, Lee S, Wibom R, Olson L, Larsson NG. Impaired mitochondrial transport and Parkin-independent degeneration of respiratory chain-deficient dopamine neurons in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2011;108:12937–12942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103295108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Pickrell AM, Pinto M, Hida A, Moraes CT. Striatal dysfunctions associated with mitochondrial DNA damage in dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. J. Neurosci. 2011;31:17649–17658. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4871-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Song L, Shan Y, Lloyd KC, Cortopassi GA. Mutant Twinkle increases dopaminergic neurodegeneration, mtDNA deletions and modulates Parkin expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012;21(23):5147–58. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Calvaruso MA, Willems P, van den Brand M, Valsecchi F, Kruse S, Palmiter R, Smeitink J, Nijtmans L. Mitochondrial complex III stabilizes complex I in the absence of NDUFS4 to provide partial activity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012;21:115–120. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wallace DC, Brown MD, Lott MT. Mitochondrial DNA variation in human evolution and disease. Gene. 1999;238:211–230. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Finnila S, Lehtonen MS, Majamaa K. Phylogenetic network for European mtDNA. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001;68:1475–1484. doi: 10.1086/320591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Herrnstadt C, Elson JL, Fahy E, Preston G, Turnbull DM, Anderson C, Ghosh SS, Olefsky JM, Beal MF, Davis RE, Howell N. Reduced-median-network analysis of complete mitochondrial DNA coding-region sequences for the major African Asian and European haplogroups. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002;70:1152–1171. doi: 10.1086/339933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Torroni A, Huoponen K, Francalacci P, Petrozzi M, Morelli L, Scozzari R, Obinu D, Savontaus ML, Wallace DC. Classification of European mtDNAs from an analysis of three European populations. Genetics. 1996;144:1835–1850. doi: 10.1093/genetics/144.4.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Torroni A, Richards M, Macaulay V, Forster P, Villems R, Norby S, Savontaus ML, Huoponen K, Scozzari R, Bandelt HJ. mtDNA haplogroups and frequency patterns in Europe. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000;66:1173–1177. doi: 10.1086/302789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Gomez-Duran A, Pacheu-Grau D, Lopez-Gallardo E, Diez-Sanchez C, Montoya J, Lopez-Perez MJ, Ruiz-Pesini E. Unmasking the causes of multifactorial disorders: OXPHOS differences between mitochondrial haplogroups. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010;19:3343–3353. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kong QP, Yao YG, Sun C, Bandelt HJ, Zhu CL, Zhang YP. Phylogeny of east Asian mitochondrial DNA lineages inferred from complete sequences. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003;73:671–676. doi: 10.1086/377718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Niemi AK, Moilanen JS, Tanaka M, Hervonen A, Hurme M, Lehtimaki T, Arai Y, Hirose N, Majamaa K. A combination of three common inherited mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms promotes longevity in Finnish and Japanese subjects. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2005;13:166–170. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Silva WA, Jr., Bonatto SL, Holanda AJ, Ribeiro-Dos-Santos AK, Paixao BM, Goldman GH, Abe-Sandes K, Rodriguez-Delfin L, Barbosa M, Paco-Larson ML, Petzl-Erler ML, Valente V, Santos SE, Zago MA. Mitochondrial genome diversity of Native Americans supports a single early entry of founder populations into America. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002;71:187–192. doi: 10.1086/341358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tanaka M, Takeyasu T, Fuku N, Li-Jun G, Kurata M. Mitochondrial genome single nucleotide polymorphisms and their phenotypes in the Japanese. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004;1011:7–20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-41088-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Swerdlow RH, Parks JK, Davis JN, 2nd; Cassarino DS, Trimmer PA, Currie LJ, Dougherty J, Bridges WS, Bennett JP, Jr., Wooten GF, Parker WD. Matrilineal inheritance of complex I dysfunction in a multigenerational Parkinson's disease family. Ann Neurol. 1998;44:873–881. doi: 10.1002/ana.410440605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Wooten GF, Currie LJ, Bennett JP, Harrison MB, Trugman JM, Parker WD Jr. Maternal inheritance in Parkinson's disease. Ann. Neurol. 1997;41:265–268. doi: 10.1002/ana.410410218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Simon DK, Pankratz N, Kissell DK, Pauciulo MW, Halter CA, Rudolph A, Pfeiffer RF, Nichols WC, Foroud T. Maternal inheritance and mitochondrial DNA variants in familial Parkinson's disease. BMC. Med. Genet. 2010;11:53. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Simon DK, Mayeux R, Marder K, Kowall NW, Beal MF, Johns DR. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in complex I and tRNA genes in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 2000;54:703–709. doi: 10.1212/wnl.54.3.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Vives-Bauza C, Andreu AL, Manfredi G, Beal MF, Janetzky B, Gruenewald TH, Lin MT. Sequence analysis of the entire mitochondrial genome in Parkinson's disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;290:1593–1601. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Brown MD, Shoffner JM, Kim YL, Jun AS, Graham BH, Cabell MF, Gurley DS, Wallace DC. Mitochondrial DNA sequence analysis of four Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1996;61:283–289. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960122)61:3<283::AID-AJMG15>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ross OA, McCormack R, Maxwell LD, Duguid RA, Quinn DJ, Barnett YA, Rea IM, El-Agnaf OM, Gibson JM, Wallace A, Middleton D, Curran MD. mt4216C variant in linkage with the mtDNA TJ cluster may confer a susceptibility to mitochondrial dysfunction resulting in an increased risk of Parkinson's disease in the Irish. Exp. Gerontol. 2003;38:397–405. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(02)00266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Huerta C, Castro MG, Coto E, Blazquez M, Ribacoba R, Guisasola LM, Salvador C, Martinez C, Lahoz CH, Alvarez V. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms and risk of Parkinson's disease in Spanish population. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005;236:49–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2005.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Autere J, Moilanen JS, Finnila S, Soininen H, Mannermaa A, Hartikainen P, Hallikainen M, Majamaa K. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms as risk factors for Parkinson's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia. Hum. Genet. 2004;115:29–35. doi: 10.1007/s00439-004-1123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Pyle A, Foltynie T, Tiangyou W, Lambert C, Keers SM, Allcock LM, Davison J, Lewis SJ, Perry RH, Barker R, Burn DJ, Chinnery PF. Mitochondrial DNA haplogroup cluster UKJT reduces the risk of PD. Ann. Neurol. 2005;57:564–567. doi: 10.1002/ana.20417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Ghezzi D, Marelli C, Achilli A, Goldwurm S, Pezzoli G, Barone P, Pellecchia MT, Stanzione P, Brusa L, Bentivoglio AR, Bonuccelli U, Petrozzi L, Abbruzzese G, Marchese R, Cortelli P, Grimaldi D, Martinelli P, Ferrarese C, Garavaglia B, Sangiorgi S, Carelli V, Torroni A, Albanese A, Zeviani M. Mitochondrial DNA haplogroup K is associated with a lower risk of Parkinson's disease in Italians. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2005;13:748–752. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.van der Walt JM, Nicodemus KK, Martin ER, Scott WK, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Haines JL, Koller WC, Lyons K, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Colcher A, Hiner BC, Jankovic J, Ondo WG, Allen FH, Jr., Goetz CG, Small GW, Mastaglia F, Stajich JM, McLaurin AC, Middleton LT, Scott BL, Schmechel DE, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM. Mitochondrial polymorphisms significantly reduce the risk of Parkinson disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003;72:804–811. doi: 10.1086/373937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Khusnutdinova E, Gilyazova I, Ruiz-Pesini E, Derbeneva O, Khusainova R, Khidiyatova I, Magzhanov R, Wallace DC. A mitochondrial etiology of neurodegenerative diseases: evidence from Parkinson's disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008;1147:1–20. doi: 10.1196/annals.1427.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Mehta P, Mellick GD, Rowe DB, Halliday GM, Jones MM, Manwaring N, Vandebona H, Silburn PA, Wang JJ, Mitchell P, Sue CM. Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups J and K are not protective for Parkinson's disease in the Australian community. Mov. Disord. 2009;24:290–292. doi: 10.1002/mds.22389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Latsoudis H, Spanaki C, Chlouverakis G, Plaitakis A. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms and haplogroups in Parkinson's disease and control individuals with a similar genetic background. J. Hum. Genet. 2008;53:349–356. doi: 10.1007/s10038-008-0259-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gaweda-Walerych K, Maruszak A, Safranow K, Bialecka M, Klodowska-Duda G, Czyzewski K, Slawek J, Rudzinska M, Styczynska M, Opala G, Drozdzik M, Canter JA, Barcikowska M, Zekanowski C. Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups and subhaplogroups are associated with Parkinson's disease risk in a Polish PD cohort. J. Neural. Transm. 2008;115:1521–1526. doi: 10.1007/s00702-008-0121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ruiz-Pesini E, Lapena AC, Diez-Sanchez C, Perez-Martos A, Montoya J, Alvarez E, Diaz M, Urries A, Montoro L, Lopez-Perez MJ, Enriquez JA. Human mtDNA haplogroups associated with high or reduced sper-matozoa motility. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000;67:682–696. doi: 10.1086/303040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ruiz-Pesini E, Mishmar D, Brandon M, Procaccio V, Wallace DC. Effects of purifying and adaptive selection on regional variation in human mtDNA. Science. 2004;303:223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.1088434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Wallace DC. The mitochondrial genome in human adaptive radiation and disease: on the road to therapeutics and performance enhancement. Gene. 2005;354:169–180. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Montiel-Sosa F, Ruiz-Pesini E, Enriquez JA, Marcuello A, Diez-Sanchez C, Montoya J, Wallace DC, Lopez-Perez MJ. Differences of sperm motility in mitochondrial DNA haplogroup U sublineages. Gene. 2006;368:21–27. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Sun C, Kong QP, Zhang YP. The role of climate in human mitochondrial DNA evolution: a reappraisal. Genomics. 2007;89:338–342. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Amo T, Brand MD. Were inefficient mitochondrial haplogroups selected during migrations of modern humans?.A test using modular kinetic analysis of coupling in mitochondria from cybrid cell lines. Biochem. J. 2007;404:345–351. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Elson JL, Turnbull DM, Taylor RW. Testing the adaptive selection of human mtDNA haplogroups: an experimental bioenergetics approach. Biochem. J. 2007;404:e3–5. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kivisild T, Shen P, Wall DP, Do B, Sung R, Davis K, Passarino G, Underhill PA, Scharfe C, Torroni A, Scozzari R, Modiano D, Coppa A, de Knijff P, Feldman M, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Oefner PJ. The role of selection in the evolution of human mitochondrial genomes. Genetics. 2006;172:373–387. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.043901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Maruszak A, Safranow K, Branicki W, Gaweda-Walerych K, Pospiech E, Gabryelewicz T, Canter JA, Barcikowska M, Zekanowski C. The impact of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA variants on late-onset Alzheimer's disease risk. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2011;27:197–210. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Niemi AK, Hervonen A, Hurme M, Karhunen PJ, Jylha M, Majamaa K. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms associated with longevity in a Finnish population. Hum. Genet. 2003;112:29–33. doi: 10.1007/s00439-002-0843-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Dominguez-Garrido E, Martinez-Redondo D, Martin-Ruiz C, Gomez-Duran A, Ruiz-Pesini E, Madero P, Tamparillas M, Montoya J, von Zglinicki T, Diez-Sanchez C, Lopez-Perez MJ. Association of mitochondrial haplogroup J and mtDNA oxidative damage in two different North Spain elderly populations. Biogerontology. 2009;10:435–442. doi: 10.1007/s10522-008-9186-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.De Benedictis G, Rose G, Carrieri G, De Luca M, Falcone E, Passarino G, Bonafe M, Monti D, Baggio G, Bertolini S, Mari D, Mattace R, Franceschi C. Mitochondrial DNA inherited variants are associated with successful aging and longevity in humans. Faseb. J. 1999;13:1532–1536. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.13.12.1532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Ross OA, McCormack R, Curran MD, Duguid RA, Barnett YA, Rea IM, Middleton D. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism: its role in longevity of the Irish population. Exp. Gerontol. 2001;36:1161–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(01)00094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Rego-Perez I, Fernandez-Moreno M, Fernandez-Lopez C, Arenas J, Blanco FJ. Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups: role in the prevalence and severity of knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:2387–2396. doi: 10.1002/art.23659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Rego I, Fernandez-Moreno M, Fernandez-Lopez C, Gomez-Reino JJ, Gonzalez A, Arenas J, Blanco FJ. Role of European mitochondrial DNA haplogroups in the prevalence of hip osteoarthritis in Galicia, Northern Spain. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010;69:210–213. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.105254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Marcuello A, Martinez-Redondo D, Dahmani Y, Casajus JA, Ruiz-Pesini E, Montoya J, Lopez-Perez MJ, Diez-Sanchez C. Human mitochondrial variants influence on oxygen consumption. Mitochondrion. 2009;9(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2008.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Martinez-Redondo D, Marcuello A, Casajus JA, Ara I, Dahmani Y, Montoya J, Ruiz-Pesini E, Lopez-Perez MJ, Diez-Sanchez C. Human mitochondrial haplogroup H the highest VO2max consumer is it a paradox. Mitochondrion. 2010;10:102–107. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2009.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Fernandez-Moreno M, Tamayo M, Soto-Hermida A, Mosquera A, Oreiro N, Fernandez-Lopez C, Fernandez JL, Rego-Perez I, Blanco FJ. mtDNA haplogroup J Modulates telomere length and Nitric Oxide production. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011;12:283. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Bellizzi D, D'Aquila P, Giordano M, Montesanto A, Passarino G. Global DNA methylation levels are modulated by mitochondrial DNA variants. Epigenomics. 2012;4:17–27. doi: 10.2217/epi.11.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Kenney MC, Chwa M, Atilano SR, Pavlis JM, Falatoon-zadeh P, Ramirez C, Malik D, Hsu T, Woo G, Soe K, Nesburn AB, Boyer DS, Kuppermann BD, Jazwinski SM, Miceli MV, Wallace DC, Udar N. Mitochondrial DNA variants mediate energy production and expression levels for CFH, C3 and EFEMP1 genes: implications for age-related macular degeneration. PLoS One. 2013;8:e54339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Hudson G, Faini D, Stutt A, Eccles M, Robinson L, Burn DJ, Chinnery PF. No evidence of substantia nigra telomere shortening in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2011;32:2107 e2103–2105. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.05.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Maeda T, Guan JZ, Koyanagi M, Higuchi Y, Makino N. Aging-associated alteration of telomere length and subtelomeric status in female patients with Parkinson's disease. J. Neurogenet. 2012;26:245–251. doi: 10.3109/01677063.2011.651665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Watfa G, Dragonas C, Brosche T, Dittrich R, Sieber CC, Alecu C, Benetos A, Nzietchueng R. Study of telomere length and different markers of oxidative stress in patients with Parkinson's disease. J. Nutr. Health Aging. 2011;15:277–281. doi: 10.1007/s12603-010-0275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Eerola J, Kananen L, Manninen K, Hellstrom O, Tienari PJ, Hovatta I. No evidence for shorter leukocyte telomere length in Parkinson's disease patients. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010;65:1181–1184. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glq125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Wang H, Chen H, Gao X, McGrath M, Deer D, De Vivo I, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A. Telomere length and risk of Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 2008;23:302–305. doi: 10.1002/mds.21867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Brown MD, Starikovskaya E, Derbeneva O, Hosseini S, Allen JC, Mikhailovskaya IE, Sukernik RI, Wallace DC. The role of mtDNA background in disease expression: a new primary LHON mutation associated with Western Eurasian haplogroup J. Hum. Genet. 2002;110:130–138. doi: 10.1007/s00439-001-0660-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Brown MD, Sun F, Wallace DC. Clustering of Caucasian Leber hereditary optic neuropathy patients containing the 11778 or 14484 mutations on an mtDNA lineage. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997;60:381–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Arning L, Haghikia A, Taherzadeh-Fard E, Saft C, Andrich J, Pula B, Hoxtermann S, Wieczorek S, Akkad DA, Perrech M, Gold R, Epplen JT, Chan A. Mitochondrial haplogroup H correlates with ATP levels and age at onset in Huntington disease. J. Mol. Med. (Berl) 2010;88:431–436. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0589-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Baudouin SV, Saunders D, Tiangyou W, Elson JL, Poynter J, Pyle A, Keers S, Turnbull DM, Howell N, Chinnery PF. Mitochondrial DNA and survival after sepsis: a prospective study. Lancet. 2005;366:2118–2121. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67890-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Rosa A, Fonseca BV, Krug T, Manso H, Gouveia L, Albergaria I, Gaspar G, Correia M, Viana-Baptista M, Simoes RM, Pinto AN, Taipa R, Ferreira C, Fontes JR, Silva MR, Gabriel JP, Matos I, Lopes G, Ferro JM, Vicente AM, Oliveira SA. Mitochondrial haplogroup H1 is protective for ischemic stroke in Portuguese patients. BMC Med. Genet. 2008;9:57. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-9-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Hudson G, Nalls M, Evans JR, Breen DP, Winder-Rhodes S, Morrison KE, Morris HR, Williams-Gray CH, Barker RA, Singleton AB, Hardy J, Wood NE, Burn DJ, Chinnery PF. Two-stage association study and meta-analysis of mitochondrial DNA variants in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2013;80:2042–2048. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318294b434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Maruszak A, Canter JA, Styczynska M, Zekanowski C, Barcikowska M. Mitochondrial haplogroup H and Alzheimer's disease-Is there a connection?. Neurobiol. Aging. 2008;30(11):1749–1755. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Coto E, Gomez J, Alonso B, Corao AI, Diaz M, Menendez M, Martinez C, Calatayud MT, Moris G, Alvarez V. Late-onset Alzheimer's disease is associated with mitochondrial DNA 7028C/haplogroup H and D310 poly-C tract heteroplasmy. Neurogenetics. 2011;12:345–346. doi: 10.1007/s10048-011-0295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Carelli V, Vergani L, Bernazzi B, Zampieron C, Bucchi L, Valentino M, Rengo C, Torroni A, Martinuzzi A. Respiratory function in cybrid cell lines carrying European mtDNA haplogroups: implications for Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2002;1588:7–14. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(02)00097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Amo T, Yadava N, Oh R, Nicholls DG, Brand MD. Experimental assessment of bioenergetic differences caused by the common European mitochondrial DNA haplogroups H and T. Gene. 2008;411:69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.01.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Mueller EE, Brunner SM, Mayr JA, Stanger O, Sperl W, Kofler B. Functional differences between mitochondrial haplogroup T and haplogroup H in HEK293 cybrid cells. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Tanaka M, Fuku N, Nishigaki Y, Matsuo H, Segawa T, Watanabe S, Kato K, Yokoi K, Ito M, Nozawa Y, Yamada Y. Women with mitochondrial haplogroup N9a are protected against metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2007;56:518–521. doi: 10.2337/db06-1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Fuku N, Park KS, Yamada Y, Nishigaki Y, Cho YM, Matsuo H, Segawa T, Watanabe S, Kato K, Yokoi K, Nozawa Y, Lee HK, Tanaka M. Mitochondrial haplogroup N9a confers resistance against type 2 diabetes in Asians. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007;80:407–415. doi: 10.1086/512202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Takasaki S. Mitochondrial haplogroups associated with Japanese centenarians, Alzheimer's patients, Parkinson's patients type 2 diabetic patients and healthy non-obese young males. J. Genet. Genomics. 2009;36:425–434. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Takasaki S. Mitochondrial haplogroups associated with Japanese Alzheimer's patients. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2009;41:407–410. doi: 10.1007/s10863-009-9240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Hwang S, Kwak SH, Bhak J, Kang HS, Lee YR, Koo BK, Park KS, Lee HK, Cho YM. Gene expression pattern in transmitochondrial cytoplasmic hybrid cells harboring type 2 diabetes-associated mitochondrial DNA haplogroups. PLoS. One. 2011;6:e22116. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Lin TK, Lin HY, Chen SD, Chuang YC, Chuang JH, Wang PW, Huang ST, Tiao MM, Chen JB, Liou CW. The creation of cybrids harboring mitochondrial haplogroups in the Taiwanese population of ethnic Chinese background: an extensive in vitro tool for the study of mitochondrial genomic variations. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012;2012:824275. doi: 10.1155/2012/824275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Pesce V, Nicassio L, Fracasso F, Musicco C, Cantatore P, Gadaleta MN. Acetyl-L-carnitine activates the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivators PGC-1alpha/PGC-1beta-dependent signaling cascade of mitochondrial biogenesis and decreases the oxidized peroxiredoxins content in old rat liver. Rejuvenation. Res. 2012;15:136–139. doi: 10.1089/rej.2011.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Lee HK, Song JH, Shin CS, Park DJ, Park KS, Lee KU, Koh CS. Decreased mitochondrial DNA content in peripheral blood precedes the development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1998;42:161–167. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(98)00110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Picca A, Fracasso F, Pesce V, Cantatore P, Joseph AM, Leeuwenburgh C, Gadaleta MN, Lezza AM. Age- and calorie restriction-related changes in rat brain mitochondrial DNA and TFAM binding. Age (Dordr) 2012;35(5):1607–1620. doi: 10.1007/s11357-012-9465-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Cree LM, Patel SK, Pyle A, Lynn S, Turnbull DM, Chinnery PF, Walker M. Age-related decline in mito-chondrial DNA copy number in isolated human pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 2008;51:1440–1443. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-1054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Short KR, Bigelow ML, Kahl J, Singh R, Coenen-Schimke J, Raghavakaimal S, Nair KS. Decline in skeletal muscle mitochondrial function with aging in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2005;102:5618–5623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501559102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Monickaraj F, Aravind S, Gokulakrishnan K, Sathishkumar C, Prabu P, Prabu D, Mohan V, Balasubramanyam M. Accelerated aging as evidenced by increased telomere shortening and mitochondrial DNA depletion in patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012;365:343–350. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Barrientos A, Casademont J, Cardellach F, Estivill X, Urbano-Marquez A, Nunes V. Reduced steady-state levels of mitochondrial RNA and increased mitochondrial DNA amount in human brain with aging. Brain. Res. Mol. Brain. Res. 1997;52:284–289. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(97)00278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Blokhin A, Vyshkina T, Komoly S, Kalman B. Variations in mitochondrial DNA copy numbers in MS brains. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2008;35:283–287. doi: 10.1007/s12031-008-9115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Keeney PM, Quigley CK, Dunham LD, Papageorge CM, Iyer S, Thomas RR, Schwarz KM, Trimmer PA, Khan SM, Portell FR, Bergquist KE, Bennett Jr JP. Mitochondrial Gene Therapy Augments Mitochondrial Physiology in a Parkinson's Disease Cell Model. Hum. Gene. Ther. 2009;20(8):897–907. doi: 10.1089/hum.2009.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Borland MK, Mohanakumar KP, Rubinstein JD, Keeney PM, Xie J, Capaldi R, Dunham LD, Trimmer PA, Bennett JP Jr. Relationships among molecular genetic and respiratory properties of Parkinson's disease cybrid cells show similarities to Parkinson's brain tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1792:68–74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Iwaasa M, Umeda S, Ohsato T, Takamatsu C, Fukuoh A, Iwasaki H, Shinagawa H, Hamasaki N, Kang D. 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion, a toxin that can cause parkinsonism, alters branched structures of DNA. J. Neurochem. 2002;82:30–37. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.00996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Umeda S, Muta T, Ohsato T, Takamatsu C, Hamasaki N, Kang D. The D-loop structure of human mtDNA is destabilized directly by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+) a parkinsonism-causing toxin. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000;267:200–206. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.00990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Kraytsberg Y, Kudryavtseva E, McKee AC, Geula C, Kowall NW, Khrapko K. Mitochondrial DNA deletions are abundant and cause functional impairment in aged human substantia nigra neurons. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:518–520. doi: 10.1038/ng1778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Hori A, Yoshida M, Shibata T, Ling F. Reactive oxygen species regulate DNA copy number in isolated yeast mitochondria by triggering recombination-mediated replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:749–761. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Moreno-Loshuertos R, Acin-Perez R, Fernandez-Silva P, Movilla N, Perez-Martos A, Rodriguez de Cordoba S, Gallardo ME, Enriquez JA. Differences in reactive oxygen species production explain the phenotypes associated with common mouse mitochondrial DNA variants. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:1261–1268. doi: 10.1038/ng1897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Lee HC, Wei YH. Mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial DNA maintenance of mammalian cells under oxidative stress. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2005;37:822–834. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Suissa S, Wang Z, Poole J, Wittkopp S, Feder J, Shutt TE, Wallace DC, Shadel GS, Mishmar D. Ancient mtDNA genetic variants modulate mtDNA transcription and replication. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Scarpulla RC. Transcriptional paradigms in mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Physiol. Rev. 2008;88:611–638. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00025.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Holt IJ, Reyes A. Human Mitochondrial DNA Replication. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2012 doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Coskun PE, Beal MF, Wallace DC. Alzheimer's brains harbor somatic mtDNA control-region mutations that suppress mitochondrial transcription and replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2004;101:10726–10731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403649101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Simon DK, Lin MT, Zheng L, Liu GJ, Ahn CH, Kim LM, Mauck WM, Twu F, Beal MF, Johns DR. Somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations in cortex and substantia nigra in aging and Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2004;25:71–81. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(03)00037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Schoeler S, Hertel S, Haroon MF, Winkler-Stuck K, Mawrin C, Kirches E. Absence of major accumulation of mitochondrial ND5 mutations in Parkinson patient muscle. Clin. Neuropathol. 2007;26:164–168. doi: 10.5414/npp26164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Smigrodzki R, Parks J, Parker WD. High frequency of mitochondrial complex I mutations in Parkinson's disease and aging. Neurobiol. Aging. 2004;25:1273–1281. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.02.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Mawrin C, Kirches E, Krause G, Schneider-Stock R, Bogerts B, Vorwerk CK, Dietzmann K. Region-specific analysis of mitochondrial DNA deletions in neurodegenerative disorders in humans. Neurosci. Lett. 2004;357:111–114. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2003.11.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Lin MT, Cantuti-Castelvetri I, Zheng K, Jackson KE, Tan YB, Arzberger T, Lees AJ, Betensky RA, Beal MF, Simon DK. Somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations in early parkinson and incidental lewy body disease. Ann. Neurol. 2012;71:850–854. doi: 10.1002/ana.23568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Esterbauer H, Oberkofler H, Krempler F, Patsch W. Human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 (PPARGC1) gene: cDNA sequence genomic organization, chromosomal localization, and tissue ex-pression. Genomics. 1999;62:98–102. doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.5977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Scarpulla RC. Metabolic control of mitochondrial biogenesis through the PGC-1 family regulatory network. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1813:1269–1278. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.09.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Scarpulla RC. Nuclear control of respiratory gene expression in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2006;97:673–683. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Scarpulla RC. Nuclear control of respiratory chain expression by nuclear respiratory factors and PGC-1-related coactivator. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008;1147:321–334. doi: 10.1196/annals.1427.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Hattori N, Yoshino H, Tanaka M, Suzuki H, Mizuno Y. Genotype in the 24-kDa subunit gene (NDUFV2) of mitochondrial complex I and susceptibility to Parkinson disease. Genomics. 1998;49:52–58. doi: 10.1006/geno.1997.5192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Nishioka K, Vilarino-Guell C, Cobb SA, Kachergus JM, Ross OA, Hentati E, Hentati F, Farrer MJ. Genetic variation of the mitochondrial complex I subunit NDUFV2 and Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 2010;16:686–687. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2010.09.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Clark J, Reddy S, Zheng K, Betensky RA, Simon DK. Association of PGC-1alpha polymorphisms with age of onset and risk of Parkinson's disease. BMC. Med. Genet. 2011;12:69. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-12-69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Ling C, Poulsen P, Carlsson E, Ridderstrale M, Almgren P, Wojtaszewski J, Beck-Nielsen H, Groop L, Vaag A. Multiple environmental and genetic factors influence skeletal muscle PGC-1alpha and PGC-1beta gene expression in twins. J. Clin. Invest. 2004;114:1518–1526. doi: 10.1172/JCI21889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Deeb SS, Brunzell JD. The Role of the PGC1alpha Gly482Ser Polymorphism in Weight Gain due to Intensive Diabetes Therapy. PPAR. Res. 2009;2009:649286. doi: 10.1155/2009/649286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Prabhakar S, Vinish M, Das CP, Anand A. Occurrence of PARK2 mutations in a never-smoker population with Parkinson's disease in North India. Neuroepidemiology. 2010;35:152–159. doi: 10.1159/000313855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Ek J, Andersen G, Urhammer SA, Gaede PH, Drivsholm T, Borch-Johnsen K, Hansen T, Pedersen O. Mutation analysis of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 (PGC-1) and relationships of identified amino acid polymorphisms to Type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2001;44:2220–2226. doi: 10.1007/s001250100032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Vimaleswaran KS, Luan J, Andersen G, Muller YL, Wheeler E, Brito EC, O'Rahilly S, Pedersen O, Baier LJ, Knowler WC, Barroso I, Wareham NJ, Loos RJ, Franks PW. The Gly482Ser genotype at the PPARGC1A gene and elevated blood pressure: a meta-analysis involving 13 949 individuals. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008;105:1352–1358. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.90423.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Zheng B, Liao Z, Locascio JJ, Lesniak KA, Roderick SS, Watt ML, Eklund AC, Zhang-James Y, Kim PD, Hauser MA, Grunblatt E, Moran LB, Mandel SA, Riederer P, Miller RM, Federoff HJ, Wullner U, Papapetropoulos S, Youdim MB, Cantuti-Castelvetri I, Young AB, Vance JM, Davis RL, Hedreen JC, Adler CH, Beach TG, Graeber MB, Middleton FA, Rochet JC, Scherzer CR. PGC-1alpha a potential therapeutic target for early intervention in Parkinson's disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010;2:52ra73. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Shin JH, Ko HS, Kang H, Lee Y, Lee YI, Pletinkova O, Troconso JC, Dawson VL, Dawson TM. PARIS (ZNF746) repression of PGC-1alpha contributes to neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Cell. 2011;144:689–702. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Pacelli C, De Rasmo D, Signorile A, Grattagliano I, di Tullio G, D'Orazio A, Nico B, Comi GP, Ronchi D, Ferranini E, Pirolo D, Seibel P, Schubert S, Gaballo A, Villani G, Cocco T. Mitochondrial defect and PGC-1alpha dysfunction in parkin-associated familial Parkinson's disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1812:1041–1053. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Ciron C, Lengacher S, Dusonchet J, Aebischer P, Schneider BL. Sustained expression of PGC-1alpha in the rat nigrostriatal system selectively impairs dopaminergic function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012;21:1861–1876. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Jin J, Meredith GE, Chen L, Zhou Y, Xu J, Shie FS, Lockhart P, Zhang J. Quantitative proteomic analysis of mitochondrial proteins: relevance to Lewy body formation and Parkinson's disease. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005;134:119–138. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Jin J, Hulette C, Wang Y, Zhang T, Pan C, Wadhwa R, Zhang J. Proteomic identification of a stress protein, morta-lin/mthsp70/GRP75: relevance to Parkinson disease. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2006;5:1193–1204. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M500382-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Shi M, Jin J, Wang Y, Beyer RP, Kitsou E, Albin RL, Gearing M, Pan C, Zhang J. Mortalin: a protein associated with progression of Parkinson disease? J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008;67:117–124. doi: 10.1097/nen.0b013e318163354a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Chiasserini D, Tozzi A, de Iure A, Tantucci M, Susta F, Orvietani PL, Koya K, Binaglia L, Calabresi P. Mortalin inhibition in experimental Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 2011;26:1639–1647. doi: 10.1002/mds.23647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Burbulla LF, Schelling C, Kato H, Rapaport D, Woitalla D, Schiesling C, Schulte C, Sharma M, Illig T, Bauer P, Jung S, Nordheim A, Schols L, Riess O, Kruger R. Dissecting the role of the mitochondrial chaperone mortalin in Parkinson's disease functional impact of disease-related variants on mitochondrial homeostasis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010;19:4437–4452. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.De Mena L, Coto E, Sanchez-Ferrero E, Ribacoba R, Guisasola LM, Salvador C, Blazquez M, Alvarez V. Mutational screening of the mortalin gene (HSPA9) in Parkinson's disease. J. Neural. Transm. 2009;116:1289–1293. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Humphries AD, Streimann IC, Stojanovski D, Johnston AJ, Yano M, Hoogenraad NJ, Ryan MT. Dissection of the mitochondrial import and assembly pathway for human Tom40. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:11535–11543. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413816200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Cruchaga C, Nowotny P, Kauwe JS, Ridge PG, Mayo K, Bertelsen S, Hinrichs A, Fagan AM, Holtzman DM, Morris JC, Goate AM. Association and expression analyses with single-nucleotide polymorphisms in TOMM40 in Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2011;68:1013–1019. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Maruszak A, Peplonska B, Safranow K, Chodakowska-Zebrowska M, Barcikowska M, Zekanowski C. TOMM40 rs10524523 polymorphism's role in late-onset Alzheimer's disease and in longevity. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012;28:309–322. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Peplonska B, Safranow K, Gaweda-Walerych K, Maruszak A, Czyzewski K, Rudzinska M, Barcikowska M, Zekanowski C. TOMM40 and APOE common genetic variants are not Parkinson's disease risk factors. Neurobiol. Aging. 2013;34 2078:e2071–2072. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.02.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Shutt TE, Shadel GS. A compendium of human mitochondrial gene expression machinery with links to disease. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2010;51:360–379. doi: 10.1002/em.20571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Gohil VM, Nilsson R, Belcher-Timme CA, Luo B, Root DE, Mootha VK. Mitochondrial and nuclear genomic responses to loss of LRPPRC expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:13742–13747. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.098400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Mili S, Pinol-Roma S. LRP130 a pentatricopeptide motif protein with a noncanonical RNA-binding domain is bound in vivo to mitochondrial and nuclear RNAs. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003;23:4972–4982. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.14.4972-4982.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Rakovic A, Grunewald A, Voges L, Hofmann S, Orolicki S, Lohmann K, Klein C. PINK1-Interacting Proteins: Proteomic Analysis of Overexpressed PINK1. Parkinsons. Dis. 2011;2011:153979. doi: 10.4061/2011/153979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Alam TI, Kanki T, Muta T, Ukaji K, Abe Y, Nakayama H, Takio K, Hamasaki N, Kang D. Human mitochondrial DNA is packaged with TFAM. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:1640–1645. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Larsson NG, Wang J, Wilhelmsson H, Oldfors A, Rustin P, Lewandoski M, Barsh GS, Clayton DA. Mitochondrial transcription factor A is necessary for mtDNA maintenance and embryogenesis in mice. Nat. Genet. 1998;18:231–236. doi: 10.1038/ng0398-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Hayashi Y, Yoshida M, Yamato M, Ide T, Wu Z, Ochi-Shindou M, Kanki T, Kang D, Sunagawa K, Tsutsui H, Nakanishi H. Reverse of age-dependent memory impairment and mitochondrial DNA damage in microglia by an overexpression of human mitochondrial transcription factor a in mice. J. Neurosci. 2008;28:8624–8634. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1957-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Noack H, Bednarek T, Heidler J, Ladig R, Holtz J, Szibor M. TFAM-dependent and independent dynamics of mtDNA levels in C2C12 myoblasts caused by redox stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1760:141–150. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2005.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Bonawitz ND, Clayton DA, Shadel GS. Initiation and beyond: multiple functions of the human mitochondrial transcription machinery. Mol. Cell. 2006;24:813–825. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Alvarez V, Corao AI, Sanchez-Ferrero E, De Mena L, Alonso-Montes C, Huerta C, Blazquez M, Ribacoba R, Guisasola LM, Salvador C, Garcia-Castro M, Coto E. Mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) gene variation in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2008;432:79–82. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Sánchez-Ferrero ECE, Blázquez M, Ribacoba R, Guisasola LM, Salvador C, Alvarez V. Mutational screening of the mitochondrial transcription factors B1 and B2 (TFB1M and TFB2M) in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2009;15:468–470. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Gaweda-Walerych K, Safranow K, Maruszak A, Bialecka M, Klodowska-Duda G, Czyzewski K, Slawek J, Rudzinska M, Styczynska M, Opala G, Drozdzik M, Kurzawski M, Szczudlik A, Canter JA, Barcikowska M, Zekanowski C. Mitochondrial transcription factor A variants and the risk of Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010;469:24–29. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.11.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Belin AC, Bjork BF, Westerlund M, Galter D, Sydow O, Lind C, Pernold K, Rosvall L, Hakansson A, Winblad B, Nissbrandt H, Graff C, Olson L. Association study of two genetic variants in mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2007;420:257–262. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Bras JM, Sharma M, Gibbs JR, Berg D, Paisan-Ruiz C, Lichtner P, Scholz SW, Hernandez DG, Kruger R, Federoff M, Klein C, Goate A, Perlmutter J, Bonin M, Nalls MA, Illig T, Gieger C, Houlden H, Steffens M, Okun MS, Racette BA, Cookson MR, Foote KD, Fernandez HH, Traynor BJ, Schreiber S, Arepalli S, Zonozi R, Gwinn K, van der Brug M, Lopez G, Chanock SJ, Schatzkin A, Park Y, Hollenbeck A, Gao J, Huang X, Wood NW, Lorenz D, Deuschl G, Chen H, Riess O, Hardy JA, Singleton AB, Gasser T. Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson's disease. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:1308–1312. doi: 10.1038/ng.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Pankratz N, Wilk JB, Latourelle JC, DeStefano AL, Halter C, Pugh EW, Doheny KF, Gusella JF, Nichols WC, Foroud T, Myers RH. Genomewide association study for susceptibility genes contributing to familial Parkinson disease. Hum. Genet. 2009;124:593–605. doi: 10.1007/s00439-008-0582-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Gunther C, vonHadeln K, Muller-Thomsen T, Alberici A, Binetti G, Hock C, Nitsch RM, Stoppe G, Reiss J, Gal A, Finckh U. Possible association of mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) genotype with sporadic Alzheimer disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2004;369:219–223. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2004.07.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Abahuni N, Gispert S, Bauer P, Riess O, Kruger R, Becker T, Auburger G. Mitochondrial translation initiation factor 3 gene polymorphism associated with Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2007;414:126–129. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.12.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Behrouz B, Vilarino-Guell C, Heckman MG, Soto-Ortolaza AI, Aasly JO, Sando S, Lynch T, Craig D, Uitti RJ, Wszolek ZK, Ross OA, Farrer MJ. Mitochondrial translation initiation factor 3 polymorphism and Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010;486:228–230. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Anvret A, Ran C, Westerlund M, Thelander AC, Sydow O, Lind C, Hakansson A, Nissbrandt H, Galter D, Belin AC. Possible involvement of a mitochondrial translation initiation factor 3 variant causing decreased mRNA levels in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons. Dis. 2010;2010:491751. doi: 10.4061/2010/491751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Baloh RH, Salavaggione E, Milbrandt J, Pestronk A. Familial parkinsonism and ophthalmoplegia from a mutation in the mitochondrial DNA helicase twinkle. Arch Neurol. 2007;64:998–1000. doi: 10.1001/archneur.64.7.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Davidzon G, Greene P, Mancuso M, Klos KJ, Ahlskog JE, Hirano M, DiMauro S. Early-onset familial parkinsonism due to POLG mutations. Ann. Neurol. 2006;59:859–862. doi: 10.1002/ana.20831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Luoma P, Melberg A, Rinne JO, Kaukonen JA, Nupponen NN, Chalmers RM, Oldfors A, Rautakorpi I, Peltonen L, Majamaa K, Somer H, Suomalainen A. Parkinsonism premature menopause, and mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma mutations: clinical and molecular genetic study. Lancet. 2004;364:875–882. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16983-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Hudson G, Schaefer AM, Taylor RW, Tiangyou W, Gibson A, Venables G, Griffiths P, Burn DJ, Turnbull DM, Chinnery PF. Mutation of the linker region of the polymerase gamma-1 (POLG1) gene associated with progressive external ophthalmoplegia and Parkinsonism. Arch Neurol. 2007;64:553–557. doi: 10.1001/archneur.64.4.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Orsucci D, Caldarazzo Ienco E, Mancuso M, Siciliano G. POLG1-related and other "mitochondrial Parkinsonisms": an overview. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011;44:17–24. doi: 10.1007/s12031-010-9488-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Tyynismaa H, Sembongi H, Bokori-Brown M, Granycome C, Ashley N, Poulton J, Jalanko A, Spelbrink JN, Holt IJ, Suomalainen A. Twinkle helicase is essential for mtDNA maintenance and regulates mtDNA copy number. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004;13:3219–3227. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Spelbrink JN, Li FY, Tiranti V, Nikali K, Yuan QP, Tariq M, Wanrooij S, Garrido N, Comi G, Morandi L, Santoro L, Toscano A, Fabrizi GM, Somer H, Croxen R, Beeson D, Poulton J, Suomalainen A, Jacobs HT, Zeviani M, Larsson C. Human mitochondrial DNA deletions associated with mutations in the gene encoding Twinkle a phage T7 gene 4-like protein localized in mitochondria. Nat. Genet. 2001;28:223–231. doi: 10.1038/90058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Kaguni LS. DNA polymerase gamma, the mitochondrial replicase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004;73:293–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Graziewicz MA, Longley MJ, Copeland WC. DNA polymerase gamma in mitochondrial DNA replication and repair. Chem. Rev. 2006;106:383–405. doi: 10.1021/cr040463d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Luoma PT, Eerola J, Ahola S, Hakonen AH, Hellstrom O, Kivisto KT, Tienari PJ, Suomalainen A. Mi-tochondrial DNA polymerase gamma variants in idiopathic sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2007;69:1152–1159. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000276955.23735.eb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Eerola J, Luoma PT, Peuralinna T, Scholz S, Paisan-Ruiz C, Suomalainen A, Singleton AB, Tienari PJ. POLG1 polyglutamine tract variants associated with Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010;477:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.04.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Anvret A, Westerlund M, Sydow O, Willows T, Lind C, Galter D, Belin AC. Variations of the CAG trinucleotide repeat in DNA polymerase gamma (POLG1) is associated with Parkinson's disease in Sweden. Neurosci. Lett. 2010;485:117–120. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Balafkan N, Tzoulis C, Muller B, Haugarvoll K, Tysnes OB, Larsen JP, Bindoff LA. Number of CAG repeats in POLG1 and its association with Parkinson disease in the Norwegian population. Mitochondrion. 2012;12(6):640–643. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2012.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Hudson G, Tiangyou W, Stutt A, Eccles M, Robinson L, Burn DJ, Chinnery PF. No association between common POLG1 variants and sporadic idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 2009;24:1092–1094. doi: 10.1002/mds.22310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Spelbrink JN, Toivonen JM, Hakkaart GA, Kurkela JM, Cooper HM, Lehtinen SK, Lecrenier N, Back JW, Speijer D, Foury F, Jacobs HT. In vivo functional analysis of the human mitochondrial DNA polymerase POLG expressed in cultured human cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:24818–24828. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000559200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Gaweda-Walerych K, Safranow K, Jasinska-Myga B, Bialecka M, Klodowska-Duda G, Rudzinska M, Czyzewski K, Cobb SA, Slawek J, Styczynska M, Opala G, Drozdzik M, Nishioka K, Farrer MJ, Ross OA, Wszolek ZK, Barcikowska M, Zekanowski C. PARK2 variability in Polish Parkinson's disease patients--interaction with mitochondrial haplogroups. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 2012;18:520–524. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.01.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Lucking CB, Chesneau V, Lohmann E, Verpillat P, Dulac C, Bonnet AM, Gasparini F, Agid Y, Durr A, Brice A. Coding polymorphisms in the parkin gene and susceptibility to Parkinson disease. Arch. Neurol. 2003;60:1253–1256. doi: 10.1001/archneur.60.9.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Wu YR, Wu CH, Chao CY, Kuan CC, Zhang WL, Wang CK, Chang CY, Chang YC, Lee-Chen GJ, Chen CM. Genetic analysis of Parkin in early onset Parkinson's disease (PD): Novel intron 9 g > a single nucleotide polymorphism and risk of Taiwanese PD. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2010;153B:229–234. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Aguiar Pde C, Lessa PS, Godeiro CJr, Barsottini O, Felicio AC, Borges V, Silva SM, Saba RA, Ferraz HB, Moreira-Filho CA, Andrade LA. Genetic and environmental findings in early-onset Parkinson's disease Brazilian patients. Mov. Disord. 2008;23:1228–1233. doi: 10.1002/mds.22032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Wittkopp S, Staimer N, Tjoa T, Gillen D, Daher N, Shafer M, Schauer JJ, Sioutas C, Delfino RJ. Mito-chondrial genetic background modifies the relationship between traffic-related air pollution exposure and systemic biomarkers of inflammation. PLoS One. 2013;8:e64444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Henchcliffe C, Beal MF. Mitochondrial biology and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease pathogenesis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2008;4:600–609. doi: 10.1038/ncpneuro0924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Pihlstrom L, Axelsson G, Bjornara KA, Dizdar N, Fardell C, Forsgren L, Holmberg B, Larsen JP, Linder J, Nissbrandt H, Tysnes OB, Ohman E, Dietrichs E, Toft M. Supportive evidence for 11 loci from genome-wide association studies in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2012;34(6):1708.e7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Liu X, Cheng R, Verbitsky M, Kisselev S, Browne A, Mejia-Sanatana H, Louis ED, Cote LJ, Andrews H, Waters C, Ford B, Frucht S, Fahn S, Marder K, Clark LN, Lee JH. Genome-wide association study identifies candidate genes for Parkinson's disease in an Ashkenazi Jewish population. BMC Med. Genet. 2011;12:104. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-12-104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Sharma M, Ioannidis JP, Aasly JO, Annesi G, Brice A, Van Broeckhoven C, Bertram L, Bozi M, Crosiers D, Clarke C, Facheris M, Farrer M, Garraux G, Gispert S, Auburger G, Vilarino-Guell C, Hadjigeorgiou GM, Hicks AA, Hattori N, Jeon B, Lesage S, Lill CM, Lin JJ, Lynch T, Lichtner P, Lang AE, Mok V, Jasinska-Myga B, Mellick GD, Morrison KE, Opala G, Pramstaller PP, Pichler I, Park SS, Quattrone A, Rogaeva E, Ross OA, Stefanis L, Stockton JD, Satake W, Silburn PA, Theuns J, Tan EK, Toda T, Tomiyama H, Uitti RJ, Wirdefeldt K, Wszolek Z, Xiromerisiou G, Yueh KC, Zhao Y, Gasser T, Maraganore D, Kruger R. Large-scale replication and heterogeneity in Parkinson disease genetic loci. Neurology. 2012;79:659–667. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318264e353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Trotta L, Guella I, Solda G, Sironi F, Tesei S, Canesi M, Pezzoli G, Goldwurm S, Duga S, Asselta R. SNCA and MAPT genes: Independent and joint effects in Parkinson disease in the Italian population. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 2012;18:257–262. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Ding H, Sarokhan AK, Roderick SS, Bakshi R, Maher NE, Ashourian P, Kan CG, Chang S, Santarlasci A, Swords KE, Ravina BM, Hayes MT, Sohur US, Wills AM, Flaherty AW, Unni VK, Hung AY, Selkoe DJ, Schwarzschild MA, Schlossmacher MG, Sudarsky LR, Growdon JH, Ivinson AJ, Hyman BT, Scherzer CR. Association of SNCA with Parkinson: replication in the Harvard NeuroDiscovery Center Biomarker Study. Mov. Disord. 2011;26:2283–2286. doi: 10.1002/mds.23934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Mata IF, Yearout D, Alvarez V, Coto E, de Mena L, Ribacoba R, Lorenzo-Betancor O, Samaranch L, Pastor P, Cervantes S, Infante J, Garcia-Gorostiaga I, Sierra M, Combarros O, Snapinn KW, Edwards KL, Zabetian CP. Replication of MAPT and SNCA, but not PARK16-18, as susceptibility genes for Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 2011;26:819–823. doi: 10.1002/mds.23642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Simon-Sanchez J, van Hilten JJ, van de Warrenburg B, Post B, Berendse HW, Arepalli S, Hernandez DG, de Bie RM, Velseboer D, Scheffer H, Bloem B, van Dijk KD, Rivadeneira F, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Rizzu P, Bochdanovits Z, Singleton AB, Heutink P. Genome-wide association study confirms extant PD risk loci among the Dutch. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2011;19:655–661. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2010.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Rhodes SL, Sinsheimer JS, Bordelon Y, Bronstein JM, Ritz B. Replication of GWAS associations for GAK and MAPT in Parkinson's disease. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2011;75:195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2010.00616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Tan EK, Kwok HH, Tan LC, Zhao WT, Prakash KM, Au WL, Pavanni R, Ng YY, Satake W, Zhao Y, Toda T, Liu JJ. Analysis of GWAS-linked loci in Parkinson disease reaffirms PARK16 as a susceptibility locus. Neurology. 2010;75:508–512. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181eccfcd. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Satake W, Nakabayashi Y, Mizuta I, Hirota Y, Ito C, Kubo M, Kawaguchi T, Tsunoda T, Watanabe M, Takeda A, Tomiyama H, Nakashima K, Hasegawa K, Obata F, Yoshikawa T, Kawakami H, Sakoda S, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Murata M, Nakamura Y, Toda T. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson's disease. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:1303–1307. doi: 10.1038/ng.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Tsuboi Y. Environmental-genetic interactions in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Exp. Neurobiol. 2012;21:123–128. doi: 10.5607/en.2012.21.3.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Berg D. Is pre-motor diagnosis possible?--The European experience. Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 2012;18(Suppl 1 ):S195–198. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(11)70061-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]