Abstract
This report describes the preparation and characterization of antisera to human trophoblast membranes. Rabbit antisera were raised to trophoblast microvilli prepared by differential ultracentrifugation. Antibodies to serum proteins were removed by solid-phase immunoabsorption with normal human serum, and indirect immunofluorescence experiments with cryostat sections of human placentas showed that the absorbed anti-trophoblast sera reacted with trophoblasts as well as with stromal cells and endothelium of chorionic villi. The antisera also produced membrane fluorescence when studied on viable lymphocytes and certain human cell lines. These anti-trophoblast sera were also lymphocytotoxic, and this reaction was abolished by prior absorption of the antisera with leukocytes. The leukocyte-absorbed anti-trophoblast sera retained their ability to react with trophoblasts and certain human cell lines, but no longer reacted with lymphocytes or placental stromal cells and endothelium. Two categories of trophoblast membrane antigens are thus defined: one present on trophoblasts and certain human cells lines (tentatively designated TA1), and the other on trophoblasts and lymphocytes, villous fibroblasts, and endothelium (tentatively designated TA2). A working hypothesis is proposed stating that normal pregnancy involves the generation of anti-TA2 subsequent to blastocyst implantation and entrance of trophoblasts into the maternal circulation. This involves a mechanism similar to allogeneic cell stimulation and results in antibodies that block either the recognition or cytotoxicity of TA1. Failure to mount this response allows TA1 recognition and trophoblast immunopathology. Experimental and clinical studies in support of this working hypothesis, particularly involving abortion and toxemia, are cited from published reports.
Keywords: placentas, immunity, oncofetal, membranes
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. Mechanisms of tolerance and autoimmunity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jul;32(4):283–293. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankhurst A. D., Torrigiani G., Allison A. C. Lymphocytes binding human thyroglobulin in healthy people and its relevance to tolerance for autoantigens. Lancet. 1973 Feb 3;1(7797):226–230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer A. E., Billingham R. E. Immunobiology of mammalian reproduction. Adv Immunol. 1971;14:1–84. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beer A. E., Billingham R. E., Yang S. L. Further evidence concerning the autoantigenic status of the trophoblast. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1177–1184. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breshnihan B., Grigor R. R., Oliver M., Lewkonia R. M., Hughes G. R., Lovins R. E., Faulk W. P. Immunological mechanism for spontaneous abortion in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1977 Dec 10;2(8050):1205–1207. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90441-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Wada H. G., Sussman H. H. The plasma membrane of human placenta. Isolation of microvillus membrane and characterization of protein and glycoprotein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4139–4146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Hijmans W. Recent developments in immunofluorescence. Prog Allergy. 1972;16:9–39. doi: 10.1159/000393067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Jeannet M., Creighton W. D., Carbonara A. Immunological studies of the human placenta. Characterization of immunoglobulins on trophoblastic basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1011–1019. doi: 10.1172/JCI107844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Johnson P. M. Immunological studies of human placentae: identification and distribution of proteins in mature chorionic villi. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Feb;27(2):365–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Sanderson A. R., Temple A. Distribution of MHC antigens in human placental chorionic villi. Transplant Proc. 1977 Jun;9(2):1379–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Temple A. Distribution of beta2 microglobulin and HLA in chorionic villi of human placentae. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):799–802. doi: 10.1038/262799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney J. G., Tovey L. A., Scott J. S. Influence of previous blood-transfusion on incidence of pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 1977 Apr 23;1(8017):874–875. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91199-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Snary D., Crumpton M. J. Expression of HLA system antigens on placenta. Transplantation. 1976 Dec;22(6):595–603. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197612000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y. P., Grudzinskas J. G., Jeffrey D., Chard T. Concentrations of pregnancy-specific beta 1-glycoprotein in maternal blood in normal pregnancy and in intrauterine growth retardation. Lancet. 1977 Feb 12;1(8007):331–333. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M., Faulk W. P., Wang A. C. Immunological studies of human placentae: subclass and fragment specificity of binding of aggregated IgG by placental endothelial cells. Immunology. 1976 Oct;31(4):659–664. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H. The allogeneic effect on immune responses: model for regulatory influences of T lymphocytes on the immune system. Transplant Rev. 1972;12:141–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komlos L., Zamir R., Joshua H., Halbrecht I. Common HLA antigens in couples with repeated abortions. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 May;7(3):330–335. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
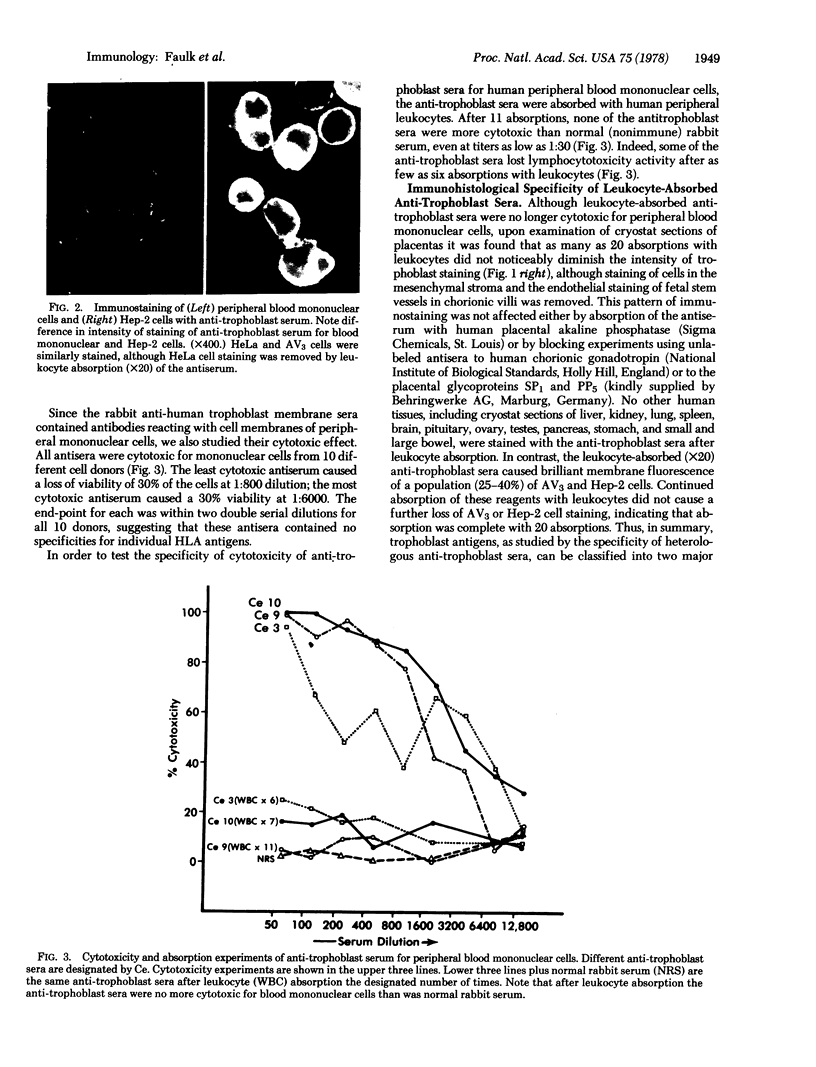
- McCormick J. N., Faulk W. P., Fox H., Fudenberg H. H. Immunohistological and elution studies of the human placenta. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Kitzmiller J. L., Carpenter C. B., Garovoy M. R., David J. R. Maternal-fetal relation. Absence of an immunologic blocking factor from the serum of women with chronic abortions. N Engl J Med. 1976 Nov 25;295(22):1209–1213. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197611252952201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Beer A. E., Stastny P. Immunogenetic factors in preeclampsia and eclampsia. Erythrocyte, histocompatibility, and Y-dependent antigens. JAMA. 1976 Jan 26;235(4):402–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. C., Brush M. G., Luckett S. Preparation of human placental villous surface membrane. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):302–303. doi: 10.1038/252302b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woehler M. E., Chism G. E., Cox W. R., Lindeman J. G., Lovins R. E. Purification of DNP specific antibodies using sepharose bound DNP-para-aminobenzoylglutamate. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jan;6(3):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]