Abstract
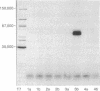
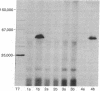
Incorporation of phosphorus from [gamma-32P]ATP into protein was catalyzed by specific immunoprecipitates from avian sarcoma virus (ASV)-transformed avian and mammalian cells. This incorporation was observed only when antiserum from tumor-bearing rabbits able to specifically precipitate the ASV sarcoma gene product, p60src, was used to immunoprecipitate antigens from transformed cell lysates. Immunoprecipitates of extracts from normal cells or cells infected with a transformation-defective ASV mutant showed no activity in this assay, nor did any immune complexes formed with normal rabbit serum and any of the cell extracts tested. The expression of the protein kinase activity (ATP:protein phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.37) was growth temperature-dependent in cells infected with an ASV mutant temperature-sensitive for the transformation. These results on an enzymatic activity associated with the ASV transforming protein are discussed in terms of protein phosphorylation as a mechanism for viral transformation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ash J. F., Vogt P. K., Singer S. J. Reversion from transformed to normal phenotype by inhibition of protein synthesis in rat kidney cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3603–3607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs P. M., Milne B. S., Graf T., Bauer H. Oncogenicity of non-transforming mutants of avian sarcoma viruses. J Gen Virol. 1973 Mar;18(3):399–403. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-3-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier W., Singer S. J. On the mechanism of ATP-induced shape changes in human erythrocyte membranes. II. The role of ATP. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):647–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Antibody to virion structural proteins in mammals bearing avian sarcoma virus-induced tumors. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):429–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. C., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Properties of mammalian cells transformed by temperature-sensitive mutants of avian sarcoma virus. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):513–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng C. T., Stehelin D., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Characteristics of virus-specific RNA in avian sarcoma virus-transformed BHK-21 cells and revertants. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):313–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. The effects of reciprocal changes in temperature on the transformed state of cells infected with a rous sarcoma virus mutant. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):470–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson I. Reversion in Hamster Cells Transformed by Rous Sarcoma Virus. Science. 1965 Jun 25;148(3678):1731–1733. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3678.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. S. Rous sarcoma virus: a function required for the maintenance of the transformed state. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1021–1023. doi: 10.1038/2271021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a polypeptide encoded by the avian sarcoma virus src gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1567–1571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Translation of 35S and of subgenomic regions of avian sarcoma virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4661–4665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Guntaka R. V., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Purification of DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences required for neoplastic transformation of fibroblasts by avian sarcoma viruses. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):349–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima K., Vogt P. K. Temperature sensitive mutants of an avian sarcoma virus. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):930–931. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K. Spontaneous segregation of nontransforming viruses from cloned sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P., Beemon K., Vogt P. K. Mapping RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs: sarcoma-specific oligonucleotides are near the poly(A) end and oligonucleotides common to sarcoma and transformation-defective viruses are at the poly(A) end. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1051–1070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1051-1070.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]