Abstract
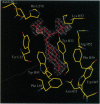
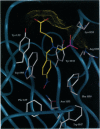
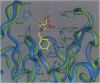
The x-ray crystal structures of the sulfide oxidase antibody 28B4 and of antibody 28B4 complexed with hapten have been solved at 2.2-angstrom and 1.9-angstrom resolution, respectively. To our knowledge, these structures are the highest resolution catalytic antibody structures to date and provide insight into the molecular mechanism of this antibody-catalyzed monooxygenation reaction. Specifically, the data suggest that entropic restriction plays a fundamental role in catalysis through the precise alignment of the thioether substrate and oxidant. The antibody active site also stabilizes developing charge on both sulfur and periodate in the transition state via cation-pi and electrostatic interactions, respectively. In addition to demonstrating that the active site of antibody 28B4 does indeed reflect the mechanistic information programmed in the aminophosphonic acid hapten, these high-resolution structures provide a basis for enhancing turnover rates through mutagenesis and improved hapten design.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amit A. G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of an antigen-antibody complex at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):747–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2426778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo J. H., Taussig M. J., Wilson I. A. Molecular basis of crossreactivity and the limits of antibody-antigen complementarity. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):859–863. doi: 10.1038/365859a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach L. A., Hsieh S., Brown A. L., Rechler M. M. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-6 inhibits IGF-II-induced differentiation of L6A1 myoblasts. Endocrinology. 1994 Nov;135(5):2168–2176. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.5.7525263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burley S. K., Petsko G. A. Aromatic-aromatic interaction: a mechanism of protein structure stabilization. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.3892686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonnier J. B., Carpenter E., Gigant B., Golinelli-Pimpaneau B., Eshhar Z., Green B. S., Knossow M. Crystal structure of the complex of a catalytic antibody Fab fragment with a transition state analog: structural similarities in esterase-like catalytic antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 5;92(25):11721–11725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S., Griffin J., Huang H., Calame K., Hood L. A single VH gene segment encodes the immune response to phosphorylcholine: somatic mutation is correlated with the class of the antibody. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Padlan E. A., Sheriff S. Antibody-antigen complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:439–473. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty D. A., Stauffer D. A. Acetylcholine binding by a synthetic receptor: implications for biological recognition. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1558–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.2274786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golinelli-Pimpaneau B., Gigant B., Bizebard T., Navaza J., Saludjian P., Zemel R., Tawfik D. S., Eshhar Z., Green B. S., Knossow M. Crystal structure of a catalytic antibody Fab with esterase-like activity. Structure. 1994 Mar 15;2(3):175–183. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes M. R., Stura E. A., Hilvert D., Wilson I. A. Routes to catalysis: structure of a catalytic antibody and comparison with its natural counterpart. Science. 1994 Feb 4;263(5147):646–652. doi: 10.1126/science.8303271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakoby W. B., Ziegler D. M. The enzymes of detoxication. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20715–20718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpf R. A., Dougherty D. A. A mechanism for ion selectivity in potassium channels: computational studies of cation-pi interactions. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1708–1710. doi: 10.1126/science.8378771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. I., Jencks W. P. Entropic contributions to rate accelerations in enzymic and intramolecular reactions and the chelate effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1678–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten P. A., Gray N. S., Yang P. L., Marks C. B., Wedemayer G. J., Boniface J. J., Stevens R. C., Schultz P. G. The immunological evolution of catalysis. Science. 1996 Feb 23;271(5252):1086–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5252.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P. G., Lerner R. A. From molecular diversity to catalysis: lessons from the immune system. Science. 1995 Sep 29;269(5232):1835–1842. doi: 10.1126/science.7569920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Davies D. R. The three-dimensional structure of a phosphorylcholine-binding mouse immunoglobulin Fab and the nature of the antigen binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield R. L., Fieser T. M., Lerner R. A., Wilson I. A. Crystal structures of an antibody to a peptide and its complex with peptide antigen at 2.8 A. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):712–719. doi: 10.1126/science.2333521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich H. D., Patten P. A., Yang P. L., Romesberg F. E., Schultz P. G. Expression studies of catalytic antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 5;92(25):11907–11911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Stanfield R. L. Antibody-antigen interactions: new structures and new conformational changes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1994 Dec;4(6):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. H. Enzymatic catalysts in organic synthesis. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1145–1152. doi: 10.1126/science.2658059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G. W., Guo J., Huang W., Fletterick R. J., Scanlan T. S. Crystal structure of a catalytic antibody with a serine protease active site. Science. 1994 Aug 19;265(5175):1059–1064. doi: 10.1126/science.8066444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]