Abstract
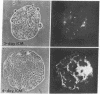
The expression of a high molecular weight cell surface glycoprotein (LETS, fibronectin) by preimplantation mouse embryos as well as cultured teratocarcinoma stem cells was detected by using indirect immunofluorescent staining. When each stage of preimplantation embryonic development was tested for the presence of LETS protein, none was observed on two-cell, four-cell, or eight-cell embryos, or on the morula or the outer cell layer (trophectoderm) of the early or late blastocyst. However, when the inner cell mass was isolated by immunosurgery, positive staining was observed. The intensity of the staining was significantly greater on the inner cell mass isolated from the expanded (day 4) blastocyst than on that from the early (day 3) blastocyst.
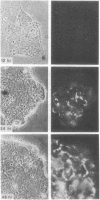
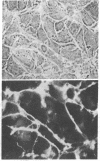
Certain established cell lines of teratocarcinoma stem cells (embryonal carcinoma cells) also express cell surface LETS protein. “Nullipotent” (Nulli-SCC-1) as well as pluripotent (PSA 1) embryonal carcinoma cell lines have deposits of LETS protein concentrated in areas of cell-cell contact. In addition, a teratocarcinoma-derived endodermal cell line (PYS) was found to be capable of depositing LETS onto the substratum in a fibrillar network.
Taken together, our results indicate that LETS protein is synthesized at a specific stage of preimplantation mouse embryonic development. In particular, they suggest that LETS protein is a product of the embryonic ectoderm, and that some types of embryonic endoderm are also capable of synthesizing this protein.
Keywords: cell-cell adhesion, embryonal carcinoma cells, inner cell mass, endoderm, embryonic ectoderm
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali I. U., Mautner V., Lanza R., Hynes R. O. Restoration of normal morphology, adhesion and cytoskeleton in transformed cells by addition of a transformation-sensitive surface protein. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K. Changes in cellular glycoproteins after transformation: identification of specific glycoproteins and antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B. Alteration in cell surface LETS protein during myogenesis. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Gallimore P. H., McDougall J. K. Correlation between tumor induction and the large external transformation sensitive protein on the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3570–3574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Gudor R. C., Sun T. T., Chen A. B., Mosesson M. W. Control of a cell surface major glycoprotein by epidermal growth factor. Science. 1977 Aug 19;197(4305):776–778. doi: 10.1126/science.302030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Maitland N., Gallimore P. H., McDougall J. K. Detection of the large external transformation-sensitive protein on some epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Apr;106(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley D. R. Cell surface proteins of NIL1 hamster fibroblasts labeled by a galactose oxidase, tritiated borohydride method. Cell. 1974 Oct;3(2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damjanov I., Solter D. Experimental teratoma. Curr Top Pathol. 1974;59:69–130. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65857-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N. M. A comparison of membrane proteins of normal and transformed cells by lactoperoxidase labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):489–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Cell surface proteins and malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;458(1):73–107. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Martin G. S., Shearer M., Critchley D. R., Epstein C. J. Viral transformation of rat myoblasts: effects on fusion and surface properties. Dev Biol. 1976 Jan;48(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E. Fibroblast surface antigen (SF): the external glycoprotein lost in proteolytic stimulation and maligant transfromation. Int J Cancer. 1976 Feb 15;17(2):261–269. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman J. M., Speers W. C., Swartzendruber D. E., Pierce G. B. Neoplastic differentiation: characteristics of cell lines derived from a murine teratocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Aug;84(1):13–27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Evans M. J. Differentiation of clonal lines of teratocarcinoma cells: formation of embryoid bodies in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas as a model system for the study of embryogenesis and neoplasia. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. F., Avner P., Gaillard J., Guenet J. L., Jakob H., Jacob F. Cell lines derived from teratocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4224–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E. Plasma membrane glycoprotein which mediates adhesion of fibroblasts to collagen. Nature. 1976 Aug 5;262(5568):497–500. doi: 10.1038/262497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A., Kuusela P., Linder E. Fibroblast surface antigen: a new serum protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 18;322(2):352–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solter D., Knowles B. B. Immunosurgery of mouse blastocyst. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5099–5102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. R., Smith R. E., Joklik W. K. Changes in membrane polypeptides that occur when chick embryo fibroblasts and NRK cells are transformed with avian sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):86–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng N. N., Bo Chen L. The role of surface proteins in cell proliferation as studied with thrombin and other proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):413–417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E., Linder E., Wartiovaara J., Keski-Oja J., Kuusela P., Saksela O. Fibroblast surface antigen (SF): molecular properties, distribution in vitro and in vivo, and altered expression in transformed cells. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(1):63–70. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E., Westermark B., Ponten J. A common cell-type specific surface antigen in cultured human glial cells and fibroblasts: loss in malignant cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):64–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartiovaara J., Leivo I., Virtanen I., Vaheri A., Graham C. F. Appearance of fibronectin during differentiation of mouse teratocarcinoma in vitro. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):355–356. doi: 10.1038/272355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Weston J. A. Isolation of a major cell surface glycoprotein from fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3492–3496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. Cell surface protein partially restores morphology, adhesiveness, and contact inhibition of movement to transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. The major cell surface glycoprotein of chick embryo fibroblasts is an agglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetter B. R., Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Effects of protease treatment on growth, morphology, adhesion, and cell surface proteins of secondary chick embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]