Abstract
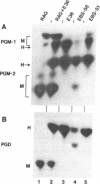
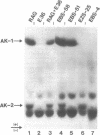
It is possible to generate interspecific somatic cell hybrids that preferentially segregate mouse chromosomes, thus making possible mapping of mouse genes. Therefore, comparison of the linkage relationships of homologous genes in man and mouse is now possible. Chinese hamster × mouse somatic cell hybrids segregating mouse chromosomes were tested for the expression of mouse enolase (ENO-1; EC 4.2.1.11, McKusick no. 17245), 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase [PGD; EC 1.1.1.44, McKusick no. 17220], phosphoglucomutase-2 (PGM-2; EC 2.7.5.1, McKusick no. 17190), and adenylate kinase-2 (AK-2; EC 2.7.4.3, McKusick no. 10302). In man, genes coding for the homologous forms of these enzymes have been assigned to the short arm of human chromosome 1. Analysis of 41 primary, independent, hybrid clones indicated that, in the mouse, ENO-1 and AK-2 are syntenic with PGD and PGM-2 and therefore can be assigned to mouse chromosome 4. In contrast, they were asyntenic with 21 other enzymes including mouse dipeptidase-1 (DIP-1, human PEP-C; EC 3.4.11.*, McKusick no. 17000) assigned to human chromosome arm 1q and mouse chromosome 1. Karyologic analysis confirmed this assignment. These data demonstrate that a large autosomal region (21 map units in the mouse and 51 map units in the human male) has been conserved in the evolution of mouse chromosome 4 and the short arm of human chromosome 1. Identification of such conserved regions will contribute to our understanding of the evolution of the mammalian genome and could suggest gene location by homology mapping.
Keywords: hybrid cells, comparative mapping, enzyme electrophoresis, mouse gene mapping
Full text
PDF
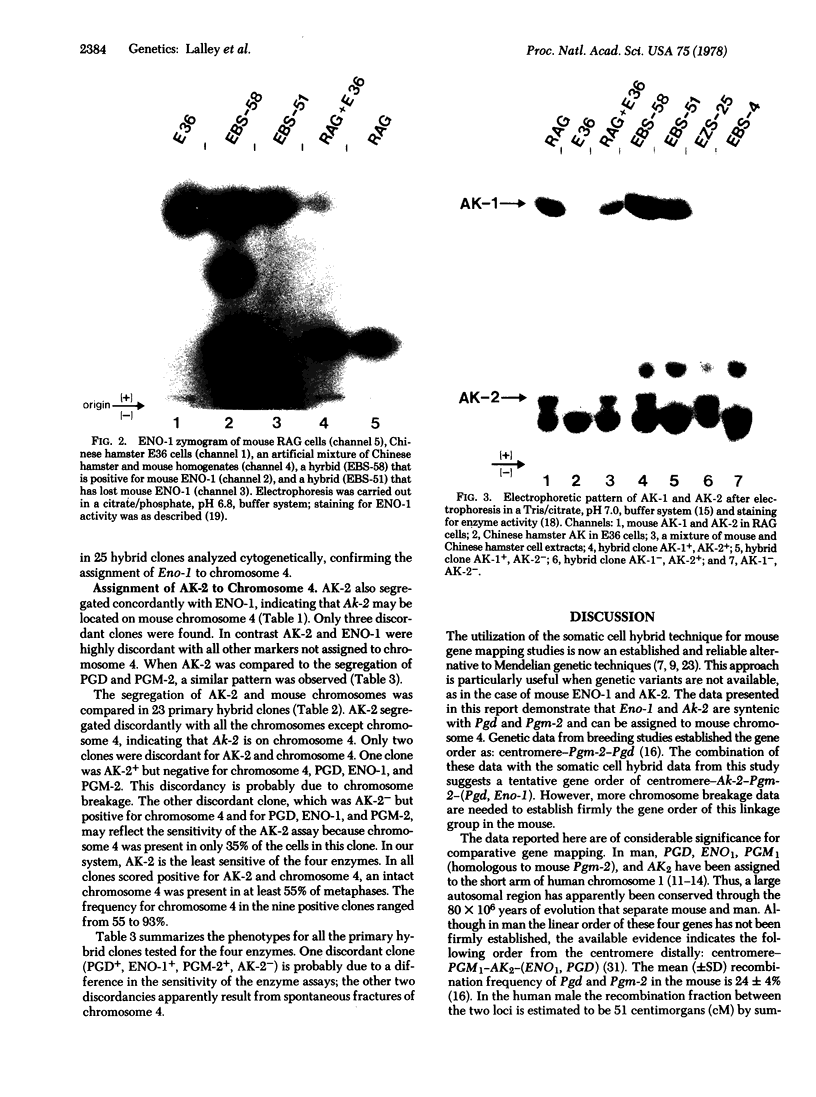
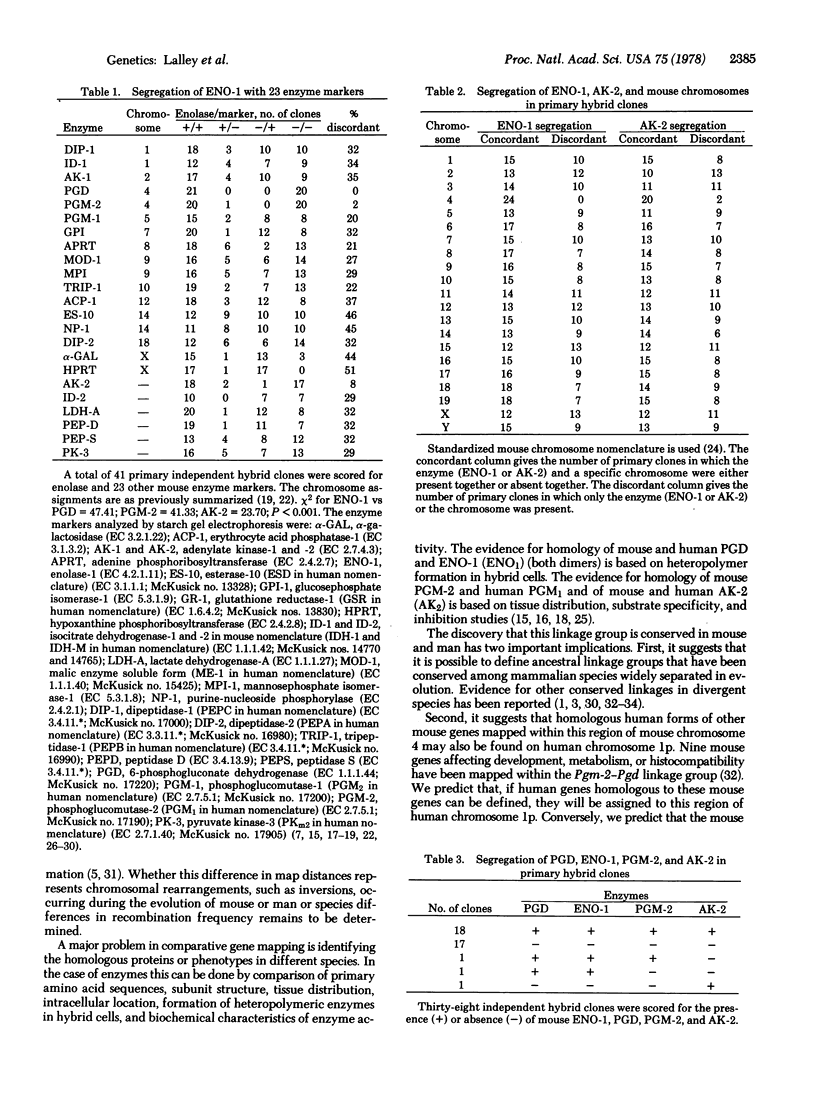

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruns G. A., Regina V. M. Adenylate kinase 2, a mitochondrial enzyme. Biochem Genet. 1977 Jun;15(5-6):477–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00520192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V. M. 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (PGD) genetics in the mouse: linkage with metabolically related enzyme loci. Biochem Genet. 1975 Dec;13(11-12):849–856. doi: 10.1007/BF00484415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V. M., Shows T. B. Somatic cell genetic evidence for X-chromosome linkage of three enzymes in the mouse. Nature. 1976 Feb 26;259(5545):665–667. doi: 10.1038/259665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Evidence for ancient tetraploidy and conservation of linkage groups in mammalian chromosomes. Nature. 1972 Aug 25;238(5365):455–457. doi: 10.1038/238455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas G. R., McAlpine P. J., Hamerton J. L. Regional localization of loci for human PGM and 6PGD on human chromosome one by use of hybrids of Chinese hamster-human somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2737–2740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finaz C., Van Cong N., Cochet C., Frézal J., de Grouchy J. Fifty-million-year evolution of chromosome 1 in the primates. Evidence from banding and gene mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;18(3):160–164. doi: 10.1159/000130760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Lalley P. A., Moss W., Ivy J., Minna J. D. Gene mapping in Mus musculus by interspecific cell hybridization: assignment of the genes for tripeptidase-1 to chromosome 10, dipeptidase-2 to chromosome 18, acid phosphatase-1 to chromosome 12, and adenylate kinase-1 to chromosome 2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(2-3):57–84. doi: 10.1159/000130799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Human gene mapping 3. Baltimore Conference (1975). Third International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping. Report of the committee on comparative mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):75–82. doi: 10.1159/000130558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Human gene mapping 3. Baltimore Conference (1975). Third International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping. Report of the committee on nomenclature. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):65–74. doi: 10.1159/000130557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongsma A., van Someren H., Westerveld A., Hagemeijer A., Pearson P. Localization of genes on human chromosomes by studies of human-Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Assignment of PGM3 to chromosome C6 and regional mapping of the PGD, PGM1 and pep-C genes on chromosome A1. Humangenetik. 1973 Dec 10;20(3):195–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00385730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of the genes for thymidine kinase and galactokinase to Mus musculus chromosome 11 and the preferential segregation of this chromosome in Chinese hamster/mouse somatic cell hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Mar;3(2):121–133. doi: 10.1007/BF01551809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C., Nichols E., Ruddle F. H. Gene linkage analysis in the mouse by somatic cell hybridization: assignment of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase to chromosome 8 and alpha-galactosidase to the X chromosome. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):371–382. doi: 10.1007/BF01538668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Brown J. A., Eddy R. L., Haley L. L., Byers M. G., Goggin A. P., Shows T. B. Human beta-glucuronidase: assignment of the structural gene to chromosome 7 using somatic cell hybrids. Biochem Genet. 1977 Apr;15(3-4):367–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00484467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Rattazzi M. C., Shows T. B. Human beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidases A and B: expression and linkage relationships in somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1569–1573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Truslove G. M. Electrophoretic heterogeneity of mouse erythrocyte peptidases. Biochem Genet. 1969 Oct;3(5):493–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00485609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A., Ruddle F. H. The status of the gene map of the human chromosomes. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):390–405. doi: 10.1126/science.850784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P., Doppert B. A., Hagemeijer A., Westerveld A. Proceedings: The human loci for phosphopyruvate hydratase and guanylate kinase are syntenic with the PGD-PGM1 linkage group in man-Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1974;13(1):130–131. doi: 10.1159/000130255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D., Coon H. G. Human times mouse hybrid cells segregating mouse chromosomes and isozymes. Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):401–404. doi: 10.1038/252401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D., Lalley P. A., Francke U. Comparative mapping using somatic cell hybrids. In Vitro. 1976 Nov;12(11):726–733. doi: 10.1007/BF02835447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D., Marshall T. H., Shaffer-Berman P. V. Chinese hamster X mouse hybrid cells segregating mouse chromosomes and isozymes. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):355–369. doi: 10.1007/BF01538667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D., Marshall T. H., Shaffer-Berman P. Gene mapping by somatic cell hybridization in species other than man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):422–426. doi: 10.1159/000130649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt M. N., Francke U. A system of nomenclature for band patterns of mouse chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1973;41(2):145–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00319691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. A review of enzyme polymorphism, linkage and electrophoretic conditions for mouse and somatic cell hybrids in starch gels. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Dec;21(12):1066–1081. doi: 10.1177/21.12.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. Ancient linkage groups and frozen accidents. Nature. 1973 Aug 3;244(5414):259–262. doi: 10.1038/244259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle F. H. Linkage analysis in man by somatic cell genetics. Nature. 1973 Mar 16;242(5394):165–169. doi: 10.1038/242165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., Povey S., Harris H. Activity of the "red cell" acid phosphatase locus in other tissues. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Jul;37(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb01812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. E., Povey S., Harris H. Adenylate kinases in man: evidence for a third locus. Ann Hum Genet. 1976 Jan;39(3):305–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1976.tb00134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack J. E., Sharp M. Comparative autosomal linkage in mammals: genetics of esterases in Mus musculus and Rattus norvegicus. Genetics. 1976 Apr;82(4):665–675. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.4.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]