Abstract
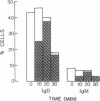
Restricted expression of immunoglobulin by a long-term B lymphoid cell line derived from a patient with X-linked agammaglobulinemia is reproted. The patient had peripheral blood B lymphocytes with surface IgD and IgM. Culture of the B cells in vitro with mitogens did not stimulate immunoglobulin secretion, although pokeweed mitogen stimulation resulted in the development of cytoplasmic IgD and IgM. The lymphoid cell line established from these B lymphocytes primarily bore surface IgD, with a small population of cells also bearing surface IgM. These cells also had cytoplasmic immunoglobulin, primarily IgD. The cell line did not have a cytoplasmic pool of immunoglobulin for export and did not secrete immunoglobulin. This B lymphoid cell line is an in vitro analogue of the arrest in differentiation of the patient's B lymphocytes. The IgD-bearing phenotype may represent a normal transitional stage in the differentiation of B lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ault K. A., Unanue E. R. Comparison of the two types of immunoglobulin-bearing lymphocytes in human blood with regard to capping and motility. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 May;7(3):394–404. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Kearney J. F., Lawton A. R., Abney E. R., Parkhouse R. M., Preud'homme J. L., Seligmann M. Generation of immunoglobulin class diversity in b cells: a discussion with emphasis on idg development. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Jun-Jul;127(3-4):573–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B., Kunkel H. G. Interaction of aggregated -globulin with B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):191–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Rosen F. S., Merler E. Identification and characterization of subpopulations of lymphocytes in human peripheral blood after fractionation on discontinuous gradients of albumin. The cellular defect in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1726–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI107354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Janossy G. Elicitation of selective T and B lymphocyte responses by cell surface binding ligands. Transplant Rev. 1972;11:87–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Shope T. C., Peterson W. D., Jr Epstein-barr virus-negative human malignant T-cell lines. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1070–1076. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin S. D., Hütteroth T. H., Lin P. K., Kennard J., Cleve H. Immunoglobulin expression of cells from human lymphoblastoid lines. II. Interrelationship among surface, cellular, and secreted immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):668–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Pontén J. Classification and biological nature of established human hematopoietic cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1975 Feb 15;15(2):321–341. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. Assay for Epstein-Barr virus based on stimulation of DNA synthesis in mixed leukocytes from human umbilical cord blood. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1065–1072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1065-1072.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S., Hug K., Faulk W. P., McCormick J. N., Gerber H. IgD on the surface of peripheral blood lymphocytes of the human newborn. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 4;242(118):155–157. doi: 10.1038/newbio242155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S., Hug K., Forni L., Pernis B. Immunoglobulin D as a lymphocyte receptor. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):965–972. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaber J. Immunoglobulin production by a human-mouse somatic cell hybrid. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Jul;93(2):343–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90459-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Immunoglobulin-receptors revisited. Science. 1975 Sep 19;189(4207):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1083069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Boxel J. A., Buell D. N. IgD on cell membranes of human lymphoid cell lines with multiple immunoglobulin classes. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):443–444. doi: 10.1038/251443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]