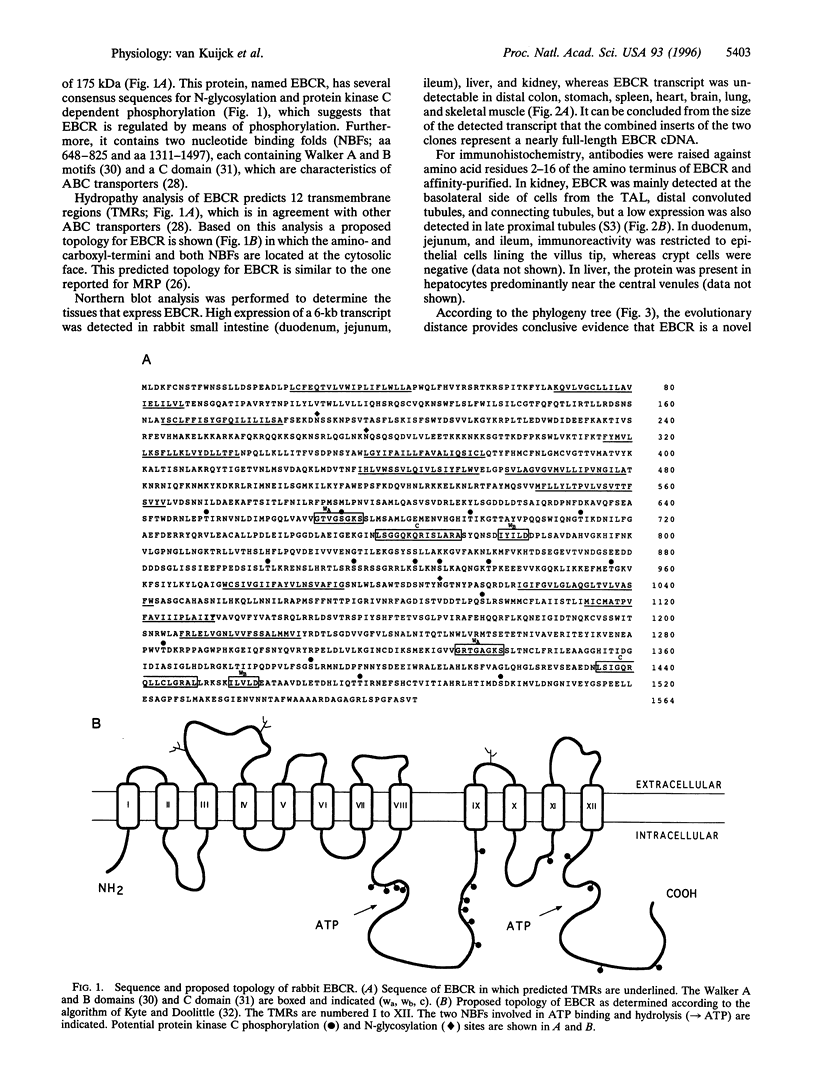
Abstract
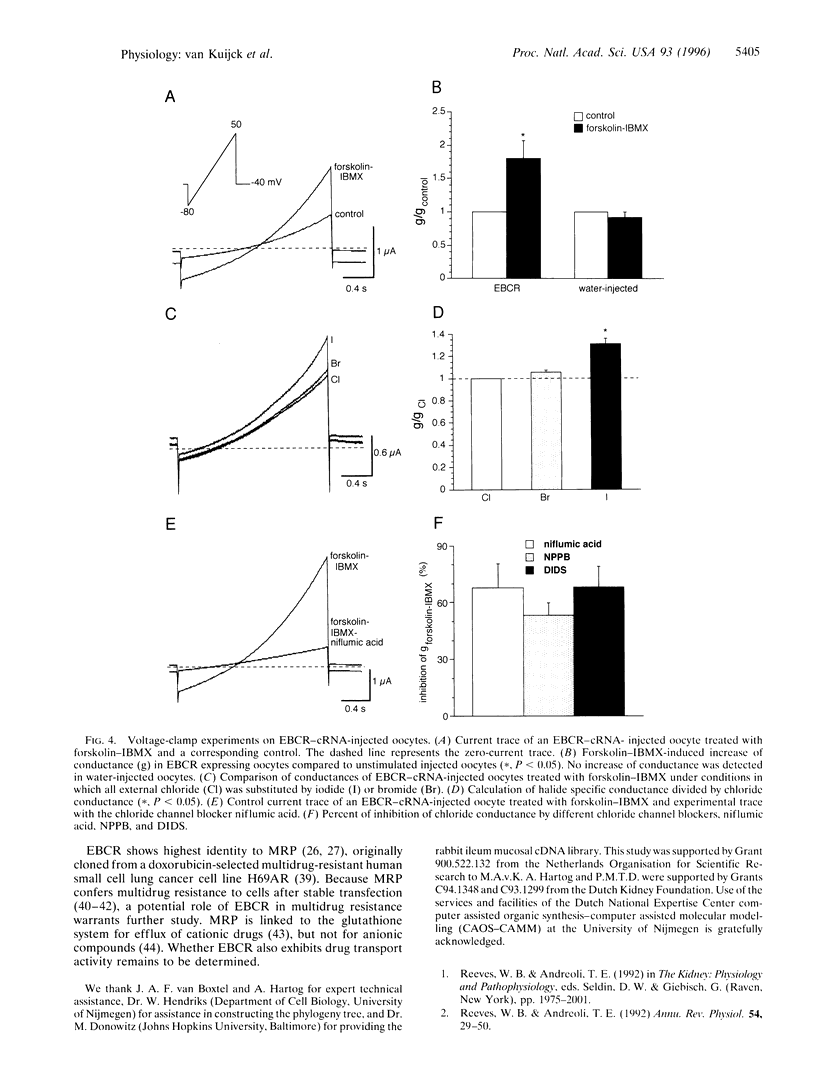
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is an ATP-regulated, cAMP-activated chloride channel located in the apical membrane of many epithelial secretory cells. Here we report cloning of a cAMP-activated epithelial basolateral chloride conductance regulator (EBCR) that appears to be a basolateral CFTR counterpart. This novel chloride channel or regulator shows 49% identity with multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) and 29% identity with CFTR. On expression in Xenopus oocytes, EBCR confers a cAMP-activated chloride conductance that is inhibited by the chloride channel blockers niflumic acid, 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamine)benzoic acid, and 4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid. Northern blot analysis reveals high expression in small intestine, kidney, and liver. In kidney, immunohistochemistry shows a conspicuous basolateral localization mainly in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop, distal convoluted tubules and to a lesser extent connecting tubules. These data suggest that in the kidney EBCR is involved in hormone-regulated chloride reabsorption.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi S., Uchida S., Ito H., Hata M., Hiroe M., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Two isoforms of a chloride channel predominantly expressed in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop and collecting ducts of rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17677–17683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. P., Gregory R. J., Thompson S., Souza D. W., Paul S., Mulligan R. C., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Demonstration that CFTR is a chloride channel by alteration of its anion selectivity. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.1712984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. PROSITE: a dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2013–2018. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barasch J., Kiss B., Prince A., Saiman L., Gruenert D., al-Awqati Q. Defective acidification of intracellular organelles in cystic fibrosis. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):70–73. doi: 10.1038/352070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear C. E., Li C. H., Kartner N., Bridges R. J., Jensen T. J., Ramjeesingh M., Riordan J. R. Purification and functional reconstitution of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):809–818. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindels R. J., Hartog A., Timmermans J., Van Os C. H. Active Ca2+ transport in primary cultures of rabbit kidney CCD: stimulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and PTH. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 2):F799–F807. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.5.F799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindels R. J., Timmermans J. A., Hartog A., Coers W., van Os C. H. Calbindin-D9k and parvalbumin are exclusively located along basolateral membranes in rat distal nephron. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Dec;2(6):1122–1129. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V261122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch A. E., Kavanaugh M. P., Varnum M. D., Adelman J. P., North R. A. Regulation by second messengers of the slowly activating, voltage-dependent potassium current expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:491–502. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang X. B., Tabcharani J. A., Hou Y. X., Jensen T. J., Kartner N., Alon N., Hanrahan J. W., Riordan J. R. Protein kinase A (PKA) still activates CFTR chloride channel after mutagenesis of all 10 PKA consensus phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11304–11311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. P., Bhardwaj G., Gerlach J. H., Mackie J. E., Grant C. E., Almquist K. C., Stewart A. J., Kurz E. U., Duncan A. M., Deeley R. G. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1650–1654. doi: 10.1126/science.1360704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. P., Deeley R. G. Multidrug resistance-associated protein: sequence correction. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):879–879. doi: 10.1126/science.8098549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen P. M., Croes H., van Aubel R. A., Ginsel L. A., van Os C. H. Water channels encoded by mutant aquaporin-2 genes in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus are impaired in their cellular routing. J Clin Invest. 1995 May;95(5):2291–2296. doi: 10.1172/JCI117920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen P. M., Verdijk M. A., Knoers N. V., Wieringa B., Monnens L. A., van Os C. H., van Oost B. A. Requirement of human renal water channel aquaporin-2 for vasopressin-dependent concentration of urine. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8140421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller N., Broxterman H. J., Währer D. C., Pinedo H. M. ATP-dependent efflux of calcein by the multidrug resistance protein (MRP): no inhibition by intracellular glutathione depletion. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jul 17;368(2):385–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00677-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong P., Jentsch T. J. Molecular basis of epithelial Cl channels. J Membr Biol. 1995 Apr;144(3):189–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00236832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. E., Valdimarsson G., Hipfner D. R., Almquist K. C., Cole S. P., Deeley R. G. Overexpression of multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP) increases resistance to natural product drugs. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 15;54(2):357–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinamard R., Chraïbi A., Teulon J. A small-conductance Cl- channel in the mouse thick ascending limb that is activated by ATP and protein kinase A. J Physiol. 1995 May 15;485(Pt 1):97–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Günther W., Pusch M., Schwappach B. Properties of voltage-gated chloride channels of the ClC gene family. J Physiol. 1995 Jan;482:19S–25S. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartner N., Augustinas O., Jensen T. J., Naismith A. L., Riordan J. R. Mislocalization of delta F508 CFTR in cystic fibrosis sweat gland. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):321–327. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieferle S., Fong P., Bens M., Vandewalle A., Jentsch T. J. Two highly homologous members of the ClC chloride channel family in both rat and human kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6943–6947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruh G. D., Chan A., Myers K., Gaughan K., Miki T., Aaronson S. A. Expression complementary DNA library transfer establishes mrp as a multidrug resistance gene. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1649–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Muchmore A. Tamm-Horsfall protein--uromodulin (1950-1990). Kidney Int. 1990 Jun;37(6):1395–1401. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirski S. E., Gerlach J. H., Cole S. P. Multidrug resistance in a human small cell lung cancer cell line selected in adriamycin. Cancer Res. 1987 May 15;47(10):2594–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulais M., Teulon J. cAMP-activated chloride channel in the basolateral membrane of the thick ascending limb of the mouse kidney. J Membr Biol. 1990 Feb;113(3):253–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01870076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. B., Andreoli T. E. Renal epithelial chloride channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:29–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. P., Gregory R. J., Anderson M. P., Manavalan P., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Effect of deleting the R domain on CFTR-generated chloride channels. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):205–207. doi: 10.1126/science.1712985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiebert E. M., Egan M. E., Hwang T. H., Fulmer S. B., Allen S. S., Cutting G. R., Guggino W. B. CFTR regulates outwardly rectifying chloride channels through an autocrine mechanism involving ATP. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibert F. S., Tabcharani J. A., Chang X. B., Dulhanty A. M., Mathews C., Hanrahan J. W., Riordan J. R. cAMP-dependent protein kinase-mediated phosphorylation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator residue Ser-753 and its role in channel activation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 3;270(5):2158–2162. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.2158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutts M. J., Canessa C. M., Olsen J. C., Hamrick M., Cohn J. A., Rossier B. C., Boucher R. C. CFTR as a cAMP-dependent regulator of sodium channels. Science. 1995 Aug 11;269(5225):847–850. doi: 10.1126/science.7543698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Sasaki S., Furukawa T., Hiraoka M., Imai T., Hirata Y., Marumo F. Molecular cloning of a chloride channel that is regulated by dehydration and expressed predominantly in kidney medulla. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3821–3824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters C. J., Reeves W. B., Andreoli T. E. Cl- channels in basolateral renal medullary vesicles: V. Comparison of basolateral mTALH Cl- channels with apical Cl- channels from jejunum and trachea. J Membr Biol. 1992 May;128(1):27–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00231868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A. S., Hebert S. C., Brenner B. M., Lytton J. Molecular characterization and nephron distribution of a family of transcripts encoding the pore-forming subunit of Ca2+ channels in the kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10494–10498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman G. J., Flens M. J., van Leusden M. R., de Haas M., Mülder H. S., Lankelma J., Pinedo H. M., Scheper R. J., Baas F., Broxterman H. J. The human multidrug resistance-associated protein MRP is a plasma membrane drug-efflux pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8822–8826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman G. J., Lankelma J., van Tellingen O., Beijnen J., Dekker H., Paulusma C., Oude Elferink R. P., Baas F., Borst P. Role of glutathione in the export of compounds from cells by the multidrug-resistance-associated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7690–7694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]