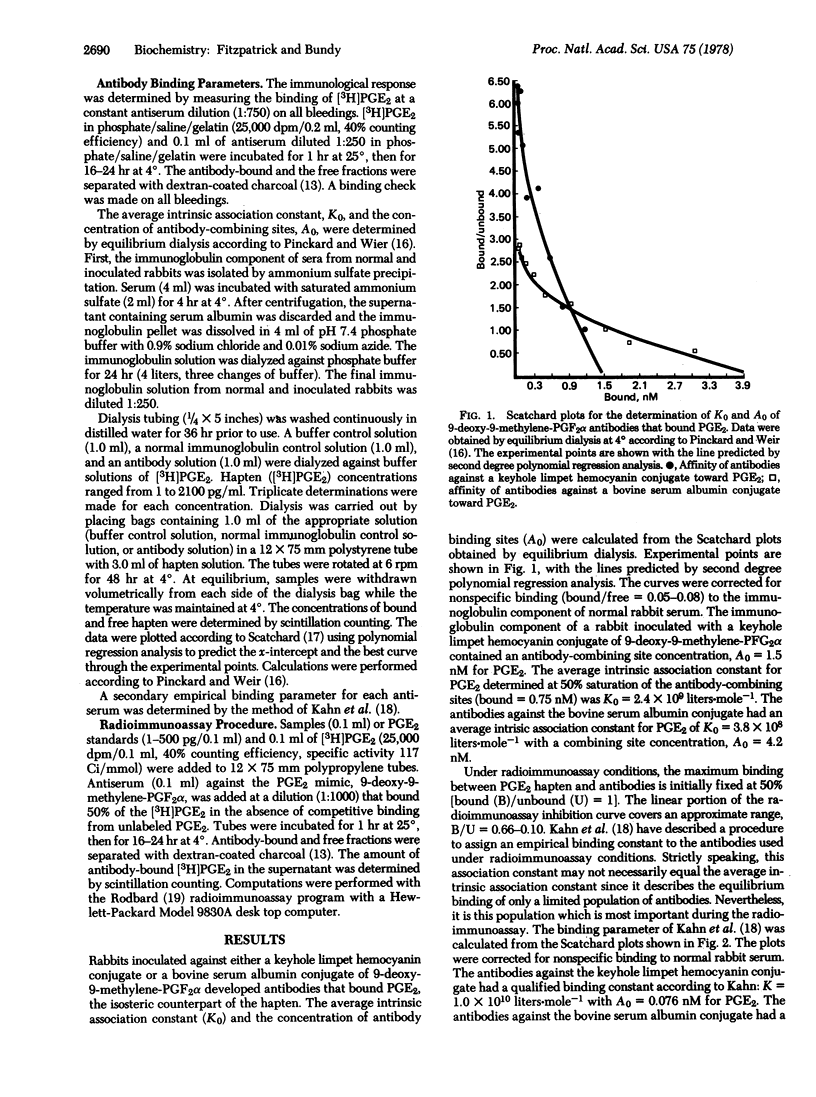
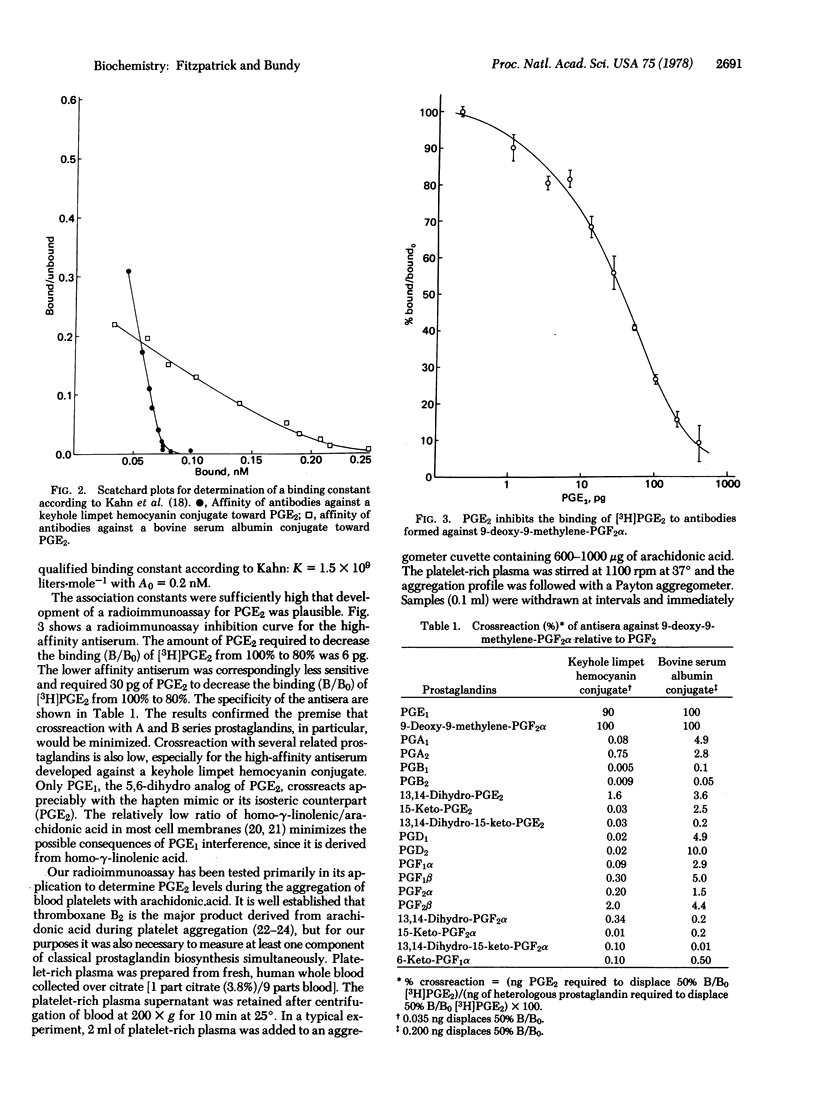
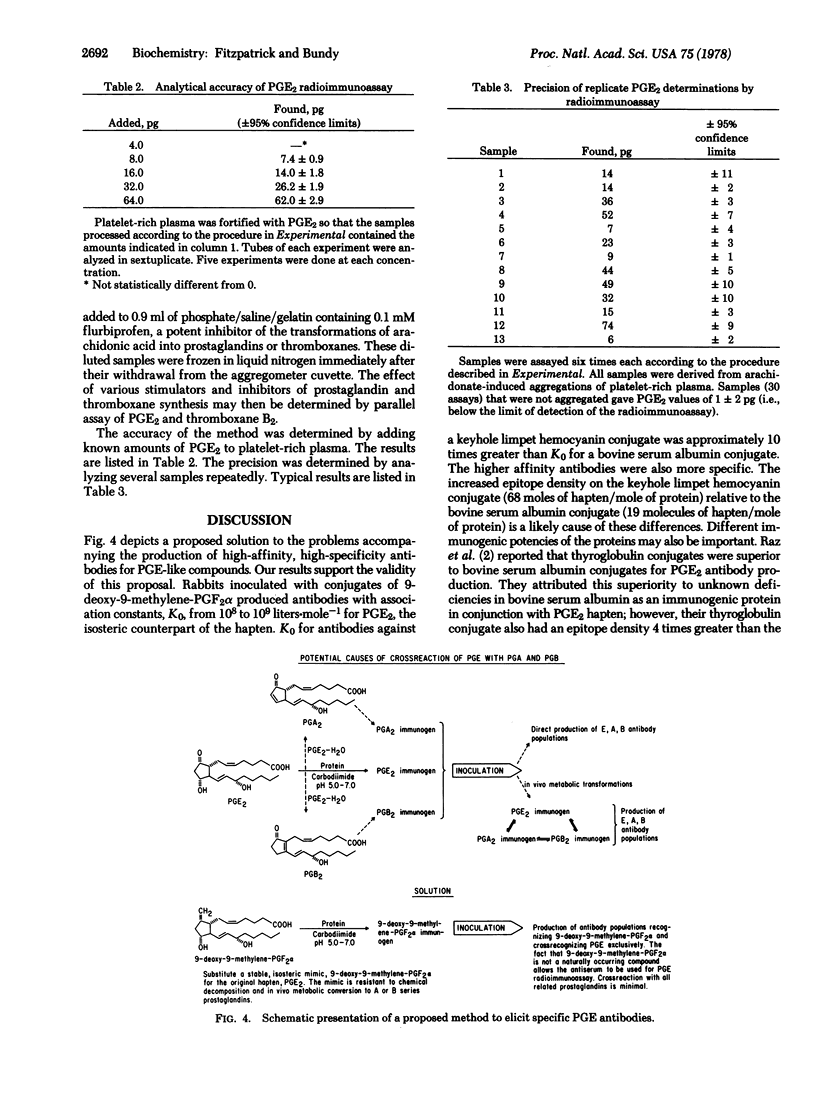
Abstract
Antibodies that recognized the prostaglandin (PG) E structure were elicited from rabbits. 9-Deoxy-9-methylene-PGF2alpha, a stable isosteric mimic of PGE2, was conjugated to two different protein immunogens and the immune response system was duped into producing antibodies with poor recognition for prostaglandins other than the hapten mimic (9-deoxy-9-methylene-PGF2alpha) and its isosteric counterparts (PGE1 and PGE2). With this procedure, crossreaction that would ordinarily arise from the chemical or metabolic instability of an authentic PGE2 immunogen was avoided. Antibodies raised against a keyhole limpet hemocyanin conjugate of 9-deoxy-9-methylene-PGF2alpha had an average intrinsic association constant, Ko = 2.6 X 10(9) liters.mole-1, for PGE2. Crossreaction was low for a number of related prostaglandins, and a sensitive radioimmunoassay procedure with a detection limit of 6 pg was developed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauminger S., Zor U., Lindner H. R. Radioimmunological assay of prostaglandin synthetase activity. Prostaglandins. 1973 Sep;4(3):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(73)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Leyssac P. P. A specific radioimmunoassay for PGE2 using an antibody with high specificity and a sephadex LH-20 microcolumn for the separation of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins. 1976 Feb;11(2):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray F., Charbonnel B., Maclouf J. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandins Falpha, E1 and E2 in human plasma. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul 29;5(4):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Thromboxanes: a new group of biologically active compounds derived from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe B. M., Behrman H. R., Parker C. W. Radioimmunoassay measurement of prostaglandins E, A, and F in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):398–405. doi: 10.1172/JCI107196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe B. M., Smith J. W., Newton W. T., Parker C. W. Radioimmunoassay for prostaglandins. Science. 1971 Feb 5;171(3970):494–496. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3970.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobke A., Peskar B. A., Peskar B. M. On the specificity of antisera against prostaglandins A2 and E2. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):192–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn D., Andrieu J. M., Dray F. Evaluation of some binding parameters of hapten-antibody complexes using dextran-coated charcoal to separate the bound and free fractions. Immunochemistry. 1974 Jul;11(7):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Gjtierrez Cernosek R. M., Van Vunakis H. Specificities of prostaglandins B 1 , F 1 , and F 2 antigen-antibody reactions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6782–6785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclouf J., Andrieu J. M., Dray F. Validity of PG E1 radioimmunoassay by using PG E1 antisera with differential binding parameters. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmsten C., Granström E., Samuelsson B. Cyclic AMP inhibits synthesis of prostaglandin endoperoxide (PGG2) in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Ullman H. L., Safier L. B. Lipid composition of subcellular particles of human blood platelets. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzi E. M., Stylos W. A. The stimultaneous use of two prostaglandin E radioimmunoassays employing two antisera of differing specificity. I. Determination of prostaglandin content in sera and culture medium of simian virus 40 transformed cells. Prostaglandins. 1974 Oct 10;8(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Bridson W., Rayford P. L. Rapid calculation of radioimmunoassay results. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Nov;74(5):770–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachman H. K., Edelstein S. J. Ultracentrifuge studies with absorption optics. IV. Molecular weight determinations at the microgram level. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2681–2705. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela M. Antigenicity: some molecular aspects. Science. 1969 Dec 12;166(3911):1365–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3911.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stylos W., Howard L., Ritzi E., Skarnes R. The preparation and characterization of prostaglandin E1 antiserum. Prostaglandins. 1974 Apr 10;6(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. C., Burke G. Antigenic activity of prostaglandins: specificities of prostaglandins E1, A1 and F2alpha antigen-antibody reactions. Prostaglandins. 1972 Jul;2(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman R. M., Caldwell B. V., Speroff L., Behrman H. R. Radioimmunoassay of the A prostaglandins. Prostaglandins. 1972 Jul;2(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


