Abstract
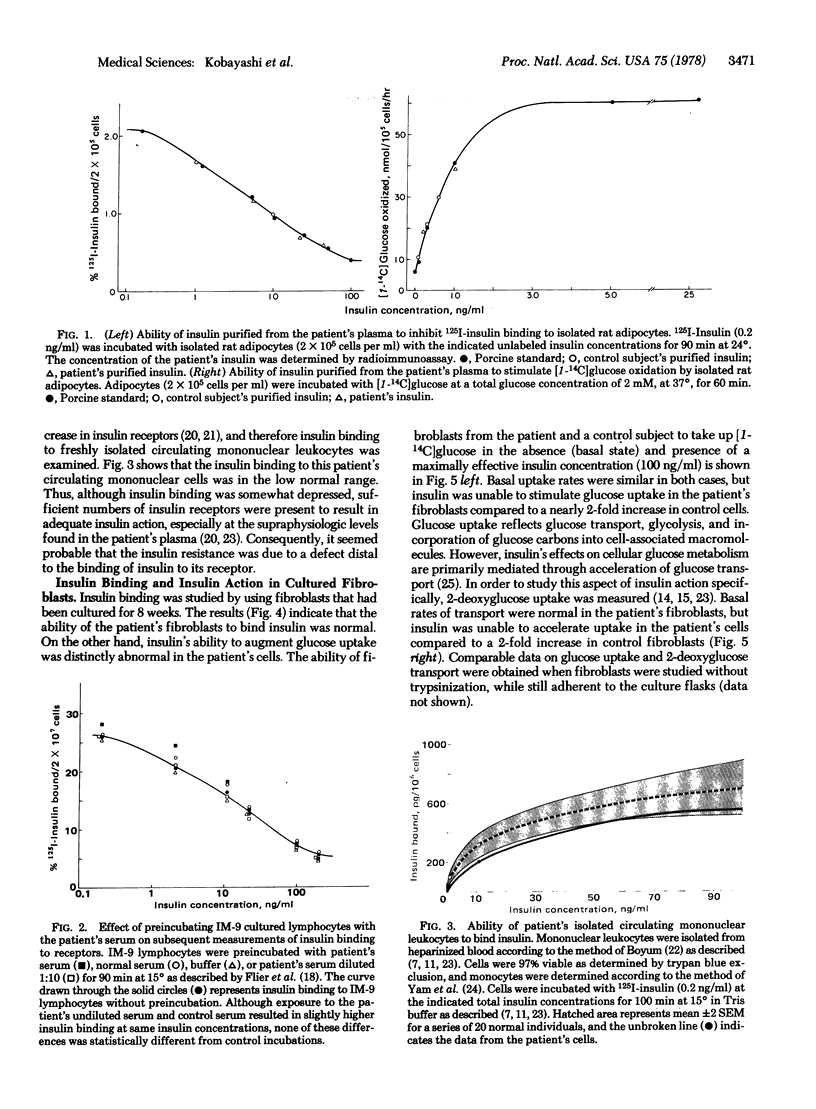
We have studied a 2-year-old girl with acanthosis nigricans, glucose intolerance, marked hyperinsulinemia, and somatic features characteristic of the leprechaunism syndrome. Circulating plasma insulin levels were increased up to 50-fold and the patient showed a blunted hypoglycemic response to an injection of exogenous insulin (0.2 units/kg), indicating the presence of severe insulin resistance. Insulin purified from the patient's plasma was normal on the basis of chromatographic, electrophoretic, and immunologic criteria. Furthermore, the purified insulin competed effectively with 125I-labeled insulin for binding to insulin receptors on cultured IM-9 lymphocytes and rat fat cells and also exhibited normal biological potency when tested on rat fat cells. Anti-insulin receptor and anti-insulin antibodies were not detected in the patient's plasma, and plasma levels of glucagon, growth hormone, and cortisol were normal. Insulin binding to the patient's circulating monuclear leukocytes was only slightly depressed into the low normal range and could not account for the severe insulin resistance. Studies on the patient's fibroblasts revealed normal levels of insulin receptors but a total absence of insulin's ability to accelerate glucose transport. Because rates of glucose transport and metabolism were normal in the basal state in the absence of insulin, we conclude that this patient's insulin resistance is due to an inherited cellular defect in the coupling mechanism between occupied insulin receptors and the plasma membrane glucose transport system.
Keywords: receptor, glucose transport, fibroblasts
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Gordon L. P., Dutton R. V., Rosenberg H. S., Rudolph A. J. Leprechaunism (Donohue's syndrome) in a low birth weight infant. South Med J. 1977 Aug;70(8):998–1001. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197708000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akanuma Y., Kuzuya T., Hayashi M., Ide T., Kuzuya N. Immunological reactivity of insulin to sepharose coupled with insulin-antibody---its use for the extraction of insulin from serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 12;38(5):947–953. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90813-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Gorden P., Roth J., Kahn C. R., De Meyts P. Fluctuations in the affinity and concentration of insulin receptors on circulating monocytes of obese patients: effects of starvation, refeeding, and dieting. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI108565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. A one-stage procedure for isolation of granulocytes and lymphocytes from human blood. General sedimentation properties of white blood cells in a 1g gravity field. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:51–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONOHUE W. L., UCHIDA I. Leprechaunism: a euphemism for a rare familial disorder. J Pediatr. 1954 Nov;45(5):505–519. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(54)80113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekaban A. Metabolic and chromosomal studies in leprechaunism. Arch Dis Child. 1965 Dec;40(214):632–636. doi: 10.1136/adc.40.214.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Bar R. S. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.170678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J., Baldwin D., Pugh W., Rubenstein A. H. Equilibrium binding assay and kinetic characterization of insulin antibodies. Diabetes. 1978 Jun;27(6):653–660. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.6.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Flier J. S., Bar R. S., Archer J. A., Gorden P., Martin M. M., Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Effects of fasting on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation in isolated rat adipocytes: relationships between insulin receptors and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1450–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI108601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Decreased insulin binding to lymphocytes from diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1172/JCI107878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Insulin binding in diabetes. Relationships with plasma insulin levels and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes. 1977 Jul;26(7):680–688. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.7.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. The effects of spontaneous obesity on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation of isolated rat adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):842–851. doi: 10.1172/JCI108360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. The insulin receptor: its role in insulin resistance of obesity and diabetes. Diabetes. 1976 Dec;25(12):1154–1162. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.12.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Reaven G. M. The human lymphocyte: a model for the study of insulin-receptor interaction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):554–560. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
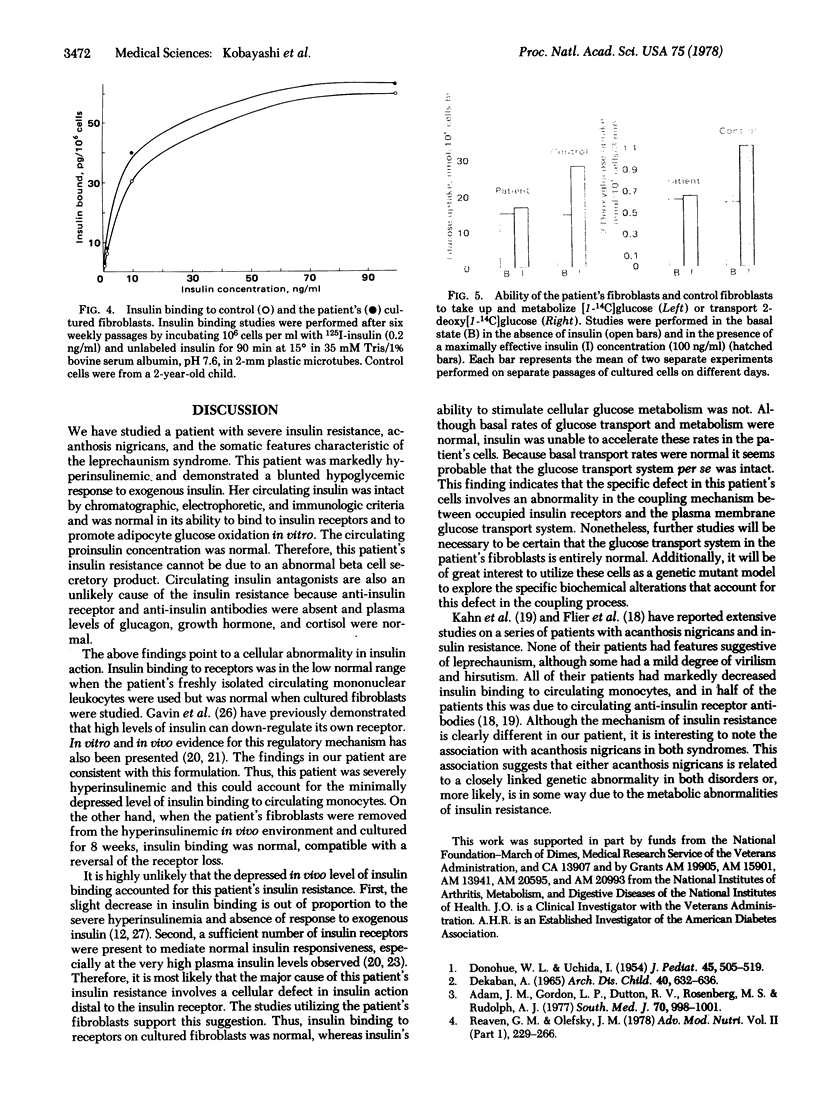
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M. Insulin receptors in cultured human fibroblasts. Diabetes. 1976 Apr;25(4):250–255. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.4.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom A. L., Starr J. I., Juhn D., Rubenstein A. H. Serum proinsulin in children and adolescents with chemical diabetes. Diabetes. 1975 Aug;24(8):753–757. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.8.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Kahn C. R., Lesniak M. A., Gorden P., De Meyts P., Megyesi K., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Soll A. H., Freychet P. Receptors for insulin, NSILA-s, and growth hormone: applications to disease states in man. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1975;31:95–139. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571131-9.50007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WICK A. N., DRURY D. R., NAKADA H. I., WOLFE J. B. Localization of the primary metabolic block produced by 2-deoxyglucose. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):963–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]