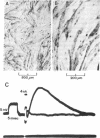
Abstract
The effects of continuous exposure to carbamylcholine (CbCho) on regulation and stabilization of acetylcholine receptors (AcChoR) were studied in cell cultures of G8, a continuous mouse muscle cell line. Exposure of cultures to 10-100 μM CbCho for 24-48 hr produced a 30-50% reduction in 125I-labeled α-bungarotoxin binding. CbCho was not found to alter cell morphology, protein metabolism, or amino acid incorporation. Electrophysiological experiments demonstrated a 75% reduction in the maximum sensitivity of the myotubes to iontophoretic application of acetylcholine (AcCho). The reduction in AcCho sensitivity appeared to represent a true loss of functional receptors because there were no changes in the passive electrical properties of the cells or in the AcCho reversal potential and because receptor desensitization appeared not to be involved. Tetrodotoxin had no effect on receptor levels, either alone or in combination with CbCho. Receptor degradation in control cells could be described kinetically as a first-order process with a half-time of 19.2 hr; turnover rate in receptors remaining after prolonged exposure to CbCho was indistinguishable from that in control cells. We conclude that a receptor-active ligand can exert negative control over AcChoR levels and that prolonged exposure to an AcCho analog is not sufficient to induce a stable population of receptors in these cells.
Keywords: neurotrophic relations, carbamylcholine, α-bungarotoxin binding, turnover kinetics
Full text
PDF
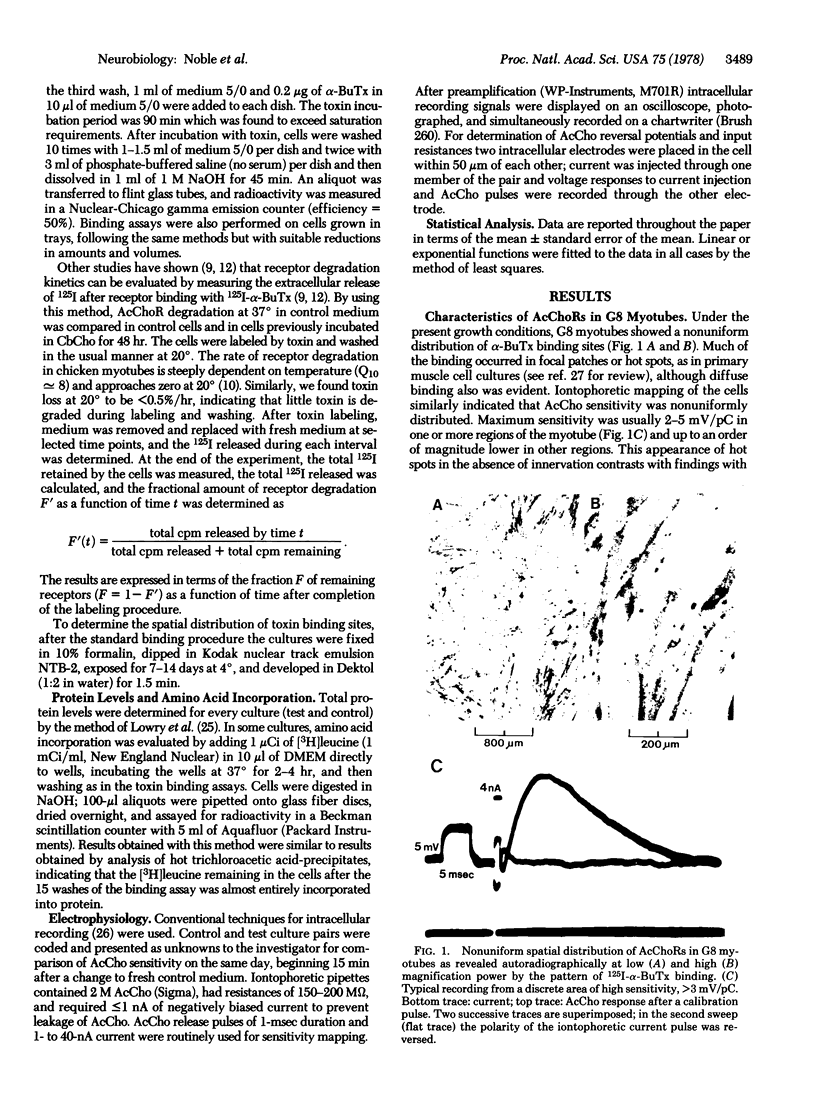
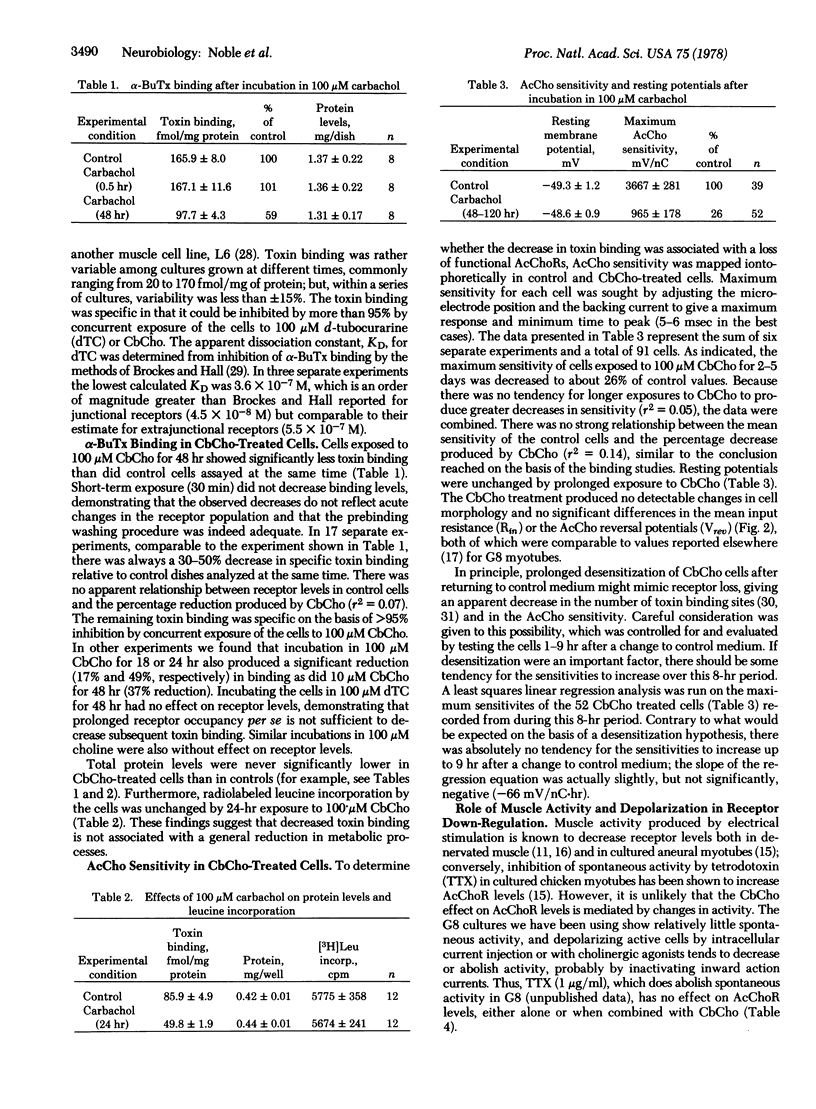
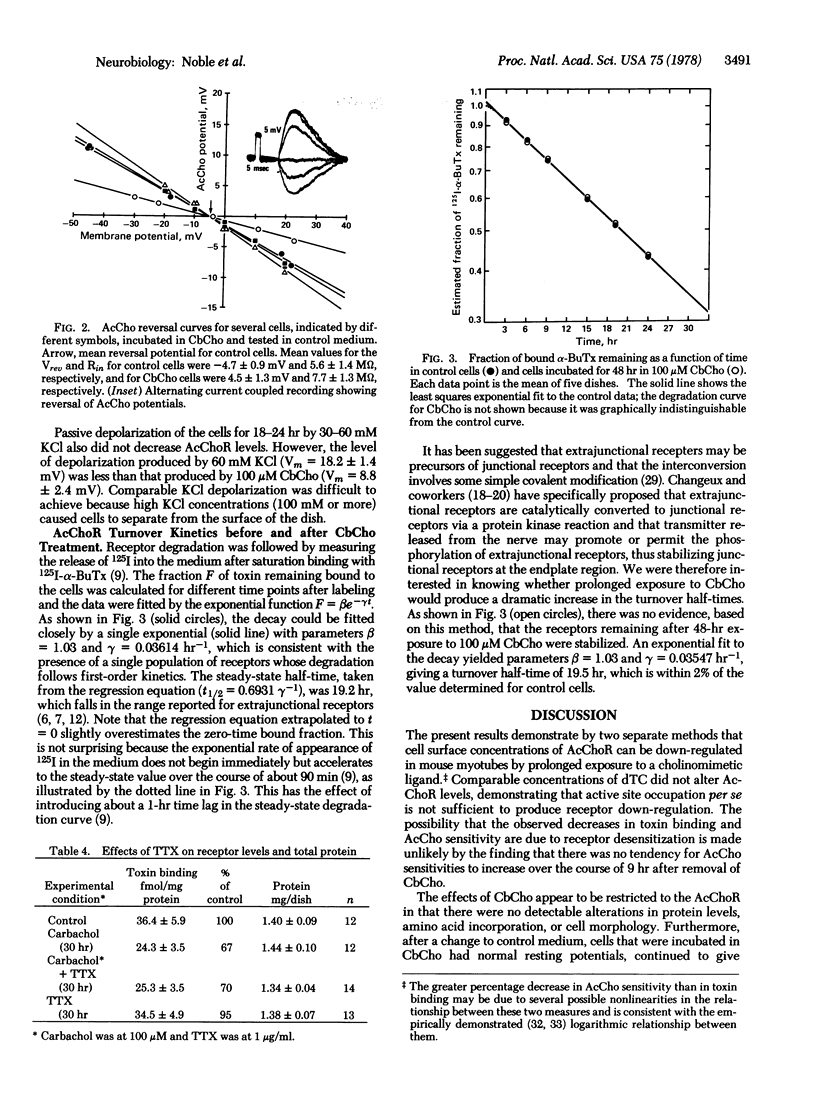

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel S. H., Anwyl R., McAdams M. W., Elias S. Accelerated degradation of acetylcholine receptor from cultured rat myotubes with myasthenia gravis sera and globulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekoff A., Betz W. J. Acetylcholine hot spots: development on myotubes cultured from aneural limb buds. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):915–917. doi: 10.1126/science.948754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Hall Z. W. Increased extrajunctional acetylcholine sensitivity produced by chronic acetylcholine sensitivity produced by chronic post-synaptic neuromuscular blockade. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(3):659–676. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Hall Z. W. Loss of alpha-bungarotoxin from junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors in rat diaphragm muscle in vivo and in organ culture. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):771–789. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Kelly R. B., Sargent P. B., Williamson P., Hall Z. W. Binding of -bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors in mammalian muscle (snake venom-denervated muscle-neonatal muscle-rat diaphragm-SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Hall Z. W. Acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated rat diaphragm muscle. II. Comparison of junctional and extrajunctional receptors. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2100–2106. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Chen T. F., Chuang S. T. N,O-di and N,N,O-tri ( 3 H) acetyl -bungarotoxins as specific labelling agents of cholinergic receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;47(1):147–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Huang M. C. Turnover of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors of the rat diaphragm. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):643–644. doi: 10.1038/253643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Danchin A. Selective stabilisation of developing synapses as a mechanism for the specification of neuronal networks. Nature. 1976 Dec 23;264(5588):705–712. doi: 10.1038/264705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiung Chang C., Jai Su M., Hsien Tung L. Appearance of new acetylcholine receptors on the baby chick biventer cervicis and denervated rat diaphragm muscles after blockade with alpha-bungarotoxin. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):449–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian C. N., Nelson P. G., Peacock J., Nirenberg M. Synapse formation between two clonal cell lines. Science. 1977 May 27;196(4293):995–998. doi: 10.1126/science.193191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D. Mechanisms of drug action at the voluntary muscle endplate. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:307–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptor turnover in membranes of developing muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1975 May;65(2):335–358. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Fambrough D. M. Synthesis of acetylcholine receptors by cultured chick myotubes and denervated mouse extensor digitorum longus muscles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):161–164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden W. F., Harvey A. L. The effect of receptor desensitization on the action of alpha-bungaro-toxin on cultured skeletal muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Jul;51(3):456–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb10683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt J. K., Ishikawa K., Lisbin S. J., Mori J. Neurotrophic effects on passive electrical properties of cultured chick skeletal muscle. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 25;110(1):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt J. K., Ishikawa K., Mori J., Shimabukuro Y. Neurotrophic effects on the electrical properties of cultured muscle produced by conditioned medium from spinal cord explants. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 10;128(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90991-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptors. Revised estimates of extrajunctional receptor density in denervated rat diaphragm. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Oct;64(4):468–472. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.4.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptors. Distribution and extrajunctional density in rat diaphragm after denervation correlated with acetylcholine sensitivity. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Sep;60(3):248–262. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey A. L., Dryden W. F. Depolarization, desensitization and the effects of tubocurarine and neostigmine in cultured skeletal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Jun;27(1):5–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S., Bevan S., Kullberg R., Lindstrom J., Rice J. Modulation of acetylcholine receptor by antibody against the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3090–3094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao I., Drachman D. B. Myasthenic immunoglobulin accelerates acetylcholine receptor degradation. Science. 1977 Apr 29;196(4289):527–529. doi: 10.1126/science.850793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolata G. B. Hormone receptors: how are they regulated? Science. 1977 May 13;196(4291):747–800. doi: 10.1126/science.196.4291.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang S. L., Kau S. T., Luh S. H. Chromatographic separation of the venom of Bungarus multicinctus and characterization of its components. J Chromatogr. 1972 Oct 5;72(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(72)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. Junctional and extra-junctional acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:24–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Changeux J. P., Gros F. Acetylcholine receptor degradation measured by pulse chase labelling. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):74–76. doi: 10.1038/264074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sobel A., Changeux J. P., Gros F. Synthesis of acetylcholine receptor during differentiation of cultured embryonic muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4028–4032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Peacock J. H., Amano T., Minna J. Electrogenesis in mouse neuroblastoma cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Jun;77(3):337–352. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainberg A., Burstein M. Decrease of acetylcholine receptor synthesis in muscle cultures by electrical stimulation. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):368–369. doi: 10.1038/264368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach J. H., Harris A. J., Patrick J., Schubert D., Heinemann S. Nerve-muscle interaction in vitro. Role of acetylcholine. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Sep;62(3):255–270. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Changeux J. P. Presence of two forms of acetylcholine receptor with different isoelectric points in the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus and their catalytic interconversion in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 1;67(3):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80543-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Sobel A., Changeux J. P. In vitro phosphorylation of the acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):540–542. doi: 10.1038/267540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins G. M. The metabolic code. Science. 1975 Sep 5;189(4205):760–763. doi: 10.1126/science.169570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]