Abstract
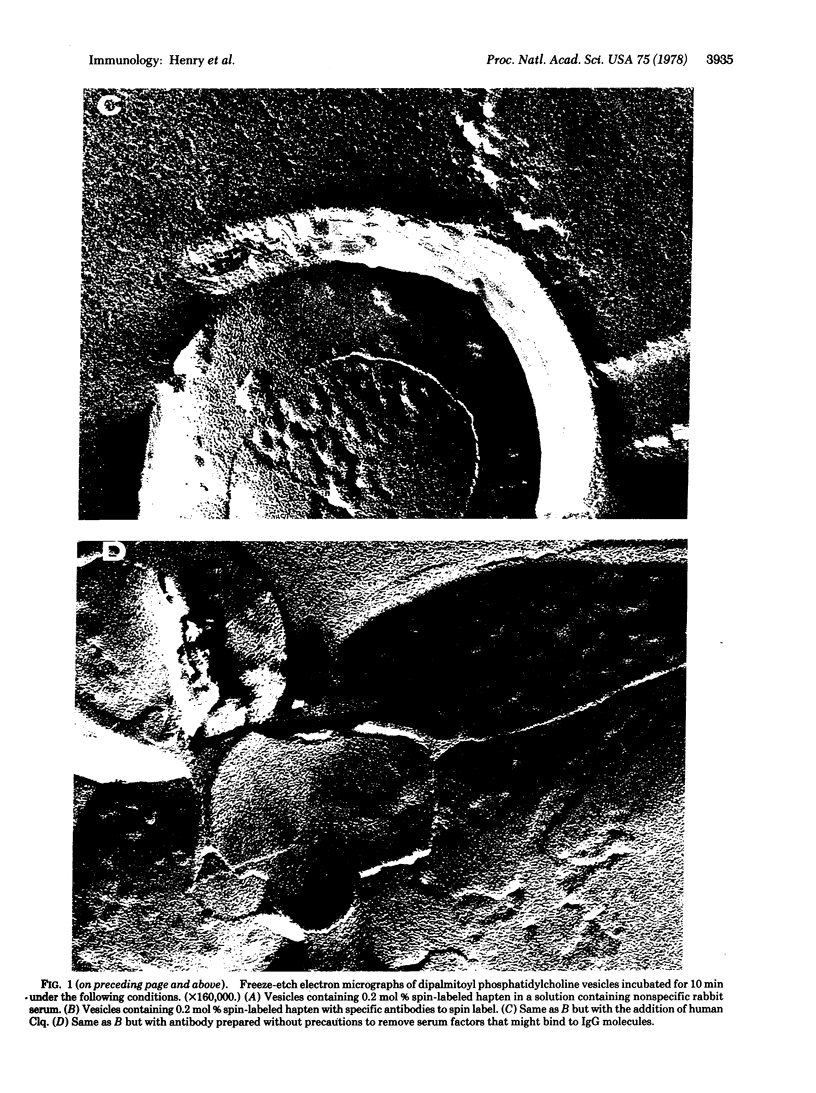
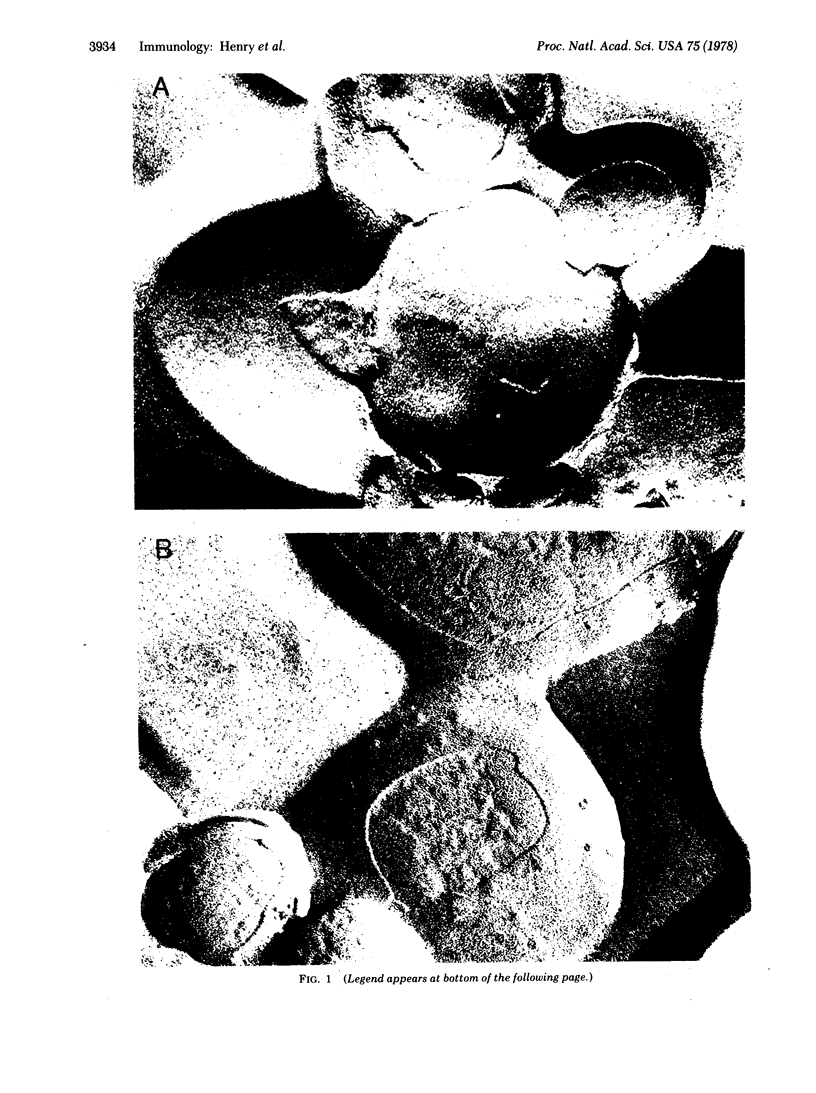
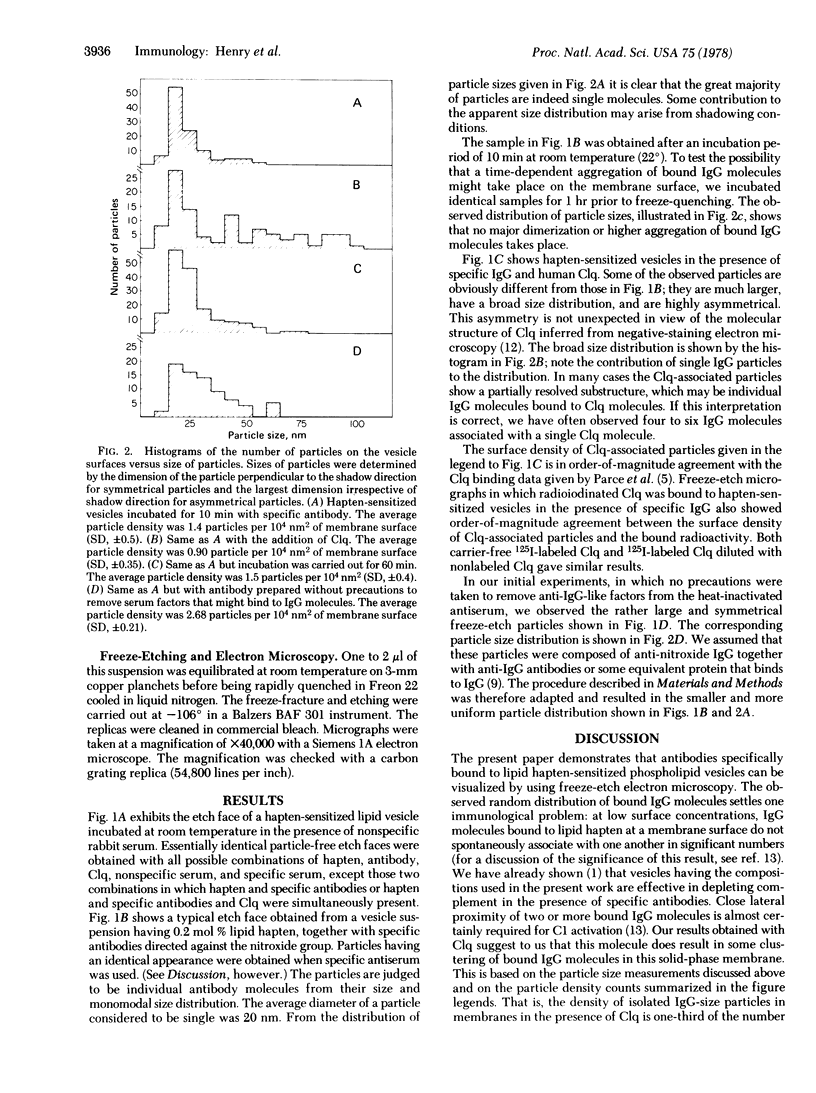
Specific IgG antibodies directed against the spin-label nitroxide group present as a lipid hapten in single-compartment lipid vesicles have been visualized by using freeze-etch electron microscopy. Individual "particles" with diameters of the order of 20 nm are identified as single IgG molecules bound to lipid hapten. No significant aggregation of these IgG molecules was observed over a period of 1 hr in a dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine vesicle at 22 degrees. Binding of the human complement component C1q results in the formation of large (approximately 50-100 nm) asymmetric particles having a partially resolved substructure that may arise from individual IgG molecules bound to the membranes as well as to C1q. The binding of C1q appears to result in a clustering of membrane-bound IgG molecules. Samples containing a serum factor (perhaps anti-IgG antibodies) exhibit some IgG clustering distinct from that produced by Clq.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assimeh S. N., Bing D. H., Painter R. H. A simple method for the isolation of the subcomponents of the first component of complement by affinity chromatography. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):225–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Chiao J. W., Bernstein D., Krause R. M. Homogenous rabbit 7S anti-IgG with antibody specificity for peptidoglycan. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1184–1193. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brûlet P., McConnell H. M. Lateral hapten mobility and immunochemistry of model membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2977–2981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brûlet P., McConnell H. M. Structural and dynamical aspects of membrane immunochemistry using model membranes. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1209–1217. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D., Bangham A. D. Large volume liposomes by an ether vaporization method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 7;443(3):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphires G. M., McConnell H. M. Antigen mobility in membranes and complement-medical immune attack. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2483–2487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries G. M., McConnell H. M. Membrane-controlled depletion of complement activity by spin-label-specific IgM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobel H. R., Villiger W., Isliker H. Chemical analysis and electron microscopy studies of human C1q prepared by different methods. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Jan;5(1):78–82. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parce J. W., Henry N., McConnell H. M. Specific antibody-dependent binding of complement component C1q to hapten-sensitized lipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1515–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. The eleventh Hopkins Memorial Lecture: The biochemistry of complement. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(6):1659–1674. doi: 10.1042/bst0051659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., McConnell H. M. Surface areas of lipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):837–840. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemasu K., Stroud R. M. Clq: rapid purification method for preparation of monospecific antisera and for biochemical studies. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






