Abstract
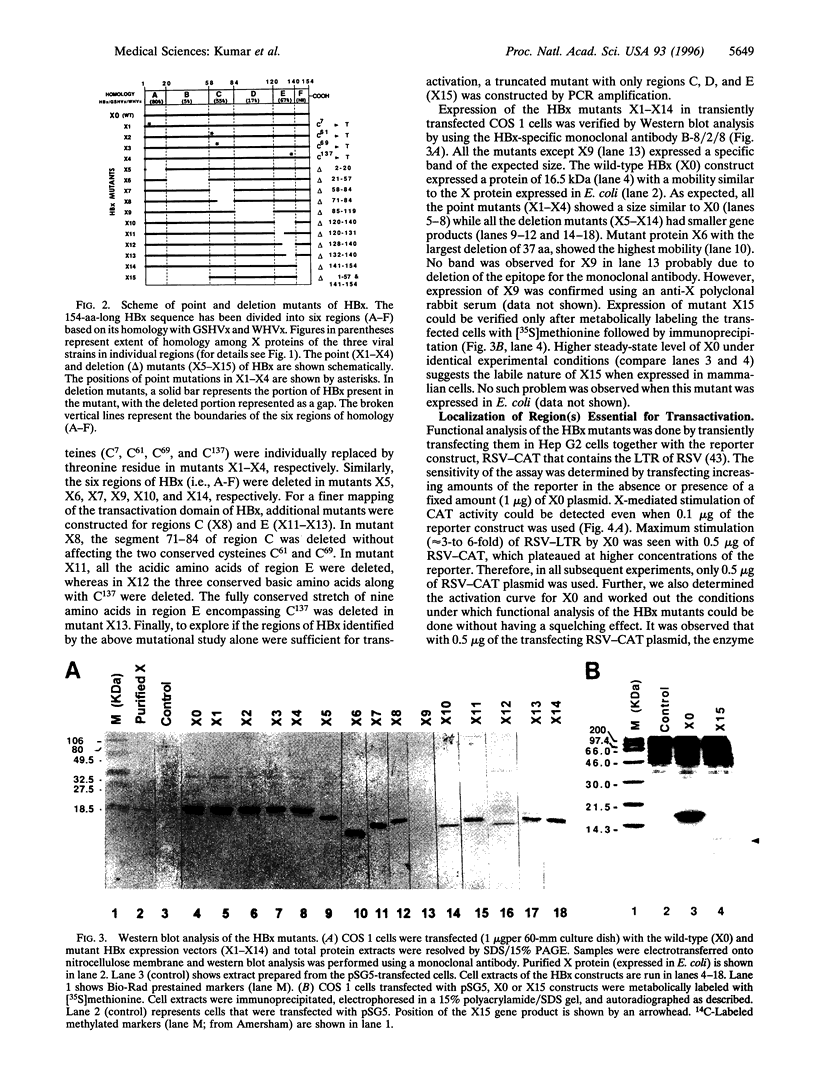
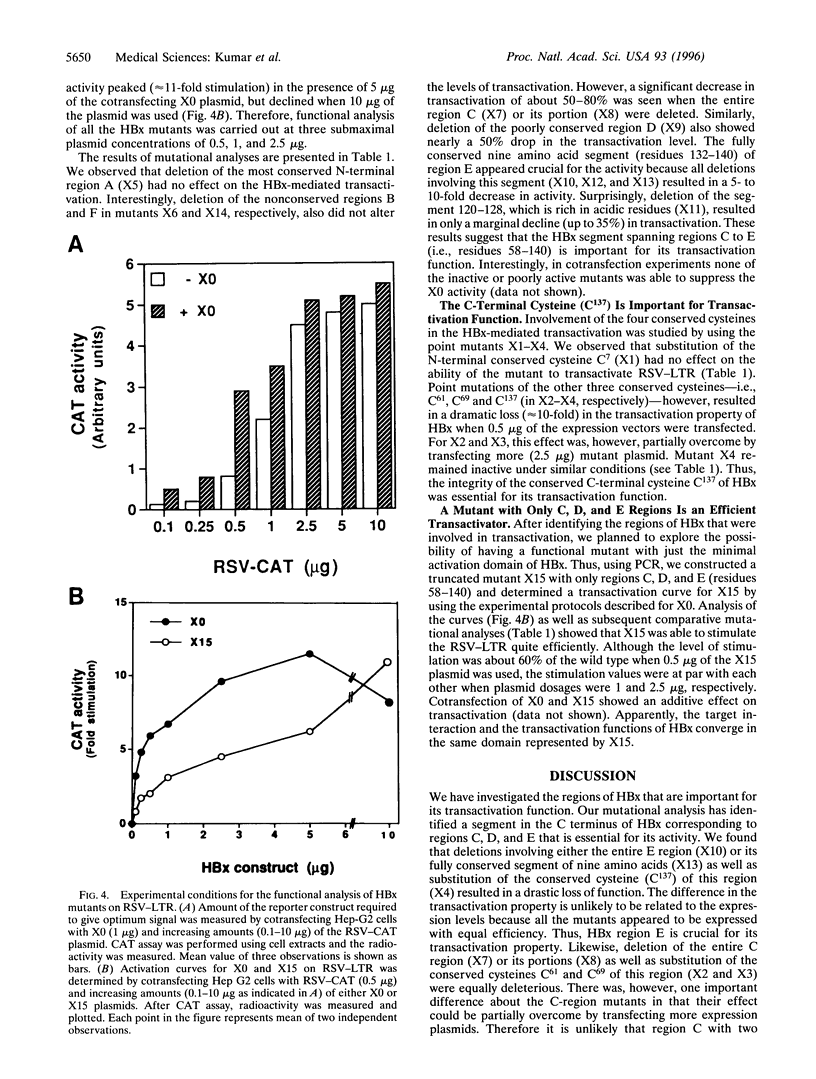
The hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) sequence (154 aa) has been divided into six regions (A-F) based on its sequence homology with X proteins of other mammalian hepadnaviruses. Regions A, C, and E are more conserved and include all the four conserved cysteines (C7, C61, C69, and C137). To localize the regions of HBx important for transactivation, a panel of 10 deletion mutants (X5-X14) and 4 single point mutants (X1-X4), each corresponding to a conserved cysteine residue, was constructed by site-directed mutagenesis. A HBx-specific monoclonal antibody was developed and used to confirm the expression of mutants by Western blot. Transactivation property of the HBx mutants was studied on Rous sarcoma virus-long terminal repeat (RSV-LTR) in transient transfection assays. We observed that deletion of the most conserved region A or substitution of the N-terminal cysteine (C7) had no effect on transactivation. Deletion of the nonconserved regions B or F also had no deleterious effects. Deletions of regions C and D resulted in a significant loss of function. Substitution of both C61 and C69 present in region C, caused almost 90% loss of activity that could be partially overcome by transfecting more expression plasmid. The fully conserved 9 amino acid segment (residues 132 to 140) within region E including C137 appeared to be crucial for its activity. Finally, a truncated mutant X15 incorporating only regions C to E (amino acids 58-140) was able to stimulate the RSV-LTR quite efficiently, suggesting a crucial role played by this domain in transactivation function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antunović J., Lemieux N., Cromlish J. A. The 17 kDa HBx protein encoded by hepatitis B virus interacts with the activation domains of Oct-1, and functions as a coactivator in the activation and repression of a human U6 promoter. Cell Mol Biol Res. 1993;39(5):463–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arii M., Takada S., Koike K. Identification of three essential regions of hepatitis B virus X protein for trans-activation function. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):397–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aufiero B., Schneider R. J. The hepatitis B virus X-gene product trans-activates both RNA polymerase II and III promoters. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):497–504. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avantaggiati M. L., Natoli G., Balsano C., Chirillo P., Artini M., De Marzio E., Collepardo D., Levrero M. The hepatitis B virus (HBV) pX transactivates the c-fos promoter through multiple cis-acting elements. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1567–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsano C., Avantaggiati M. L., Natoli G., De Marzio E., Will H., Perricaudet M., Levrero M. Full-length and truncated versions of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) X protein (pX) transactivate the cmyc protooncogene at the transcriptional level. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90379-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benn J., Schneider R. J. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein activates Ras-GTP complex formation and establishes a Ras, Raf, MAP kinase signaling cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10350–10354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong J. H., Yi M., Lin Y., Murakami S. Human RPB5, a subunit shared by eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases, binds human hepatitis B virus X protein and may play a role in X transactivation. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 3;14(1):143–150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross J. C., Wen P., Rutter W. J. Transactivation by hepatitis B virus X protein is promiscuous and dependent on mitogen-activated cellular serine/threonine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8078–8082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etiemble J., Möröy T., Trépo C., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Nucleotide sequence of the woodchuck hepatitis virus surface antigen mRNAs and the variability of three overlapping viral genes. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90325-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A., Mal T. K., Jayasuryan N., Chauhan V. S. Assignment of disulphide bonds in the X protein (HBx) of hepatitis B virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jul 26;212(3):919–924. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. Q., Vierling J. M., Siddiqui A. Trans-activation of HLA-DR gene by hepatitis B virus X gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7140–7144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. Q., Yu C. H., Vierling J. M. Up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 transcription by hepatitis B virus X protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11441–11445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameel S., Siddiqui A., Maguire H. F., Rao K. V. Hepatitis B virus X protein produced in Escherichia coli is biologically functional. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3963–3966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3963-3966.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekulé A. S., Lauer U., Weiss L., Luber B., Hofschneider P. H. Hepatitis B virus transactivator HBx uses a tumour promoter signalling pathway. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):742–745. doi: 10.1038/361742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. M., Koike K., Saito I., Miyamura T., Jay G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):317–320. doi: 10.1038/351317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. H., Kang S. K., Lee Y. I. Functional analysis of hepatitis B virus transactivator X: implication of the leucine zipper-like region and C-terminal seven conserved amino acids in functional regions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):894–903. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Stack G., Berry M., Jin J. R., Chambon P. Functional domains of the human estrogen receptor. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90581-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Elledge S. J., Butel J. S. Hepatitis B virus X protein interacts with a probable cellular DNA repair protein. J Virol. 1995 Feb;69(2):1107–1114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.2.1107-1114.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Finegold M. J., Shen R. F., DeMayo J. L., Woo S. L., Butel J. S. Hepatitis B virus transactivator X protein is not tumorigenic in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5939–5947. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5939-5947.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levrero M., Balsano C., Natoli G., Avantaggiati M. L., Elfassi E. Hepatitis B virus X protein transactivates the long terminal repeats of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3082–3086. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3082-3086.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. J., Chien M. L., Lee Y. H. Characteristics of the X gene of hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H. F., Hoeffler J. P., Siddiqui A. HBV X protein alters the DNA binding specificity of CREB and ATF-2 by protein-protein interactions. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.1827531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahé Y., Mukaida N., Kuno K., Akiyama M., Ikeda N., Matsushima K., Murakami S. Hepatitis B virus X protein transactivates human interleukin-8 gene through acting on nuclear factor kB and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-like cis-elements. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13759–13763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzo S., Clementi M., Alfani E., Bagnarelli P., Iacovacci S., Manzin A., Dandri M., Natoli G., Levrero M., Carloni G. Trans-activation of epidermal growth factor receptor gene by the hepatitis B virus X-gene product. Virology. 1993 Oct;196(2):878–882. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami S., Cheong J. H., Kaneko S. Human hepatitis virus X gene encodes a regulatory domain that represses transactivation of X protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):15118–15123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatake H., Chisaka O., Yamamoto S., Matsubara K., Koshy R. Effect of X protein on transactivation of hepatitis B virus promoters and on viral replication. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):305–314. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri I., Maguire H. F., Siddiqui A. Hepatitis B virus transactivator protein X interacts with the TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1003–1007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repp R., Keller C., Borkhardt A., Csecke A., Schaefer S., Gerlich W. H., Lampert F. Detection of a hepatitis B virus variant with a truncated X gene and enhancer II. Arch Virol. 1992;125(1-4):299–304. doi: 10.1007/BF01309646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter S. E., Whitten T. M., Quets A. T., Schloemer R. H. An internal domain of the hepatitis B virus X antigen is necessary for transactivating activity. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):841–845. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90626-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. Molecular events in the pathogenesis of hepadnavirus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Annu Rev Med. 1994;45:297–323. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.45.1.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel L., Fischer M., Schaller H. Two-codon insertion mutations of the HBx define two separate regions necessary for its trans-activation function. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):529–536. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Altschul S. F., Lipman D. J. A workbench for multiple alignment construction and analysis. Proteins. 1991;9(3):180–190. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of an infectious molecularly cloned genome of ground squirrel hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):367–375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.367-375.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Mitchell P. J., Yen T. S. Transactivation by the hepatitis B virus X protein depends on AP-2 and other transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):72–74. doi: 10.1038/344072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Yen T. S. Mutual functional antagonism of the simian virus 40 T antigen and the hepatitis B virus trans activator. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2351–2356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2351-2356.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Yen T. S., Peterlin B. M., Ou J. H. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8286–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Gaynor R., Srinivasan A., Mapoles J., Farr R. W. trans-activation of viral enhancers including long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada S., Kido H., Fukutomi A., Mori T., Koike K. Interaction of hepatitis B virus X protein with a serine protease, tryptase TL2 as an inhibitor. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada S., Koike K. Trans-activation function of a 3' truncated X gene-cell fusion product from integrated hepatitis B virus DNA in chronic hepatitis tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5628–5632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Lai M. Y., Chen D. S., Robinson W. S. Activation of protooncogene c-jun by the X protein of hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):346–350. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Schloemer R. H. Transcriptional trans-activating function of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3448–3453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3448-3453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Shimojima M., Gotoh K., Shikata T., Tanaka E., Kiyosawa K. "Silent" hepatitis B virus mutants are responsible for non-A, non-B, non-C, non-D, non-E hepatitis. Microbiol Immunol. 1994;38(4):281–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1994.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. W., Forrester K., Yeh H., Feitelson M. A., Gu J. R., Harris C. C. Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits p53 sequence-specific DNA binding, transcriptional activity, and association with transcription factor ERCC3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2230–2234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. S., Andrisani O. M. The hepatitis B virus X protein targets the basic region-leucine zipper domain of CREB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3819–3823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollersheim M., Debelka U., Hofschneider P. H. A transactivating function encoded in the hepatitis B virus X gene is conserved in the integrated state. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):545–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Zhou Z. Y., Judd A., Cartwright C. A., Robinson W. S. The hepatitis B virus-encoded transcriptional trans-activator hbx appears to be a novel protein serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):687–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm P., Hofschneider P. H., Koshy R. The HBV X-ORF encodes a transactivator: a potential factor in viral hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):169–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Taraboulos A., Ou J. H., Yen T. S. Activation of class I major histocompatibility complex gene expression by hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4025–4028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4025-4028.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou M. X., Watabe M., Watabe K. The X-gene of human hepatitis B virus transactivates the c-jun and alpha-fetoprotein genes. Arch Virol. 1994;134(3-4):369–378. doi: 10.1007/BF01310574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Medina T., Haviv I., Noiman S., Shaul Y. The X protein of hepatitis B virus has a ribo/deoxy ATPase activity. Virology. 1994 Jul;202(1):401–407. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




