Abstract
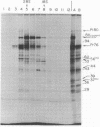
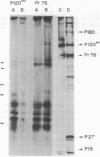
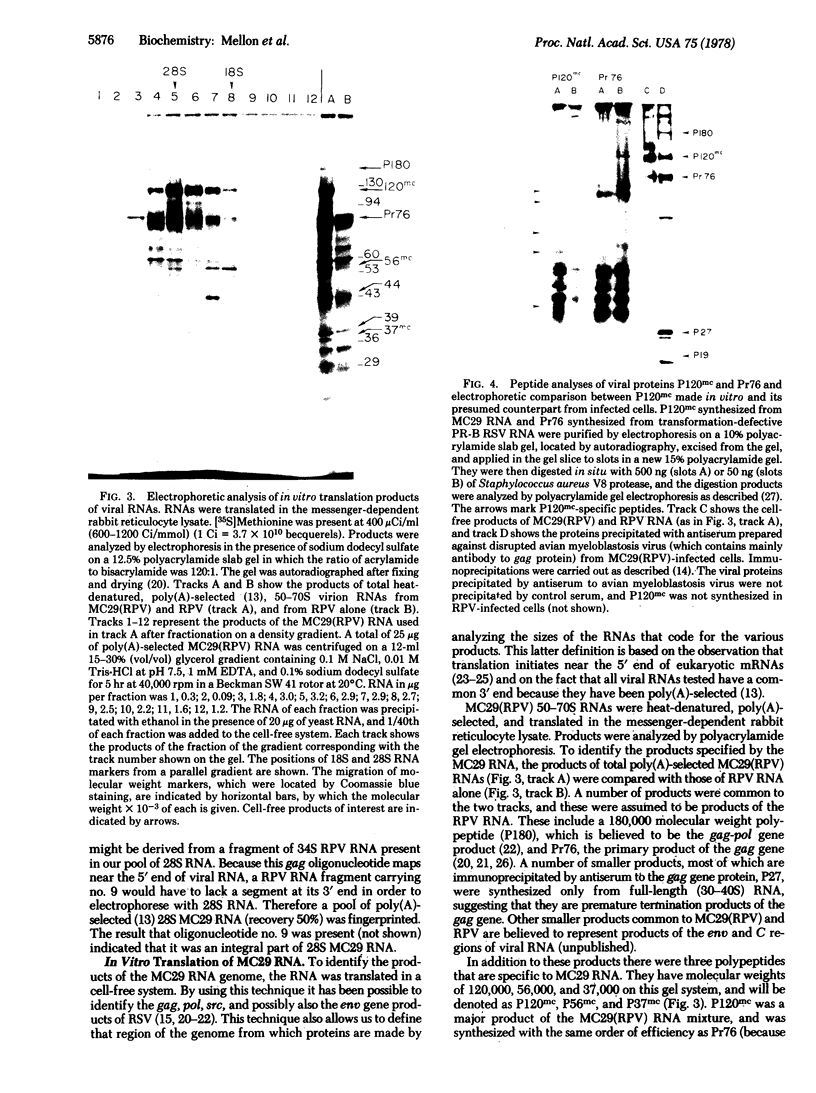
The 28S RNA of the defective avian acute leukemia virus MC29 contains two sets of sequences: 60% are hybridized by DNA complementary to other avian tumor virus RNAs (group-specific cDNA) and 40% are hybridized only by MC29-specific cDNA. Specific and group-specific sequences of viral RNA, defined in terms of their large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides, were located on a map of all large T1 oligonucleotides of viral RNA. Oligonucleotides representing MC29-specific sequences of viral RNA mapped between 0.4 and 0.7 unit from the 3′-poly(A) end. Oligonucleotides of group-specific sequences mapped between 0 and 0.4 and between 0.7 and 1 map unit. Cell-free translation of viral RNA yielded three proteins with approximate molecular weights of 120,000, 56,000, and 37,000, termed P120mc, P56mc, and P37mc. P120mc contained both MC29-specific peptides and serological determinants and peptides of the conserved, internal group-specific antigens of avian tumor viruses. P120mc is translated only from full-length 28S RNA. Furthermore, MC29 RNA contains sequences related to the group-specific antigen gene (gag), near the 5′ end, which are followed by MC29-specific sequences. We conclude that this protein is translated from the 5′ 60% of the RNA, and that it includes a segment translated from the specific sequences. It is suggested that the transforming (onc) gene of MC29 may consists of the specific and some group-specific RNA sequences and that P120mc, which is also found in transformed cells, may be the onc gene product.
Keywords: defective RNA tumor virus, oligonucleotide mapping, cell-free translation, transforming genes
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Tumor viruses: 1974. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1187–1200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. E., Brownlee G. G. AUG is the only recognisable signal sequence in the 5' non-coding regions of eukaryotic mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):84–87. doi: 10.1038/274084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Defectiveness of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: isolation of long-term nonproducer cultures and analysis of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Vogt P. K. Genetic analysis of the defectiveness in strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. Virology. 1978 Jul 15;88(2):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dina D., Beemon K., Duesberg P. The 30S Moloney sarcoma virus RNA contains leukemia virus nucleotide sequences. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):299–309. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Vogt P. K. The RNA of avian acute leukemia virus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4320–4324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Ranki M., Morser J., Käriäinen L., Smith A. E. Initiation of translation directed by 42S and 26S RNAs from Semliki Forest virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Hanafusa H. Recombination between endogenous and exogenous RNA tumor virus genes as analyzed by nucleic acid hybridization. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1367–1377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1367-1377.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. S., Moscovici C., Vogt P. K. The defectiveness of Mill Hill 2, a carcinoma-inducing avian oncovirus. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):162–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki R., Langlois A. J., Chabot J., Beard J. W. Component of strain MC29 avian leukosis virus with the property of defectiveness. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):821–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.821-827.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R. H., Billeter M. A., Weissmann C. Mapping of biological functions on RNA of avian tumor viruses: location of regions required for transformation and determination of host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Duesberg P. H., Horst J., Vogt P. K. Avian tumor virus RNA: a comparison of three sarcoma viruses and their transformation-defective derivatives by oligonucleotide fingerprinting and DNA-RNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2266–2270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisel J., Klement V., Lai M. M., Ostertag W., Duesberg P. Ribonucleic acid components of murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Marciani D. J., Papas T. S. Cell-free synthesis of the precursor polypeptide for avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4951–4954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Martin G. S., Smith A. E. Cell-free translation of virion RNA from nondefective and transformation-defective Rous sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):950–967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.950-967.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Translation of 35S and of subgenomic regions of avian sarcoma virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4661–4665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Beug H., Claviez M., Winkhardt H. J., Friis R. R., Graf T. Transformation parameters in chicken fibroblasts transformed by AEV and MC29 avian leukemia viruses. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Howk R. S., Anisowicz A., Peebles P. T., Scher C. D., Parks W. P. Separation of sarcoma virus-specific and leukemia virus-specific genetic sequences of Moloney sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4650–4654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stéhelin D., Graf T. Avian myelocytomatosis and erythroblastosis viruses lack the transforming gene src of avian sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):745–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Boyars J. K., Parks W. P., Scolnick E. M. Friend strain of spleen focus-forming virus: a recombinant between mouse type C ecotropic viral sequences and sequences related to xenotropic virus. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):361–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.361-372.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Eisenman R., Diggelmann H. Generation of avian myeloblastosis virus structural proteins by proteolytic cleavage of a precursor polypeptide. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 15;96(3):471–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P. H., Robins T., Yokota H., Vogt P. K. The terminal oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs are genetically linked. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):472–492. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P., Beemon K., Vogt P. K. Mapping RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of avian tumor virus RNAs: sarcoma-specific oligonucleotides are near the poly(A) end and oligonucleotides common to sarcoma and transformation-defective viruses are at the poly(A) end. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1051–1070. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1051-1070.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P., Mellon P., Vogt P. K. Distribution of envelope-specific and sarcoma-specific nucleotide sequences from different parents in the RNAs of avian tumor virus recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1073–1077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Galehouse D., Mellon P., Duesberg P., Mason W. S., Vogt P. K. Mapping oligonucleotides of Rous sarcoma virus RNA that segregate with polymerase and group-specific antigen markers in recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Rosenberg N., Paskind M., Shields A., Baltimore D. Identification of an Abelson murine leukemia virus-encoded protein present in transformed fibroblast and lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2488–2492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Helm K., Duesberg P. H. Translation of Rous sarcoma virus RNA in a cell-free system from ascites Krebs II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]