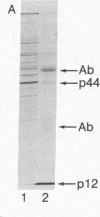
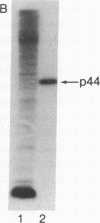
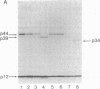
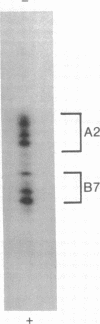
Abstract
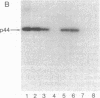
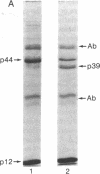
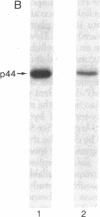
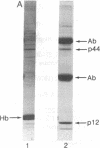
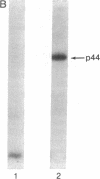
HLA-A and -B antigens are phosphorylated in transformed lymphoblastoid cells and peripheral blood lymphocytes, both incubated with 32Pi. The phosphate group is attached to HLA-A and -B heavy chain (p44) as identified by immunoprecipitation with anti-beta2-microglobulin IgG, sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, isoelectric focusing, and susceptibility to limited proteolysis by papain and trypsin. The site(s) of phosphorylation is identified as a serine residue(s) located in the hydrophilic carboxy terminus of the p44 chain. HLA antigens are also phosphorylated in isolated membranes from transformed lymphoblastoid cells that are incubated with [gamma32P]ATP. The phosphorylation of the carboxy terminus of HLA-A and -B antigens in vivo is good evidence that this portion of the molecule is intracellular. Furthermore, this modification suggests a general way in which interactions between membrane proteins and cytoskeletal elements may be regulated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ash J. F., Louvard D., Singer S. J. Antibody-induced linkages of plasma membrane proteins to intracellular actomyosin-containing filaments in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5584–5588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Singer S. J. Transmembrane interactions and the mechanism of capping of surface receptors by their specific ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5031–5035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány K., Bárány M. Phosphorylation of the 18,000-dalton light chain of myosin during a single tetanus of frog muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4752–4754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Immunochemical evidence for the transmembrane orientation of glycophorin A. Localization of ferritin-antibody conjugates in intact cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):539–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cresswell P., Turner M. J., Strominger J. L. Papain-solubilized HL-A antigens from cultured human lymphocytes contain two peptide fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H., Guild B. C., Helenius A., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Reconstitution of purified detergent-soluble HLA-A and HLA-B antigens into phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3230–3234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J., Stull J. T., Krebs E. G. Dephosphorylation of the inhibitor component of troponin by phosphorylase phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5275–5277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrow C. E., Jr, Allen J. E., Rasmussen H. Phosphorylation of an endogenous membrane protein by an endogenous, membrane-associated cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in human erythrocyte ghosts. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8145–8153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. L., Smith M. J. An association between actin and the major histocompatibility antigen H-2. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):274–278. doi: 10.1038/273274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemonnier F., Mescher T. M., sherman L., Burakoff S. The induction of cytolytic T lymphocytes with purified plasma membranes. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1114–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Humphreys R. E., Yocum R. R., Strominger J. L. Enhanced representation of HL-A antigens on human lymphocytes after mitogenesis induced by phytohemagglutinin or Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3206–3209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Humphreys R. E., Turner M. J., Strominger J. L. Heterogeneity of HL-A antigen preparations is due to variable sialic acid content. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3998–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Smillie L. B., Perry S. V. A phosphorylated light-chain component of myosin. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):105P–106P. doi: 10.1042/bj1280105p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribolow H., BARANY M. Phosphorylation of tropomyosin in live frog muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Mar;179(2):718–720. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Strominger J. L. Rapid purification of detergent-solubilized HLA antigen by affinity chromatography employing anti-beta2-microglobulin serum. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5427–5428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Terhorst C., Strominger J. L. Sequence of the COOH-terminal hydrophilic region of histocompatibility antigens HLA-A2 and HLA-B7. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5319–5324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. L., Marchesi V. T. Phosphorylation in membranes of intact human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):508–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Strominger J. L. Detergent-soluble HLA antigens contain a hydrophilic region at the COOH-terminus and a penultimate hydrophobic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2481–2485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., Brostrom C. O., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of the inhibitor component of troponin by phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5272–5274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., High C. W. Phosphorylation of skeletal muscle contractile proteins in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):1078–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Marchesi V. T. Amino-acid sequence and oligosaccharide attachment sites of human erythrocyte glycophorin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Davies P., Bechtel P., Willingham M., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of the actin-binding protein filamin. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:371–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Crumpton M. J. Orientation of cell-surface antigens in the lipid bilayer of lymphocyte plasma membrane. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):307–311. doi: 10.1038/269307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]