Abstract
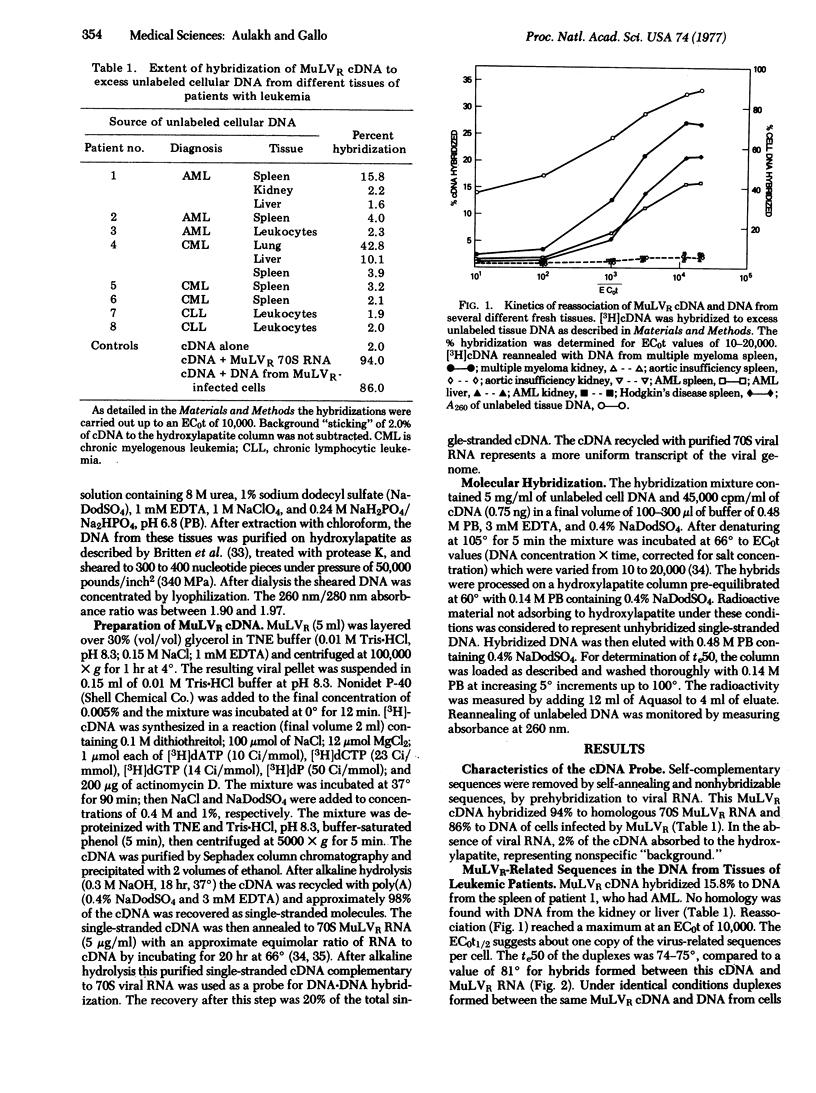
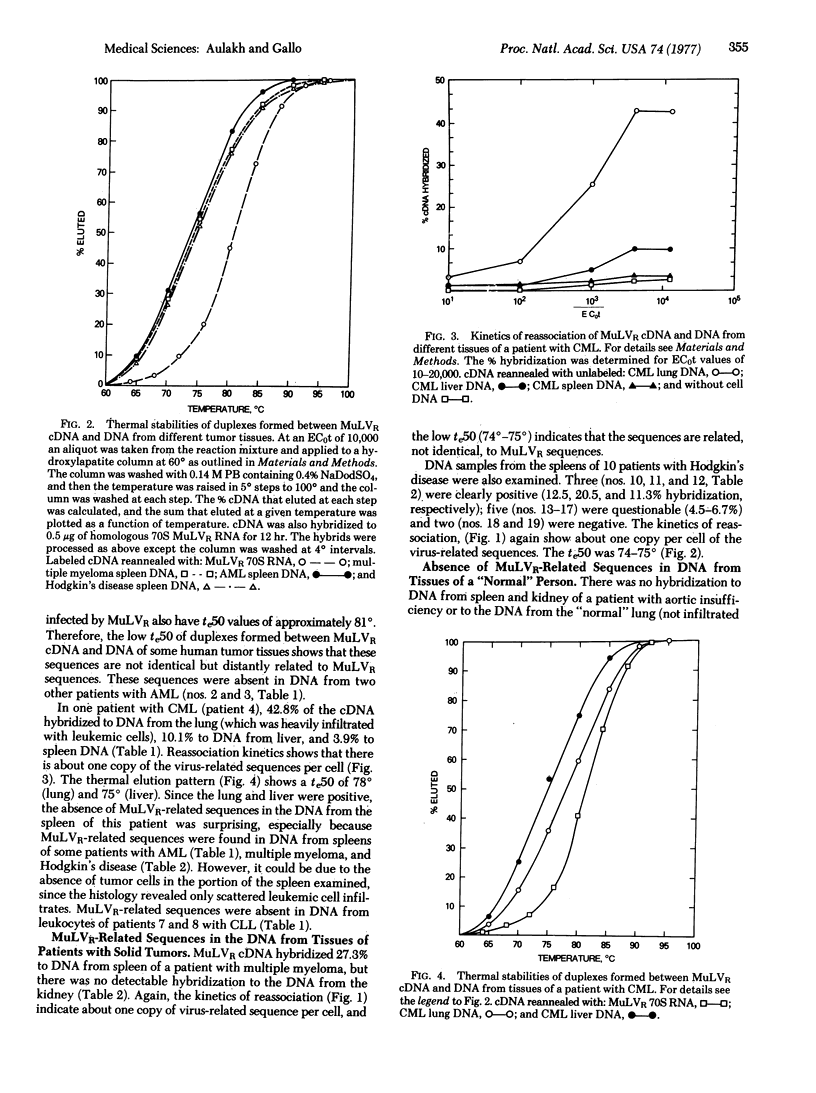
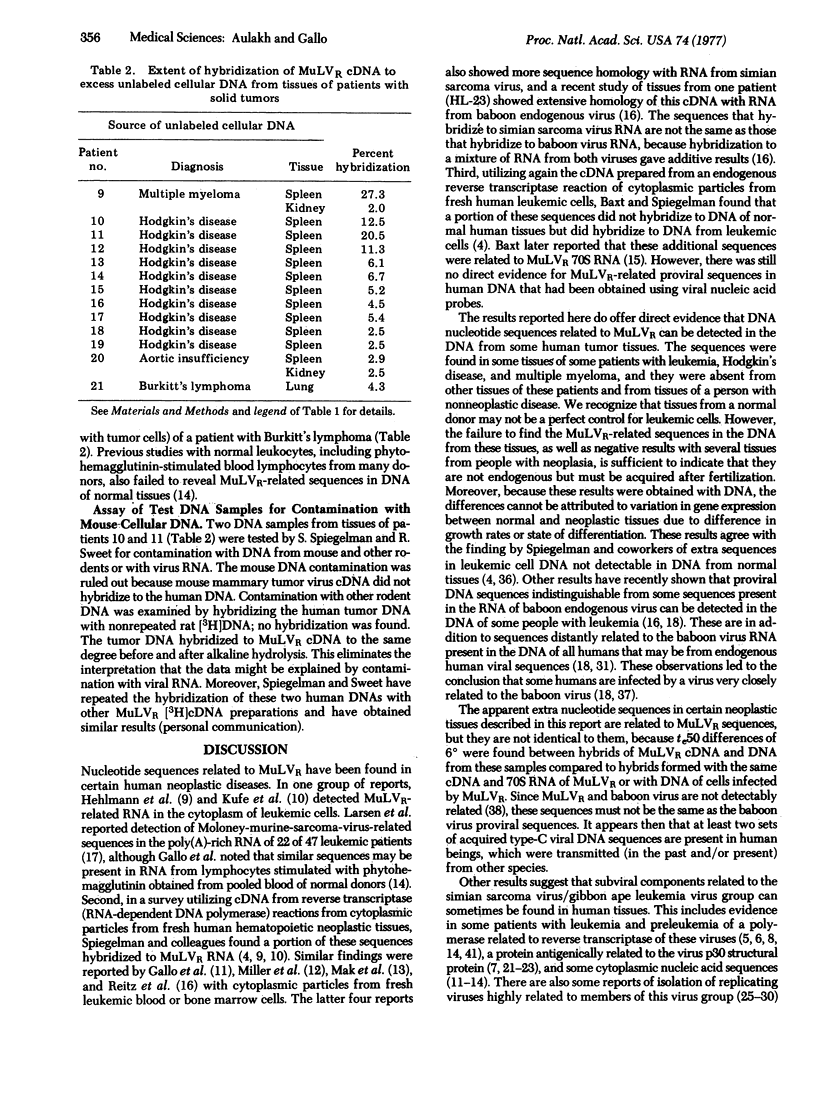
A [3H[cDNA probe synthesized from the RNA genome of Rauscher murine leukemia virus (MuLVR) and purified by hybridization to MuLVR70S RNA was hybridized to DNA from human normal and hemotopoietic neoplasia tissues. This cDNA hybridized completely to its homologous 70S RNA and was free of self-complementary sequences. Sequences complementary to MuLVR cDNA were found in DNA from tissues of some patients with leukemia (2 of 8), Hodgkin's disease (3 of 10), and one patient with multiple myeloma. DNA from spleen and kidney of a patient with nonneoplastic disease did not contain detectable MuLVR-related sequences. These virus-related sequences in the DNA from these neoplastic tissues were related but not identical to MuLVR sequences because differences of approximately 6 degrees in the midpoints of thermal elution profiles were found between the heterologous and homologous duplexes. These nucleotide sequences are not the same as the proviral sequences of baboon type-C virus previously found from some other patients with leukemia [Reitz et al. (1976) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73,2113-2117; Wong-Staal et al. (1976) Nature 262, 190-195], because there is no sequence homology between nucleic acids from MuLVR and baboon virus. The absence of these nucleic acid sequences in many tissues of patients with neoplasia and from the few tissues examined from people with nonneoplastic disease suggests that they are not endogenous elements but are acquired after fertilization. Taken together with the previous detection of baboon and woolly monkey type-C viral related components in some human tumors, the results suggest acquisition of at least three types of type-C viral sequences in the human population.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki T., Walling M. J., Bushar G. S., Liu M., Hsu K. C. Natural antibodies in sera from healthy humans to antigens on surfaces of type C RNA viruses and cells from primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2491–2495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt W. G. Sequences present in both human leukemic cell nuclear DNA and Rauscher leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt W. G., Spiegelman S. Nuclear DNA sequences present in human leukemic cells and absent in normal leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3737–3741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt W., Hehlmann R., Spiegelman S. Human leukaemic cells contain reverse transcriptase associated with a high molecular weight virus-related RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 15;240(98):72–75. doi: 10.1038/newbio240072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt W., Yates J. W., Wallace H. J., Jr, Holland J. F., Spiegelman S. Leukemia-specific DNA sequences in leukocytes of the leukemic member of identical twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2629–2632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Lieber M. M., Livingston D. M., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J., Kalter S. S. Infectious C-type virus isolated from a baboon placenta. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):17–20. doi: 10.1038/248017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of type C viral genes: I. Nucleic acid from baboon type C virus as a measure of divergence among primate species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4513–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Homology between type-C viruses of various species as determined by molecular hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3316–3320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabelman N., Waxman S., Smith W., Douglas S. D. Appearance of C-type virus-like particles after co-cultivation of a human tumor-cell line with rat (XC) cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Sep 15;16(3):355–369. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R. E., Salahuddin S. Z., Hall W. T., McCredie K. B., Gallo R. C. Growth and differentiation in culture of leukemic leukocytes from a patient with acute myelogenous leukemia and re-identification of type-C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R. E., Todaro G. J., Smith R. G., Livingston D. M., Gallo R. C. Relationship between RNA-directed DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase) from human acute leukemic blood cells and primate type-C viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1309–1313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E., Miller N. R., Mondal H., Saxinger W. C., Mayer R. J., Smith R. G., Gillespie D. H. Relationships between components in primate RNA tumor viruses and in the cytoplasm of human leukemic cells: implications to leukemogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):933–961. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Miller N. R., Saxinger W. C., Gillespie D. Primate RNA tumor virus-like DNA synthesized endogenously by RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virus-like particles from fresh human acute leukemic blood cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3219–3224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Yang S. S., Ting R. C. RNA dependent DNA polymerase of human acute leukaemic cells. Nature. 1970 Dec 5;228(5275):927–929. doi: 10.1038/228927a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hehlmann R., Kufe D., Spiegelman S. RNA in human leukemic cells related to the RNA of a mouse leukemia virus (leukocytes-RNA-DNA hybridization-rauscher virus-polysomal RNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):435–439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufe D., Hehlmann R., Spiegelman S. Human sarcomas contain RNA related to the RNA of a mouse leukemia virus. Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):182–185. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. J., Marty M., Hamelin R., Peries J., Boiron M., Tavitian A. Search for nucleic acid sequences complementary to a murine oncornaviral genome in poly(A)-rich RNA of human leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4900–4904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak T. W., Kurtz S., Manaster J., Housman D. Viral-related information in oncornavirus-lik particles isolated from cultures of marrow cells from leukemic patients in relapse and remission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):623–627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C., Mellors J. W. Antigen related to mammalian type-C RNA viral p30 proteins is located in renal glomeruli in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):233–237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. R., Saxinger W. C., Reitz M. S., Gallagher R. E., Wu A. M., Gallo R. C., Gillespie D. Systematics of RNA tumor viruses and virus-like particles of human origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3177–3181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal H., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. RNA-directed DNA polymerase from human leukemic blood cells and from primate type-C virus-producing cells: high- and low-molecular-weight forms with variant biochemical and immunological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nooter K., Aarssen A. M., Bentvelzen P., De Groot F. G., Van Pelt F. G. Isolation of infectious C-type oncornavirus from human leukaemic bone marrow cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):595–597. doi: 10.1038/256595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panem S., Prochownik E. V., Reale F. R., Kirsten W. H. Isolation of type C virions from a normal human fibroblast strain. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):297–299. doi: 10.1126/science.49927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M. S., Miller N. R., Wong-Staal F., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C., Gillespie D. H. Primate type-C virus nucleic acid sequences (woolly monkey and baboon types) in tissues from a patient with acute myelogenous leukemia and in viruses isolated from cultured cells of the same patient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2113–2117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarngadharan M. G., Sarin P. S., Reitz M. S., Gallo R. C. Reverse transcriptase activity of human acute leukaemic cells: purification of the enzyme, response to AMV 70S RNA, and characterization of the DNA product. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 15;240(98):67–72. doi: 10.1038/newbio240067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Primate type C virus p30 antigen in cells from humans with acute leukemia. Science. 1975 Mar 7;187(4179):855–857. doi: 10.1126/science.163489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Type C viral antigens in man. I. Antigens related to endogenous primate virus in human tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4703–4707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder H. W., Jr, Pincus T., Fleissner E. Specificities of human immunoglobulins reactive with antigens in preparations of several mammalian type-C viruses. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):60–73. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Search for antigens and antibodies crossreactive with type C viruses of the woolly monkeys and gibbon ape in animal models and in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., August J. T. Structural proteins of mammalian oncogenic RNA viruses: multiple antigenic determinants of the major internal protein and envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):171–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.171-180.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teich N. M., Weiss R. A., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallagher R. E., Gillespie D. H., Gallo R. C. Infective transmission and characterisation of a C-type virus released by cultured human myeloid leukaemia cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):551–555. doi: 10.1038/256551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Gallo R. C. Immunological relationship of DNA polymerase from human acute leukaemia cells and primate and mouse leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase. Nature. 1973 Jul 27;244(5413):206–209. doi: 10.1038/244206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gillespie D., Gallo R. C. Proviral sequences of baboon endogenous type C RNA virus in DNA of human leukaemic tissues. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):190–195. doi: 10.1038/262190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurcher C., Brinkhof J., Bentvelzen P., De Man J. C. C-type virus antigens detected by immunofluorescence in human bone tumour cultures. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):457–459. doi: 10.1038/254457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


