Abstract
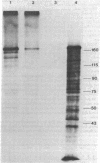
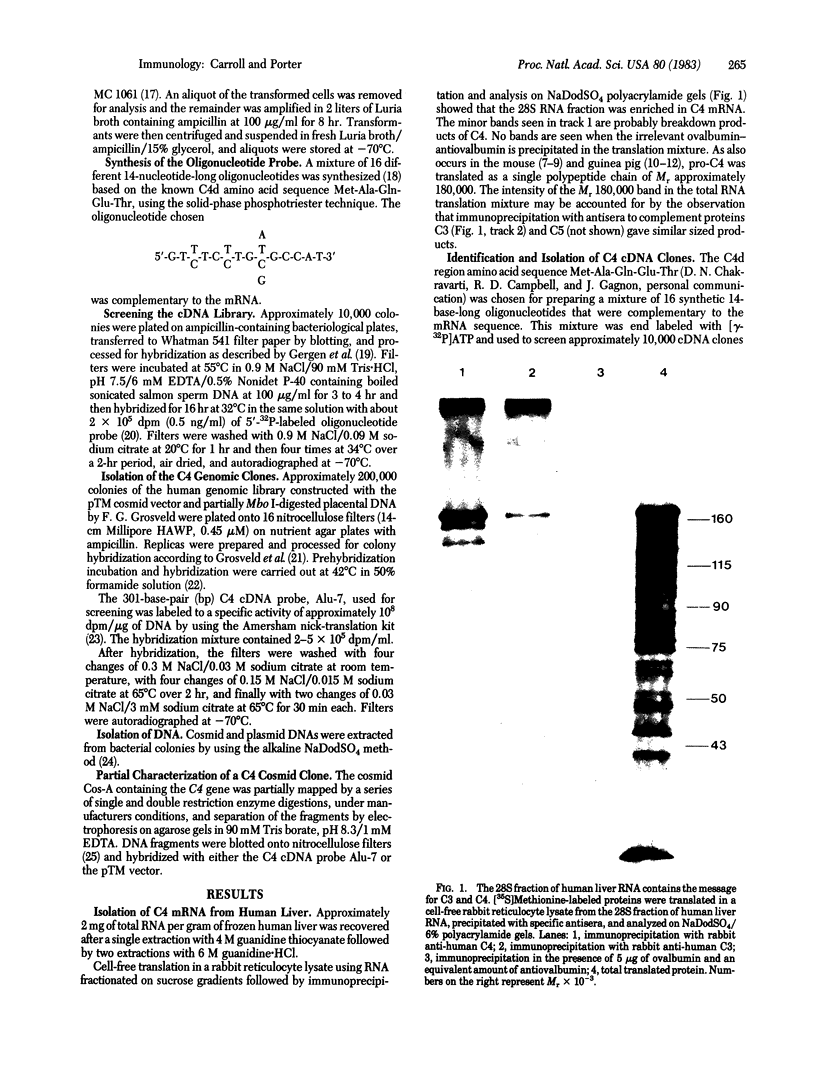
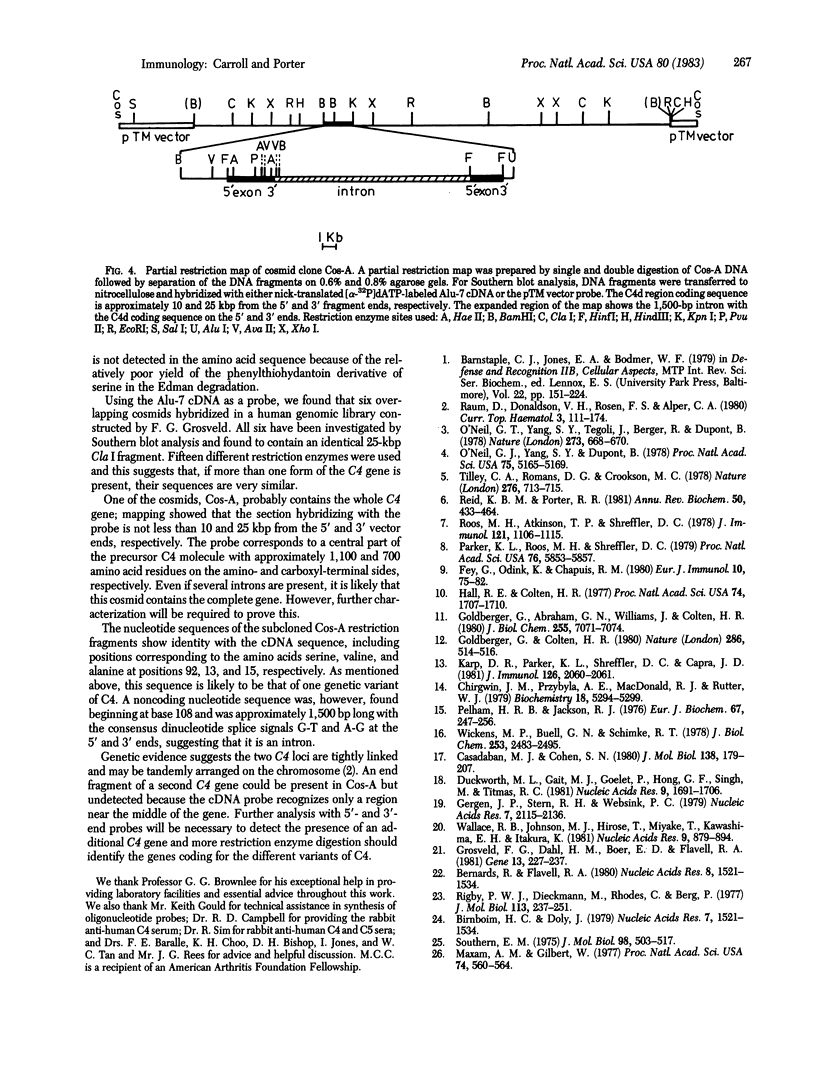
Six overlapping cosmid clones having an average insert size of 40 kilobase pairs were identified and isolated from a human genomic library by using a cDNA probe, Alu-7, specific for the amino acid sequence of C4d, a known region of the fourth component of human complement. Analysis of these genomic clones by restriction digestion and Southern blotting shows that all six probably contain the same complete C4 gene. Nucleotide sequence comparison of the genomic clone Cos-A and the cDNA clone Alu-7 shows an identical sequence except for the presence of a 1,500-base-pair intron in the genomic sequence. The amino acid sequence predicted from the nucleotide sequence agrees with the known C4d region amino acid sequence with one exception.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernards R., Flavell R. A. Physical mapping of the globin gene deletion in hereditary persistence of foetal haemoglobin (HPFH). Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1521–1534. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M. L., Gait M. J., Goelet P., Hong G. F., Singh M., Titmas R. C. Rapid synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides VI. Efficient, mechanised synthesis of heptadecadeoxyribonucleotides by an improved solid phase phosphotriester route. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1691–1706. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G., Odink K., Chapuis R. M. Synthesis of the mouse complement component C4 (Ss-protein) by peritoneal macrophages: kinetics of secretion and glycosylation of the subunits. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Feb;10(2):75–82. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Stern R. H., Wensink P. C. Filter replicas and permanent collections of recombinant DNA plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2115–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger G., Abraham G. N., Williams J., Colten H. R. NH2-terminal sequence analysis of pro-C4, the precursor of the fourth component of guinea pig complement. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7071–7074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Precursor complement protein (pro-C4) is converted in vitro to native C4 by plasmin. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):514–516. doi: 10.1038/286514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. E., Colten H. R. Cell-free synthesis of the fourth component of guinea pig complement (C4): identification of a precursor of serum C4 (pro-C4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1707–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp D. R., Parker K. L., Shreffler D. C., Capra J. D. Characterization of the murine C4 precursor (pro-C4): evidence that the carboxy-terminal subunit is the C4 gamma-chain. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):2060–2061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Yang S. Y., Dupont B. Two HLA-linked loci controlling the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Yang S. Y., Tegoli J., Berger R., Dupont B. Chido and Rodgers blood groups are distinct antigenic components of human complement C4. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):668–670. doi: 10.1038/273668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Roos M. H., Shreffler D. C. Structural characterization of the murine fourth component of complement and sex-limited protein and their precursors: evidence for two loci in the S region of the H-2 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5853–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Donaldson V. H., Rosen F. S., Alper C. A. Genetics of complement. Curr Top Hematol. 1980;3:111–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Atkinson J. P., Shreffler D. C. Molecular characterization of the Ss and Slp (C4) proteins of the mouse H-2 complex: subunit composition, chain size polymorphism, and an intracellular (PRO-Ss) precursor. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1106–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley C. A., Romans D. G., Crookston M. C. Localisation of Chido and Rodgers determinants to the C4d fragment of human C4. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):713–715. doi: 10.1038/276713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Buell G. N., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of double-stranded DNA complementary to lysozyme, ovomucoid, and ovalbumin mRNAs. Optimization for full length second strand synthesis by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2483–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]