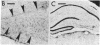Abstract
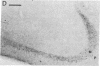
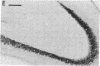
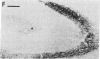
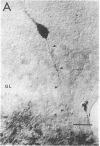
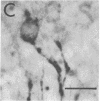
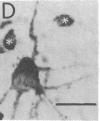
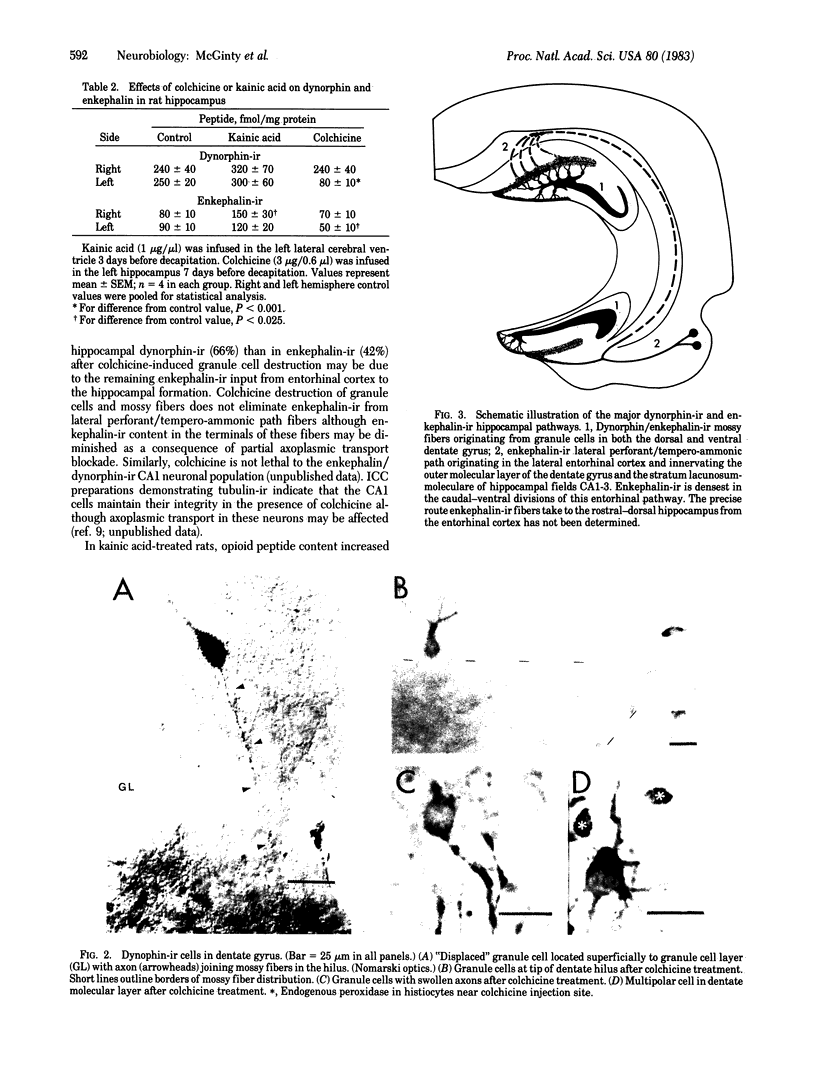
Antisera raised against synthetic dynorphin or [Leu5]enkephalin demonstrate immunostaining in hippocampal mossy fibers and in dentate granule cells. However, dynorphin immunoreactivity (ir) appears to be denser in immunocytochemical preparations and is quantitatively greater by radioimmunoassay than enkephalin-ir. Immunostaining with dynorphin antisera is eliminated by adsorption with 1-100 microM dynorphin-17 whereas immunostaining with enkephalin antisera is eliminated by adsorption with 1-100 microM [Leu5]enkephalin, dynorphin-17, dynorphin-(1-13), or alpha-neo-endorphin. Intrahippocampal colchicine injections, which selectively destroy dentate granule cells, significantly decrease the dynorphin-ir and enkephalin-ir levels in rat hippocampus. Intraventricularly administered kainic acid, which selectively destroys CA3-4 pyramidal cells, results in an increase of enkephalin immunostaining in mossy fibers and a significant increase in enkephalin-ir by radioimmunoassay in whole hippocampus. The enkephalin-ir cells and fibers in entorhinal/perirhinal cortex, which innervate rat hippocampus and dentate gyrus, do not contain dynorphin-ir.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACKSTAD T. W., KJAERHEIM A. Special axo-dendritic synapses in the hippocampal cortex: electron and light microscopic studies on the layer of mossy fibers. J Comp Neurol. 1961 Oct;117:133–159. doi: 10.1002/cne.901170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Tremblay E., Riche D., Ghilini G., Naquet R. Electrographic, clinical and pathological alterations following systemic administration of kainic acid, bicuculline or pentetrazole: metabolic mapping using the deoxyglucose method with special reference to the pathology of epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1981;6(7):1361–1391. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F., Battenberg E., Rossier J., Ling N., Guillemin R. Neurons containing beta-endorphin in rat brain exist separately from those containing enkephalin: immunocytochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1591–1595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischli W., Goldstein A., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Two "big" dynorphins from porcine pituitary. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1769–1772. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C., Brecha N., Karten H. J., Chang K. J. Localization of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity to identified axonal and neuronal populations of the rat hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 1981 May 10;198(2):335–350. doi: 10.1002/cne.901980211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazarossian V. E., Chavkin C., Goldstein A. A specific radioimmunoassay for the novel opioid peptide dynorphin. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 7;27(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt R. B., Steward O. Preferential neurotoxicity of colchicine for granule cells of the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3047–3051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Ghazarossian V. E. Immunoreactive dynorphin in pituitary and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6207–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Seeburg P., Hoffman B. J., Gage L. P., Udenfriend S. Molecular cloning establishes proenkephalin as precursor of enkephalin-containing peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):206–208. doi: 10.1038/295206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. J., Chouvet G., Bloom F. E. In vivo cellular responses to electrophoretically applied dynorphin in the rat hippocampus. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1785–1788. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Mitchell J. F., Pepper C. M. The excitation and depression of hippocampal neurones by iontophoretically applied enkephalins [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;272(1):50P–51P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Schmid R. Intrahippocampal distribution of Met5-enkephalin. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 2;205(2):415–418. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90353-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Wood P. L., Gillin J. C., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Changes of hippocampal Met-enkephalin content after recurrent motor seizures. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):231–232. doi: 10.1038/285231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Noda M., Morimoto Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for porcine beta-neo-endorphin/dynorphin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):245–249. doi: 10.1038/298245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Minamino N., Chino N., Sakakibara S., Matsuo H. The complete amino acid sequence of alpha-neo-endorphin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 15;99(3):871–878. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J., Chang K. J., Cooper B., Cuatrecasas P. Radioimmunoassay and characterization of enkephalins in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):531–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler J. V., Perry B. W., Gentry C., Cotman C. W. Degeneration of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells induced by intraventricular kainic acid. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Jul 15;192(2):333–359. doi: 10.1002/cne.901920209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler J. V., Perry B. W., Gentry C., Cotman C. W. Fate of the hippocampal mossy fiber projection after destruction of its postsynaptic targets with intraventricular kainic acid. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Mar 10;196(4):549–569. doi: 10.1002/cne.901960404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Siggins G. R., Ling N., Bloom F. E., Guillemin R. Neuronal actions of endorphins and enkephalins among brain regions: a comparative microiontophoretic study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine adrenal preproenkephalin. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):202–206. doi: 10.1038/295202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sar M., Stumpf W. E., Miller R. J., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat brain and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 1;182(1):17–37. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloviter R. S., Damiano B. P. Sustained electrical stimulation of the perforant path duplicates kainate-induced electrophysiological effects and hippocampal damage in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jul 17;24(3):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stengaard-Pedersen K., Fredens K., Larsson L. I. Enkephalin and zinc in the hippocampal mossy fiber System. Brain Res. 1981 May 11;212(1):230–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward O. Topographic organization of the projections from the entorhinal area to the hippocampal formation of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Jun 1;167(3):285–314. doi: 10.1002/cne.901670303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wamsley J. K., Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat forebrain. Brain Res. 1980 May 19;190(1):153–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Barchas J. D. Predominance of the amino-terminal octapeptide fragment of dynorphin in rat brain regions. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):77–79. doi: 10.1038/299077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Roth K. A., Barchas J. D. Immunohistochemical distribution of alpha-neo-endorphin/dynorphin neuronal systems in rat brain: evidence for colocalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):3062–3066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Roth K. A., Evans C. J., Chang J. K., Barchas J. D. Immunohistochemical localization of dynorphin (1-8) in hypothalamic magnocellular neurons: evidence for absence of proenkephalin. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1761–1764. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]