Abstract
The gene for protein A from Staphylococcus aureus was cloned into pBR322 in Escherichia coli. An immunoassay was used to detect production of the protein. Protein A produced in E. coli was found in the periplasmic space and was purified and concentrated by IgG-Sepharose affinity chromatography. DNA sequence assay of the gene revealed a region with the general features of a prokaryotic signal peptide and a fifth structural region homologous to the four repetitive regions found earlier by amino acid sequence determination of the mature protein. Upstream from the structural gene there is a possible promoter region and a ribosomal binding sequence typical of gram-positive bacteria. The initiation codon is TTG.
Full text
PDF
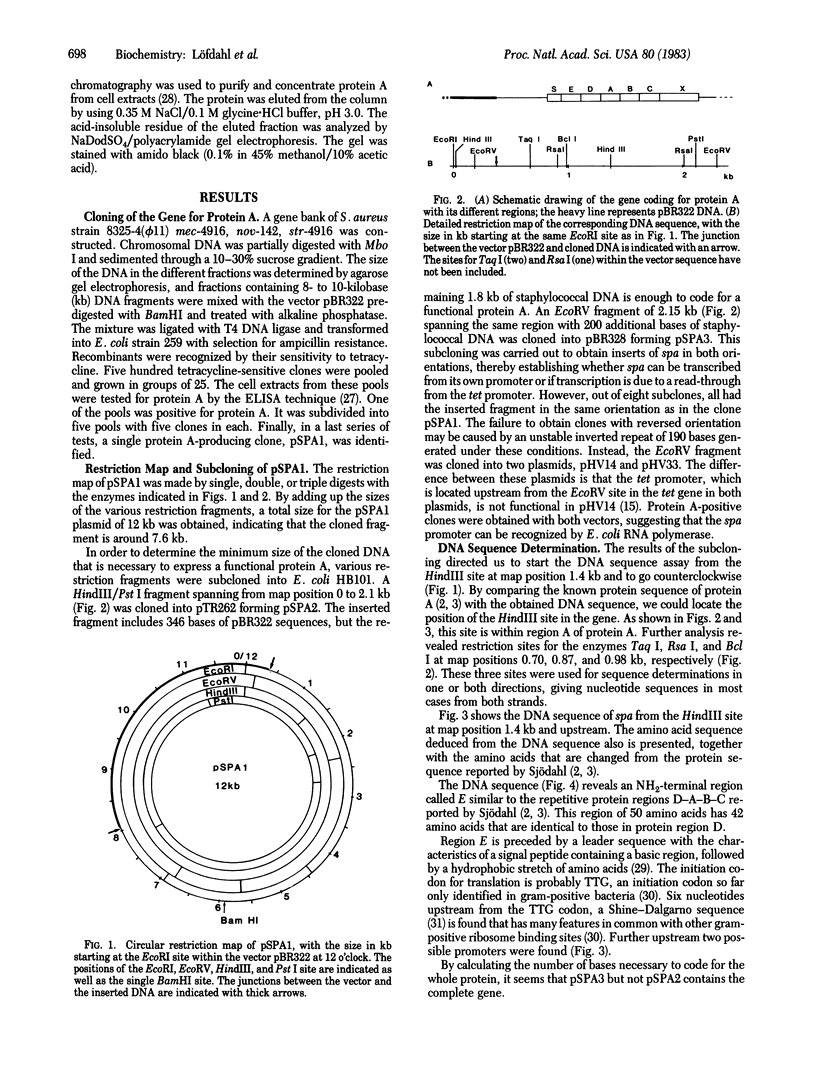
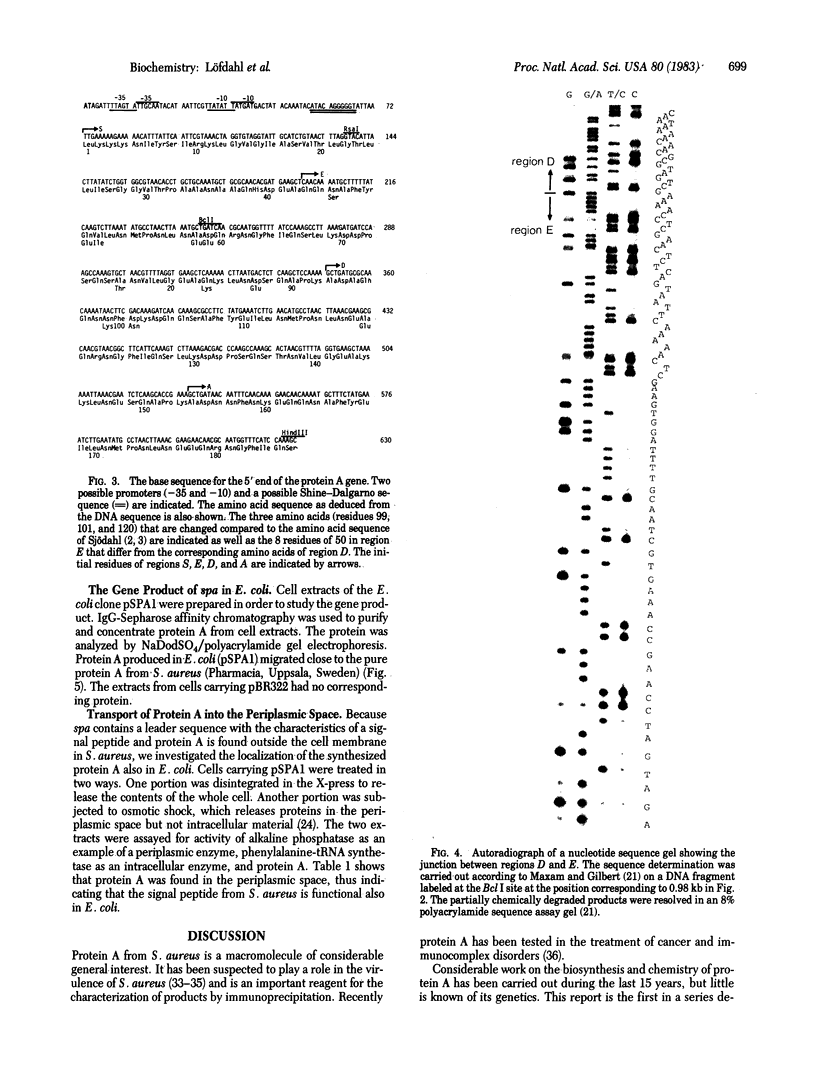


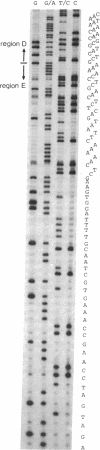
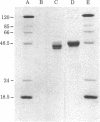
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bansal S. C., Bansal B. R., Thomas H. L., Siegel P. D., Rhoads J. E., Jr, Cooper D. R., Terman D. S., Mark R. Ex vivo removal of serum IgG in a patient with colon carcinoma: some biochemical, immunological and histological observations. Cancer. 1978 Jul;42(1):1–18. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197807)42:1<1::aid-cncr2820420102>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Petersson B. A., Sjöquist J. Some physiochemical properties of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):579–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A. Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus mutants in general and local infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):564–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPEL L. A., HARKNESS D. R., HILMOE R. J. A study of the substrate specificity and other properties of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:841–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Halegoua S. Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;7(4):339–371. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelenc P. C. Rapid purification of highly active ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90472-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroyer J., Chang S. The promoter-proximal region of the Bacillus licheniformis penicillinase gene: Nucleotide sequence and predicted leader peptide sequence. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmark R., Movitz J., Sjöquist J. Extracellular protein A from a methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 15;74(3):623–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G. Location of DNA methylation genes on the Escherichia coli K-12 genetic map. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 14;127(1):47–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00267782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B., Palla E., Niaudet B., Ehrlich S. D. DNA cloning in Bacillus subtilis. III. Efficiency of random-segment cloning and insertional inactivation vectors. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movitz J. A study on the biosynthesis of protein A in Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Oct 1;48(1):131–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movitz J. Formation of extracellular protein A by Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):291–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S. Resistance against Staphylococcus aureus. JAMA. 1971 Dec 13;218(11):1671–1673. doi: 10.1001/jama.218.11.1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Batten P. L., Murray K. Restriction of bacteriophage lambda by Escherichia coli K. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 15;81(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva I., Pettersson R. F., Kalkkinen N., Lehtovaara P., Sarvas M., Söderlund H., Takkinen K., Käriäinen L. Nucleotide sequence of the promoter and NH2-terminal signal peptide region of the alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Signäs C., Philipson L. Purification and characterization of an early glycoprotein from adenovirus type 2-infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):938–948. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.938-948.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Swanberg S. L., Poteete A., Riedel G., Backman K. A plasmid cloning vehicle allowing a positive selection for inserted fragments. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström J. E., Löfdahl S., Philipson L. Transformation reveals a chromosomal locus of the gene(s) for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):905–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.905-915.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B. Construction of a colicin E1-R factor composite plasmid in vitro: means for amplification of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.354-362.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. G., Jelenc P. C., Ehrenberg M., Kurland C. G. Rate of elongation of polyphenylalanine in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(1):193–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad S., Ericson C. Sensitized sheep red cells as a reactant for Staphylococcus aureus protein A. Methodology and epidemiology with special reference to weakly reacting methicillin-resistant strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]