Abstract
Rat adrenal mitochondria accumulated cholesterol during ether stress in vivo when side-chain cleavage was inhibited by aminoglutethimide (control = 14.6 vs. aminoglutethimide = 26.5 micrograms of cholesterol per mg of protein). This accumulation was insensitive to simultaneous administration of cycloheximide (24.2 micrograms/mg), but side chain cleavage in the mitochondria was greatly decreased. Outer and inner mitochondrial membrane fractions were separated by discontinuous Ficoll gradient centrifugation. Quantitation of marker enzymes for inner, outer, and microsomal enzymes indicated that outer membranes contained less than 5% inner membranes. The inner membrane fraction contained less than 7% outer membrane and included 90% of mitochondrial cytochrome P-450. Electron microscopy revealed outer membranes as circular intact ghosts, whereas inner membranes were largely intact and retained vesicular structure typical of intact adrenal cortex mitochondria. Administration of aminoglutethimide effected a 2-fold increase in inner membrane cholesterol (9.4 vs. 20.1 micrograms/mg) but simultaneous administration of cycloheximide completely blocked this increase (10.9 micrograms/mg). We conclude that: (i) in the presence of aminoglutethimide, stress stimulates accumulation of cholesterol in the inner membrane of adrenal mitochondria; and (ii) transfer of cholesterol from outer to inner membranes requires a cycloheximide-sensitive agent.
Full text
PDF

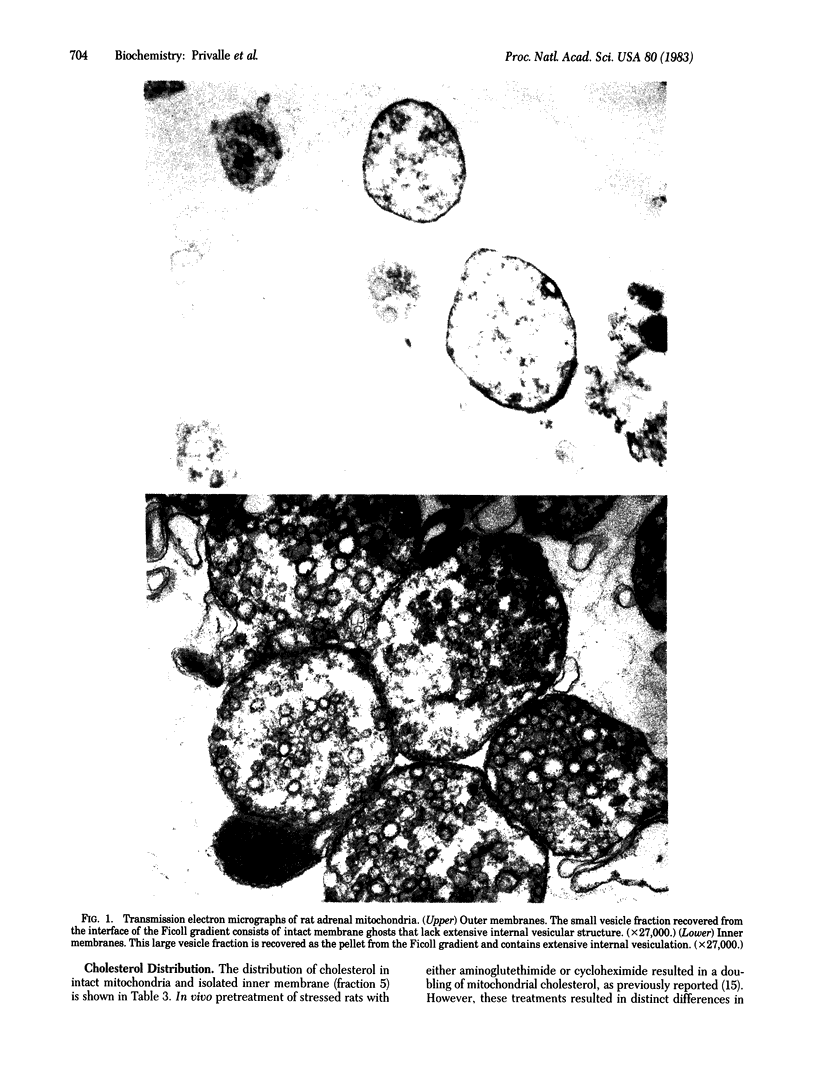


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backer J. M., Dawidowicz E. A. The rapid transmembrane movement of cholesterol in small unilamellar vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 8;551(2):260–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Kovanen P. T., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated uptake of lipoprotein-cholesterol and its utilization for steroid synthesis in the adrenal cortex. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1979;35:215–257. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571135-7.50009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P. F., Kimura T. Topological studies of cytochromes P-450scc and P-45011 beta in bovine adrenocortical inner mitochondrial membranes. Effects of controlled tryptic digestion. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10443–10448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crivello J. F., Jefcoate C. R. Intracellular movement of cholesterol in rat adrenal cells. Kinetics and effects of inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8144–8151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crivello J. F., Jefcoate C. R. Mechanisms of corticotropin action in rat adrenal cells. I. The effects of inhibitors of protein synthesis and of microfilament formation on corticosterone synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;542(2):315–329. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Sabir A. M. Polyphosphoinositides:stimulator of mitochondrial cholesterol side chain cleavage and possible identification as an adrenocorticotropin-induced, cycloheximide-sensitive, cytosolic, steroidogenic factor. Endocrinology. 1980 Jun;106(6):1869–1879. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-6-1869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Sabir A. M., Vandor S. L., Larson R. E. Are polyphosphoinositides the cycloheximide-sensitive mediator in the steroidogenic actions of adrenocorticotropin and adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate? J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5728–5734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garren L. D., Gill G. N., Masui H., Walton G. M. On the mechanism of action of ACTH. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1971;27:433–478. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571127-2.50035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefcoate C. R., Simpson E. R., Boyd G. S., Brownie A. C., Orme-Johnson W. H. The detection of different states of the P-450 cytochromes in adrenal mitochondria: changes induced by ACTH. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973;212:243–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefcoate C. R., Simpson E. R., Boyd G. S., Brownie A. C., Orme-Johnson W. H. The detection of different states of the P-450 cytochromes in adrenal mitochondria: changes induced by ACTH. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973;212:243–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefcoate C. R., Simpson E. R., Boyd G. S. Spectral properties of rat adrenal-mitochondrial cytochrome P-450. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):539–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Faust J. R., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Low density lipoprotein receptors in bovine adrenal cortex. I. Receptor-mediated uptake of low density lipoprotein and utilization of its cholesterol for steroid synthesis in cultured adrenocortical cells. Endocrinology. 1979 Mar;104(3):599–609. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-3-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambeth J. D. Cytochrome P-450scc. Cardiolipin as an effector of activity of a mitochondrial cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4757–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambeth J. D., Kitchen S. E., Farooqui A. A., Tuckey R., Kamin H. Cytochrome P-450scc-substrate interactions. Studies of binding and catalytic activity using hydroxycholesterols. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1876–1884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Dolde J., Steck T. L. The rate of transmembrane movement of cholesterol in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5321–5323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen R. C., Brownie A. C. Adrenocortical response to corticotropin is potentiated by part of the amino-terminal region of pro-corticotropin/endorphin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2239–2243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purvis J. L., Canick J. A., Mason J. I., Estabrook R. W., McCarthy J. L. Lifetime of adrenal cytochrome P-450 as influenced by ACTH. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973;212:319–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE D., HECHTER O. Studies on ACTH action in perfused bovine adrenals: the site of action of ACTH in corticosteroidogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Aug;51(2):457–469. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., Boyd G. S. Partial resolution of the mixed-function oxidase involved in the cholesterol side-chain cleavage reaction in bovine adrenal mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 27;28(6):945–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R. Cholesterol side-chain cleavage, cytochrome P450, and the control of steroidogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Mar;13(3):213–227. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., Jefcoate C. R., Brownie A. C., Boyd G. S. The effect of ether anaesthesia stress on cholesterol-side-chain cleavage and cytochrome P450 in rat-adrenal mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):442–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., McCarthy J. L., Peterson J. A. Evidence that the cycloheximide-sensitive site of adrenocorticotropic hormone action is in the mitochondrion. Changes in pregnenolone formation, cholesterol content, and the electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3135–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer T. P. Determination of the activity of succinate, NADH, choline, and alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenases. Methods Biochem Anal. 1974;22:123–175. doi: 10.1002/9780470110423.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trzeciak W. H., Boyd G. S. The effect of stress induced by ether anaesthesia on cholesterol content and cholesteryl-esterase activity in rat-adrenal cortex. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 17;37(2):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yago N., Ichii S. Submitochondrial distribution of components of the steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase and cholesterol sidechain-cleaving enzyme systems in hog adrenal cortex. J Biochem. 1969 Feb;65(2):215–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



