Abstract
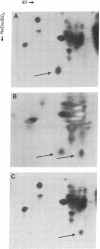
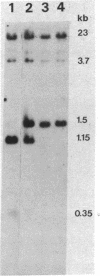
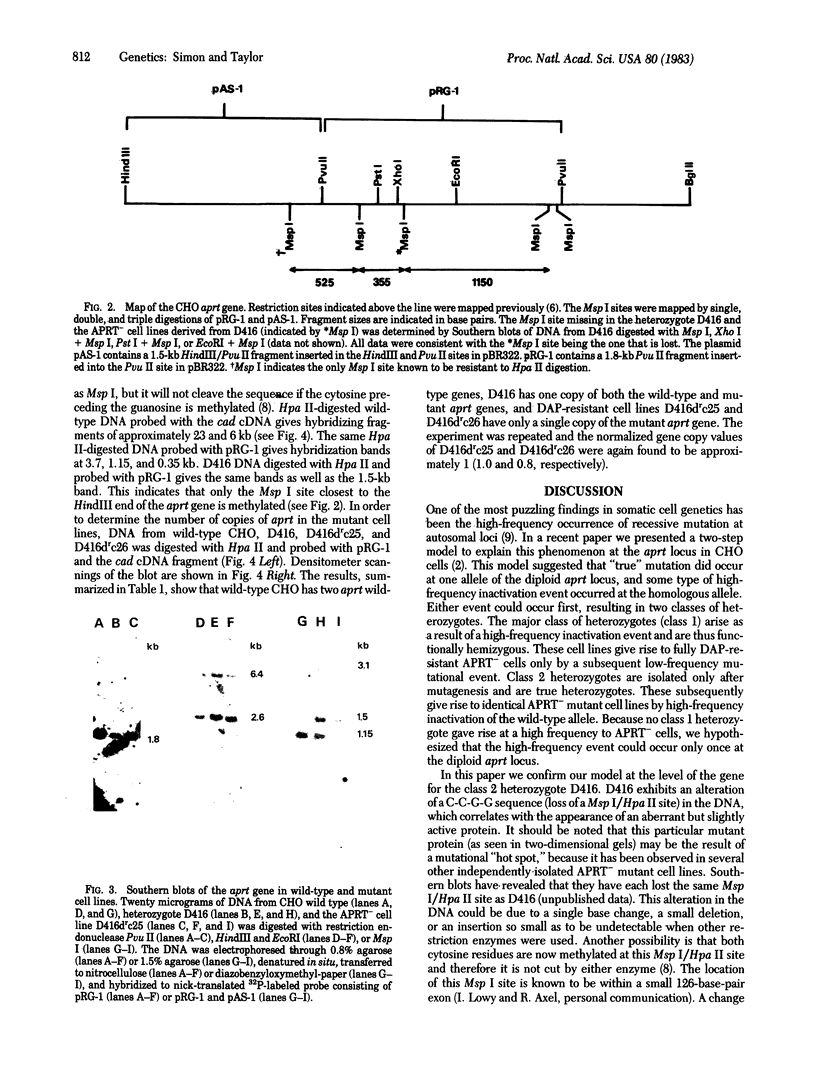
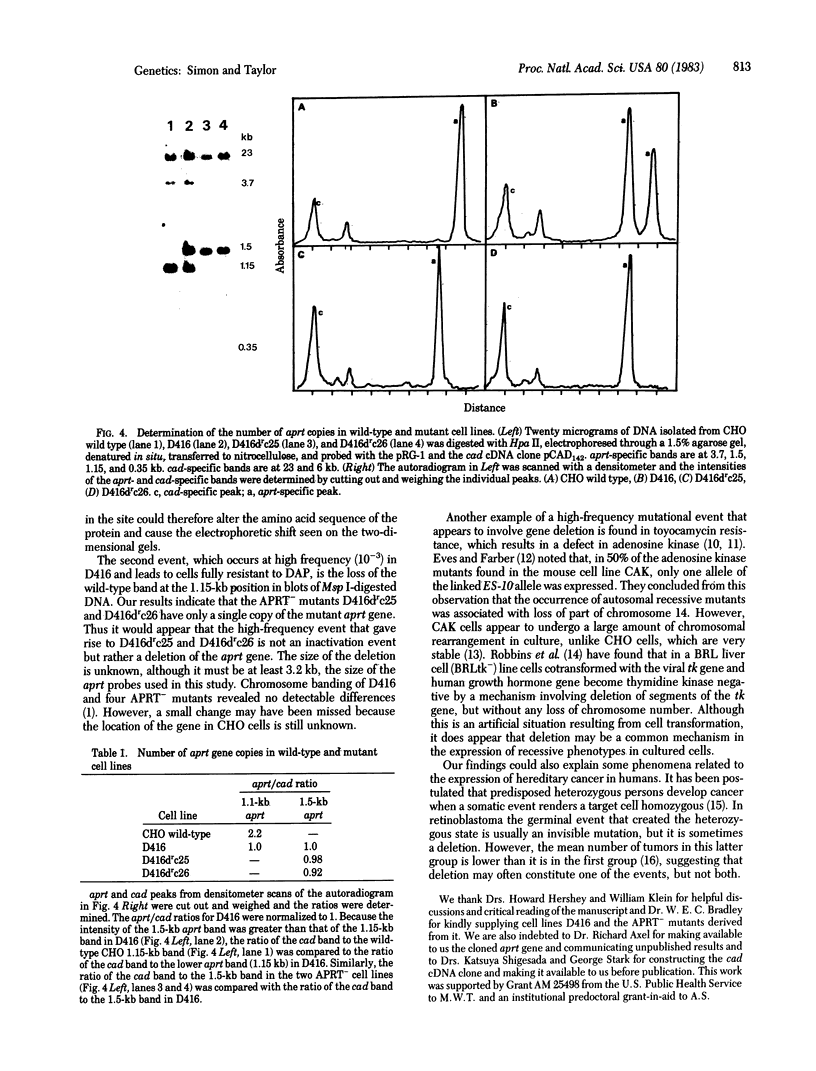
Evidence for a two-step model to explain the high-frequency expression of the recessive phenotype at the autosomal adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT; EC 2.4.2.7) locus in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells was given by Simon et al. [Simon, A. E., Taylor, M. W., Bradley, W. E. C. & Thompson, L. (1982) Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 1126-1133]. This model proposed a high-frequency event, leading to allelic inactivation or a loss of gene function, and a low-frequency event, causing a structural alteration of the APRT protein. Either event could occur first, resulting in two classes of heterozygotes. We have analyzed the low-frequency event that gave rise to the class 2 aprt heterozygote D416 and the high-frequency event that led to APRT- cells derived from D416. Genomic Southern blots of Msp I- or Hpa II-digested DNA from wild-type CHO, aprt heterozygote D416, and two APRT- cell lines derived from D416 indicate a loss of a specific Msp I/Hpa II recognition sequence at one aprt locus in the heterozygote that correlates with the production of the electrophoretically altered APRT protein found in D416. The APRT- mutants are homozygous for the loss of this Msp I/Hpa II site. By using an additional CHO gene as an internal control, it was determined that the APRT- mutants contain only a single copy of the altered aprt gene. Thus, the high-frequency event that produces APRT- mutants derived from D416 is not an inactivation event but rather a deletion of the wild-type aprt gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley W. E., Letovanec D. High-frequency nonrandom mutational event at the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (aprt) locus of sib-selected CHO variants heterozygous for aprt. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Jan;8(1):51–66. doi: 10.1007/BF01538650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eves E. M., Farber R. A. Chromosome segregation is frequently associated with the expression of recessive mutations in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1768–1772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. Genetic and biochemical characterization of mutants of CHO cells resistant to the protein synthesis inhibitor trichodermin. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 May;4(3):355–374. doi: 10.1007/BF01542848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr Retinoblastoma: a prototypic hereditary neoplasm. Semin Oncol. 1978 Mar;5(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy I., Pellicer A., Jackson J. F., Sim G. K., Silverstein S., Axel R. Isolation of transforming DNA: cloning the hamster aprt gene. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90558-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin M. S., Gottesman M. M. High frequency of mutation to tubercidin resistance in CHO cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Sep;5(5):571–583. doi: 10.1007/BF01542695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Axel R., Henderson A. S. Chromosome structure and DNA sequence alterations associated with mutation of transformed genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(3):191–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch L. On the nature of hereditable variation in cultured somatic cells. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. E., Taylor M. W., Bradley W. E., Thompson L. H. Model involving gene inactivation in the generation of autosomal recessive mutants in mammalian cells in culture. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1126–1133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong L. C., Riccardi V. M., Ferrell R. E., Sparkes R. S. Familial retinoblastoma and chromosome 13 deletion transmitted via an insertional translocation. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1501–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.7280668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Flavell R. A. MspI, an isoschizomer of hpaII which cleaves both unmethylated and methylated hpaII sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3231–3236. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Gene amplification causes overproduction of the first three enzymes of UMP synthesis in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8679–8689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton R. G., Ho C. C., Duff C. Chromosome stability in CHO cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Jan;3(1):27–45. doi: 10.1007/BF01550985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]