Abstract
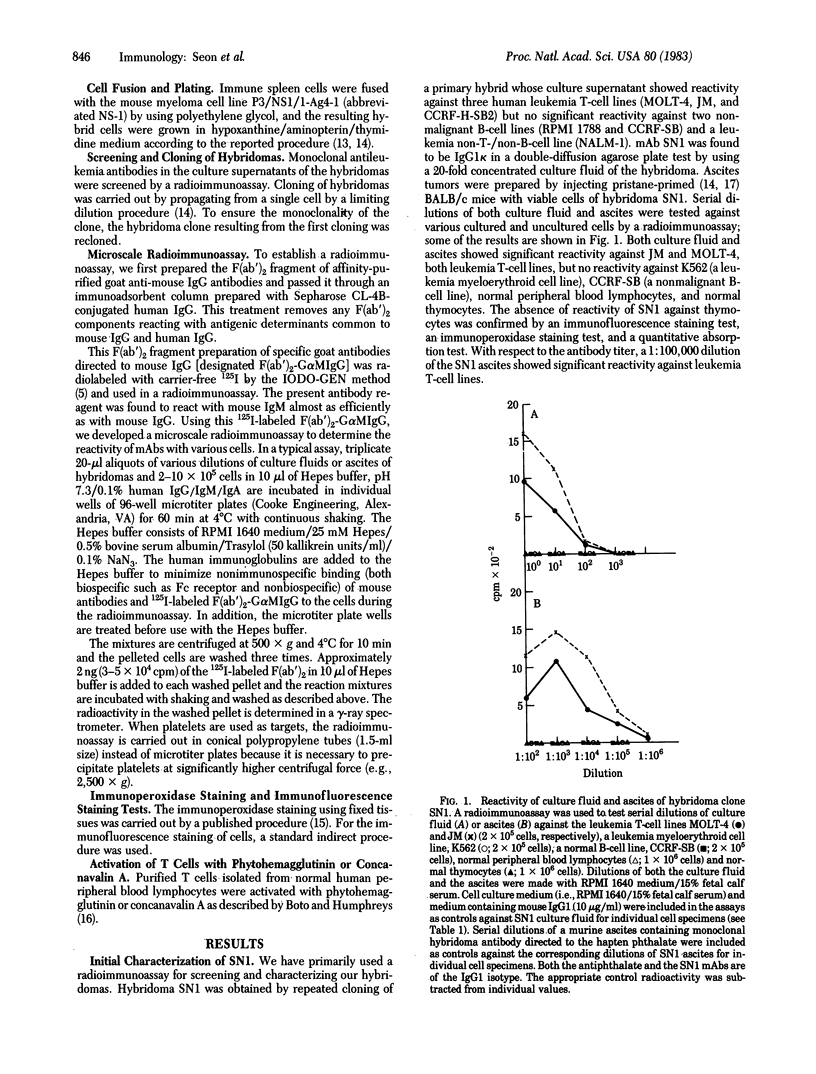
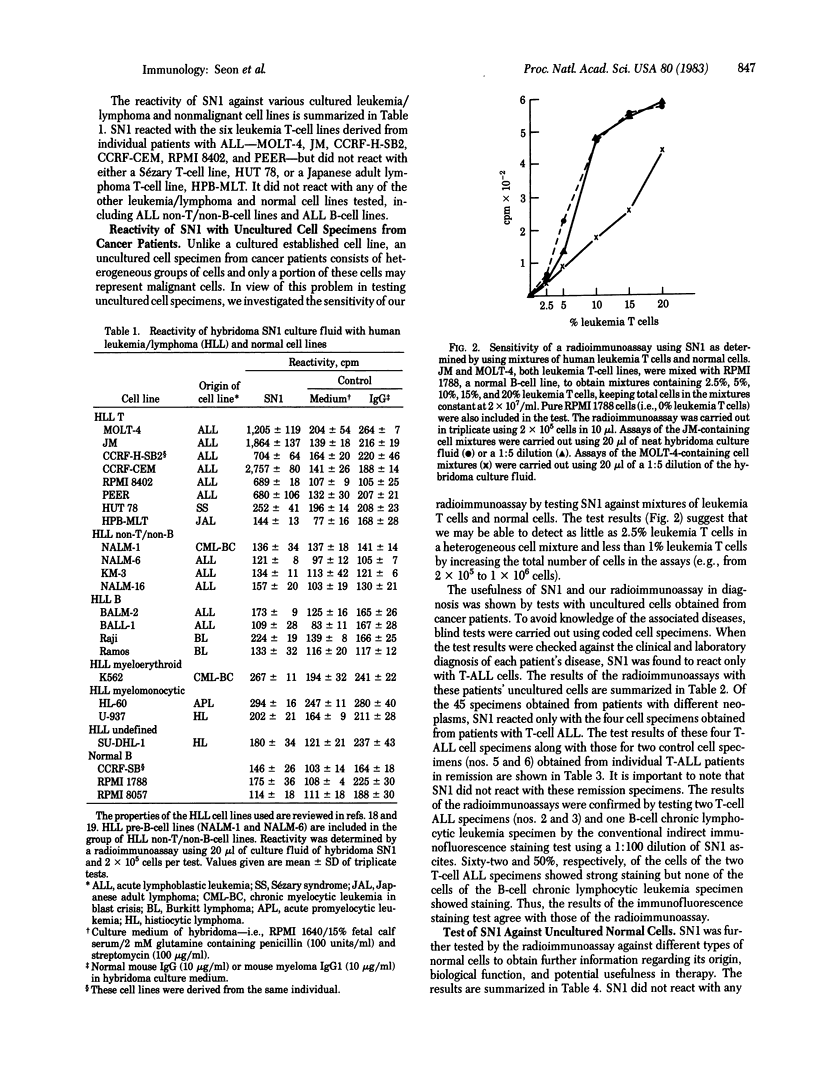
We have generated and characterized a hybridoma monoclonal antibody, termed SN1, that defines a unique human T-cell leukemia antigen. This antibody was generated by using a human leukemia antigen preparation isolated from cell membranes of MOLT-4, a leukemia T-cell line derived from a patient with T-cell-type acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). SN1 was characterized by a sensitive microscale radioimmunoassay using a variety of cultured and uncultured human cells. In selected cases, the cell specimens were further tested by immunoperoxidase staining and an immunofluorescence staining test. The results of the radioimmunoassay were in agreement with those of the two other tests. Among the various cultured malignant and nonmalignant cell lines, SN1 reacted only with leukemia T-cell lines derived from patients with T-ALL; it reacted with all six T-ALL cell lines tested—i.e., JM, CCRF-CEM, CCRF-H-SB2, RPMI 8402, PEER, and MOLT-4. In the case of uncultured cell specimens derived from cancer patients, SN1 reacted with four of four cases of T-ALL but did not react with specimens derived from 41 patients with other types of cancer. SN1 did not react with any normal human cell specimens tested, both cultured and uncultured. These specimens include normal lymphoblastoid cell lines, thymocytes, bone marrow cells, spleen cells, lymph node cells, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, lymphocytes containing B and T cells, purified T cells, monocytes, granulocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets. Furthermore, SN1 did not react with phytohemagglutinin-activated T cells nor with concanavalin A-activated T cells. The results show that monoclonal antibody SN1 defines a type of human leukemia antigen that is expressed on the cell surface of T-cell-type ALL cells. The results further show the usefulness of SN1 in the diagnosis of cancer patients and suggest its therapeutic potential. We designate this antigen TALLA, a T-cell ALL antigen.
Keywords: cell membrane antigen, hybridoma, radioimmunoassay, immunodiagnosis
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger N. L., Majerus P. W. Isolation of human platelets and platelet surface membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:149–155. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billing R., Minowada J., Cline M., Clark B., Lee K. Acute lymphocytic leukemia-associated cell membrane antigen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Aug;61(2):423–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boto W. O., Humphreys R. E. Variation in the synthesis of membrane proteins of human T lymphocytes during mitogenic activation: recognition of a 70,000 dalton protein with anti-p23,30 heteroantiserum and a novel 42,000 dalton protein with anti-p44,12 heteroantiserum. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyum A. Separation of blood leucocytes, granulocytes and lymphocytes. Tissue Antigens. 1974;4(4):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng C., Terasaki P., Chia J., Billing R. Monoclonal antibody specific for human T acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):10–11. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowell B. L., Falletta J. M., Moore J. O., Metzgar R. S. Detection and partial characterization of human thymus-leukemia antigens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Oct;65(4):691–701. doi: 10.1093/jnci/65.4.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F. Analysis of the clinical and biological significance of lymphoid phenotypes in acute leukemia. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 2):4752–4766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G., Rapson N. T., Lister T. A. Antisera to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Glycosphingolipids in cellular interaction, differentiation, and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:733–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han T., Takita H. Depression of T lymphocyte response by non-T suppressor cells in lung cancer patients: a possible prognostic value of suppressor-cell activity. Cancer. 1979 Dec;44(6):2090–2098. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197912)44:6<2090::aid-cncr2820440620>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBien T. W., Hurwitz R. L., Kersey J. H. Characterization of a xenoantiserum produced against three molar KCl-solubilized antigens obtained from a non-T, non-B (pre-B) acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):82–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Pilch J. R., Galfré G., Mason D. Y., Fabre J. W., Milstein C. A human thymocyte antigen defined by a hybrid myeloma monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):205–210. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Lennox E. The use of monoclonal antibody techniques in the study of development cell surfaces. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1980;14(Pt 2):1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Janossy G., Greaves M. F., Tsubota T., Srivastava B. I., Morikawa S., Tatsumi E. Expression of an antigen associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in human leukemia-lymphoma cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Jun;60(6):1269–1277. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.6.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Koshiba H., Sagawa K., Kubonishi I., Lok M. S., Tatsumi E., Han T., Srivastava B. I., Ohnuma T. Marker profiles of human leukemia and lymphoma cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1981;101(1):91–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00405069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa S., Tatsumi E., Baba M., Harada T., Yasuhira K. Two E-rosette-forming lymphoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1978 Feb 15;21(2):166–170. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara K., Ohashi T., Oda T., Hirano T., Kasai M., Okumura K., Tada T. Asialo GM1 as a cell-surface marker detected in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1980 Mar 20;302(12):674–677. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198003203021208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro S., Seon B. K. Several new monoclonal antibodies directed to human T-cell leukemia antigens. Cancer Res. 1982 Oct;42(10):4259–4262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro S., Seon B. K. Strong, specific anti-human leukemia antisera prepared with the use of purified cell membrane antigen. Cancer Res. 1981 Jul;41(7):2973–2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Immunoglobulin-producing tumors and myeloma proteins of mice. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):631–719. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Pesando J. M., Notis-McConarty J., Lazarus H., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody to human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):583–585. doi: 10.1038/283583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlossman S. F., Chess L., Humphreys R. E., Strominger J. L. Distribution of Ia-like molecules on the surface of normal and leukemic human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1288–1292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seon B. K., Negoro S., Minowada J., Yoshizaki K. Human T cell leukemia antigens on the cell membranes: purification molecular characterization, and preparation of specific antisera. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2580–2588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R., Ault K. A. Increase of surface Ia-like antigen expression on human monocytes independent of antigenic stimuli. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):2020–2027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Bonk A., Tolksdorf G., Lennert K., Rodt H., Gerdes J. Immunohistologic analysis of the organization of normal lymphoid tissue and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Aug;28(8):746–760. doi: 10.1177/28.8.7003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigaki N., Tokuyama H., Fukunishi T., Minowada J., Pressman D. Human cell membrane components dominant in T cell lineage: identification and characterization of human TL-like antigens. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2906–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veit B. C., Melvin S. L., Bowman W. P. Identification of a leukemia-associated antigen of human acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Jun;64(6):1321–1328. doi: 10.1093/jnci/64.6.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki K., Seon B. K., Barcos M. P., Minowada J., Pressman D. Detection and characterization of human leukemia-associated antigens on leukemic cell lines and thymocytes. I. Characterization of baboon and rabbit antisera to MOLT-4. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1943–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


