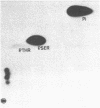
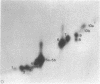
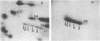
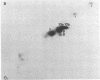
Abstract
The amino acids and tryptic peptides that become phosphorylated in 40S ribosomal protein S6 after serum stimulation of quiescent 3T3 cells were examined by two-dimensional thin-layer electrophoresis. In the maximally phosphorylated form of the protein, most of the phosphate was incorporated into serine and a small amount, into threonine. Digestion of this form of the protein with trypsin revealed 10 major phosphopeptides. All 10 contained phosphoserine and 2 of the 10 also contained phosphothreonine. Next, the five forms of increasingly phosphorylated S6 were individually separated on two-dimensional polyacrylamide gels or total S6 was isolated from cells that were stimulated for only a short time and their phosphotryptic maps were analyzed. The results showed that, as larger amounts of phosphate were added to S6, the phosphopeptides appeared in a specific order.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. M., Grundholm A., Sells B. H. Modification of ribosomal proteins during liver regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):669–676. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger D. G., Hunt T. Fertilization of sea urchin eggs is accompanied by 40 S ribosomal subunit phosphorylation. Dev Biol. 1981 Oct 30;87(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in avian sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4112–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., McConkey E. H. Preferential utilization of phosphorylated 40-S ribosomal subunits during initiation complex formation. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):535–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., McConkey E. H. Rapid alterations in initiation rate and recruitment of inactive RNA are temporally correlated with S6 phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):539–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gressner A. M., Wool I. G. The phosphorylation of liver ribosomal proteins in vivo. Evidence that only a single small subunit protein (S6) is phosphorylated. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6917–6925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Humbel R. E., Thomas G. Insulin-like growth factor: insulin or serum increase phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of stationary chick embryo fibroblasts into early G1 phase of the cell cycle. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W., Kiernan J. A. Control of the initiation of DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells: low-molecular weight nutrients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2942–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. A., Traugh J. A., Croser E. A., Traut R. R. Ribosomal proteins from rabbit reticulocytes: number and molecular weights of proteins from ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 15;93(3):391–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastick S. M., McConkey E. H. Control of ribosomal protein phosphorylation in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):917–923. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91560-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastick S. M., McConkey E. H. HeLa ribosomal protein S6. Insulin and dibutyryl cyclic AMP affect different phosphopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):583–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastick S. M., Nielsen P. J., McConkey E. H. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in suspension cultured HeLa cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):223–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00693074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Manchester K. L., Towbin H., Gordon J., Thomas G. The phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in rat tissues following cycloheximide injection, in diabetes, and after denervation of diaphragm. A simple immunological determination of the extent of S6 phosphorylation on protein blots. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12316–12321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Thomas G., Maller J. L. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg P. G., Harris T. J., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. O4-(5'-uridylyl)tyrosine is the bond between the genome-linked protein and the RNA of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4868–4872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Bowman P. D., Gordon J. The isolation and analysis of polysomes and ribosomal RNA from cells growing in monolayer culture. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Sep;108(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(77)80032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Gordon J. Multiple phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of quiescent 3T3 cells into early G1, and cellular compartmentalization of the phosphate donor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Kubler A. M., Gordon J., Jimenez de Asua L. Regulation of 40S ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1015–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Cohen P. Isolation and characterisation of cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation sites from rat liver ribosomal protein S6. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Partial purification and characterization of the maturation-promoting factor from eggs of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Grande R. W., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of 40-S ribosomal subunits by cAMP-dependent, cGMP-dependent and protease-activated protein kinases. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]