Abstract
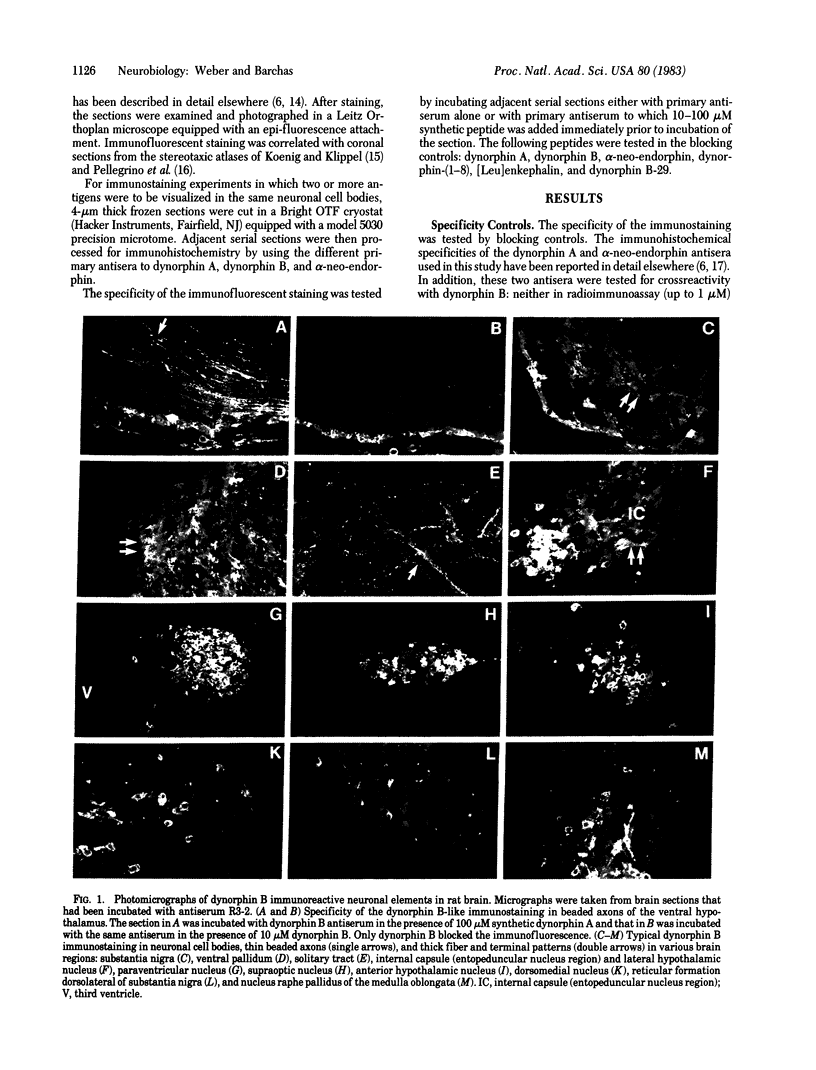
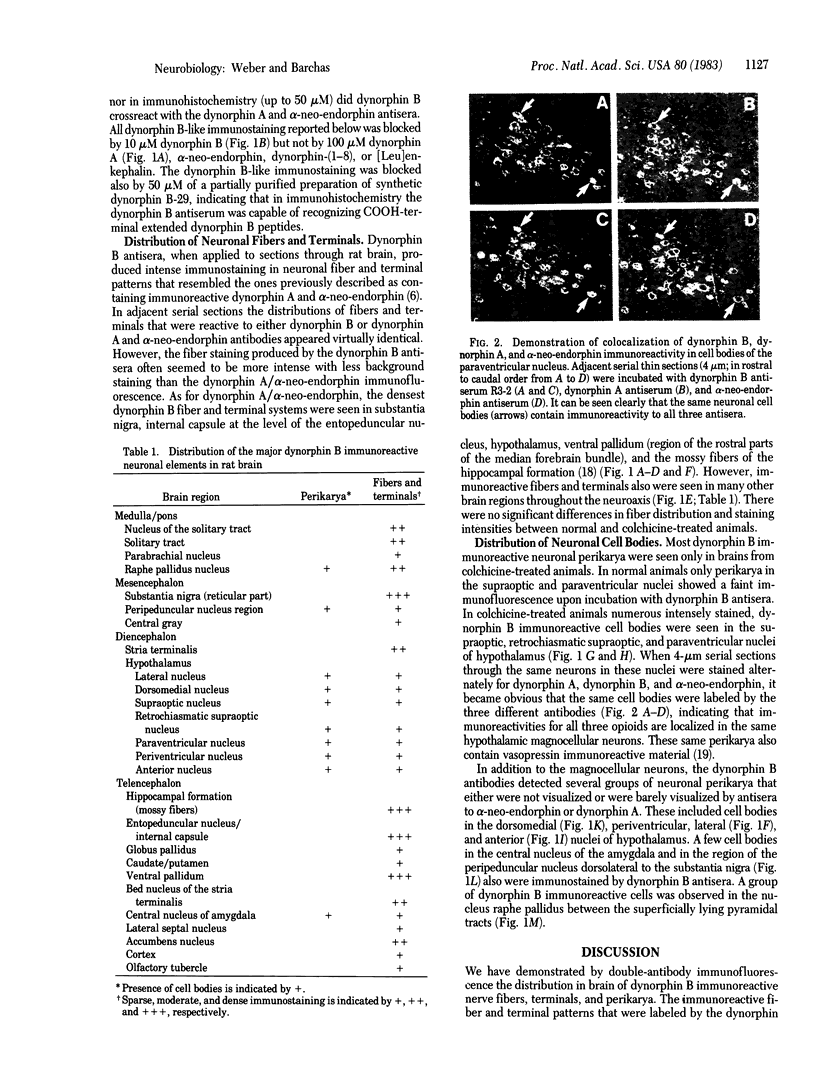
A specific antiserum was prepared against dynorphin B, an endogenous opioid peptide contained in a recently isolated 4,000-dalton dynorphin. The antiserum did not crossreact with dynorphin A, alpha-neo-endorphin, beta-neo-endorphin, dynorphin-(1-8), or [Leu]enkephalin. In immunohistochemical staining experiments on frozen sections through rat brains from normal and colchicine-treated animals, the antiserum labeled the same neuronal fiber systems previously described as containing both dynorphin A and alpha-neo-endorphin immunoreactive material. The alpha-neo-endorphin/dynorphin A immunoreactive perikarya in the hypothalamic magnocellular nuclei also were labeled by the dynorphin B antiserum. In addition, the dynorphin B antiserum revealed groups of immunoreactive neuronal cell bodies in several other hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic areas, including brain-stem, midbrain, central nucleus of amygdala, and in the dorsomedial, lateral, and anterior nuclei of hypothalamus. These perikarya had not been detected in previous studies that used dynorphin A and alpha-neo-endorphin antisera. The findings are in agreement with recent studies demonstrating a common precursor for dynorphin A, dynorphin B, and alpha-neo-endorphin. The apparently wider distribution of dynorphin B immunoreactive cell bodies compared to alpha-neo-endorphin/dynorphin A immunoreactive perikarya may be a reflection of differential processing of the precursor in different brain regions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. D., Paterson S. J., McKnight A. T., Magnan J., Kosterlitz H. W. Dynorphin and dynorphin are ligands for the kappa-subtype of opiate receptor. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):79–81. doi: 10.1038/299079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischli W., Goldstein A., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Isolation and amino acid sequence analysis of a 4,000-dalton dynorphin from porcine pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5435–5437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazarossian V. E., Chavkin C., Goldstein A. A specific radioimmunoassay for the novel opioid peptide dynorphin. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 7;27(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Fischli W., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Porcine pituitary dynorphin: complete amino acid sequence of the biologically active heptadecapeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7219–7223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Tachibana S., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Dynorphin-(1-13), an extraordinarily potent opioid peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6666–6670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Noda M., Morimoto Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for porcine beta-neo-endorphin/dynorphin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):245–249. doi: 10.1038/298245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Wahlström A., Lahm H. W., Blacher R., Ezra E., Fleminger G., Udenfriend S. Characterization of rimorphin, a new [leu]enkephalin-containing peptide from bovine posterior pituitary glands. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1849–1852. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinty J. F., Henriksen S. J., Goldstein A., Terenius L., Bloom F. E. Dynorphin is contained within hippocampal mossy fibers: immunochemical alterations after kainic acid administration and colchicine-induced neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):589–593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Kajiwara M., Watanabe Y., Ishizuka Y., Matsumiya T. The choice of opiate receptor subtype by neo-endorphins. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 23;79(3-4):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90636-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Takagi H. A note on the use of picric acid-paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative for correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience. 1982 Jul;7(7):1779–1783. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., De Martino C., Zamboni L. Fixation of ejaculated spermatozoa for electron microscopy. Nature. 1967 Oct 14;216(5111):173–174. doi: 10.1038/216173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana S., Araki K., Ohya S., Yoshida S. Isolation and structure of dynorphin, an opioid peptide, from porcine duodenum. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):339–340. doi: 10.1038/295339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Fischli W., Goldstein A., Zimmerman E., Nilaver G., van wimersma Griedanus T. B. Dynorphin and vasopressin: common localization in magnocellular neurons. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.6121376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Ghazarossian V. E., Goldstein A. Dynorphin immunocytochemical localization in brain and peripheral nervous system: preliminary studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1260–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Khachaturian H., Coy D., Taylor L., Akil H. Dynorphin is located throughout the CNS and is often co-localized with alpha-neo-endorphin. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1773–1776. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Barchas J. D. Predominance of the amino-terminal octapeptide fragment of dynorphin in rat brain regions. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):77–79. doi: 10.1038/299077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Chang J. K., Barchas J. D. Antibodies specific for alpha-N-acetyl-beta-endorphins: radioimmunoassays and detection of acetylated beta-endorphins in pituitary extracts. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):436–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Chang J. K., Barchas J. D. Brain distributions of alpha-neo-endorphin and beta-neo-endorphin: evidence for regional processing differences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91834-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Samuelsson S. J., Barchas J. D. Novel peptide neuronal system in rat brain and pituitary. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1248–1251. doi: 10.1126/science.7029714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Roth K. A., Barchas J. D. Colocalization of alpha-neo-endorphin and dynorphin immunoreactivity in hypothalamic neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):951–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90902-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Roth K. A., Barchas J. D. Immunohistochemical distribution of alpha-neo-endorphin/dynorphin neuronal systems in rat brain: evidence for colocalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):3062–3066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]