Abstract
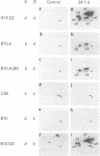
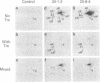
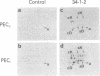
Immunoprecipitates obtained from [35S]methionine-labeled spleen cells by using monoclonal antibodies specific for H-2Kd and H-2Dd have been separated by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Analysis of these gel patterns revealed the presence of an additional product of the K end of the H-2d complex, designated here as H-2K'. To determine whether H-2K' is a unique protein or a differentially glycosylated form of the previously characterized H-2Kd histocompatibility antigen, nonglycosylated molecules labeled in the presence of tunicamycin were examined. The results showed that both H-2K and H-2K' have distinct nonglycosylated polypeptide precursor forms. The approximate molecular weight differences between the fully glycosylated and nonglycosylated molecules also indicated the presence of three oligosaccharide side chains on H-2K', as is the case with H-2Kd, whereas H-2Dd has only two oligosaccharide units. The cellular expression of H-2K' was also investigated. Comparison of H-2 antigens immunoprecipitated from normal spleen cells and from thioglycollate-induced adherent peritoneal exudate cells cultured in the presence or absence of supernatant fluids from concanavalin A-stimulated spleen cells revealed that H-2K' was not expressed on the adherent peritoneal cells. This indicates that H-2K' is expressed in a tissue-specific manner, unlike the classical histocompatibility antigens H-2K and H-2D.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cosman D., Khoury G., Jay G. Three classes of mouse H-2 messenger RNA distinguished by analysis of cDNA clones. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):73–76. doi: 10.1038/295073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. H-2 compatibility is required for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):502–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démant P., Iványi D. Further molecular complexities of H-2 K- and D-region antigens. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):146–149. doi: 10.1038/290146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démant P., Iványi D., Oudshoorn-Snoek M., Calafat J., Roos M. H. Molecular heterogeneity of H-2 antigens. Immunol Rev. 1981;60:5–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démant P., Roos M. H. Molecular heterogeneity of D-end products detected by anti-H-2.28 sera. I. A. molecule similar to Qa-2, detected in the BALB/cBy but not in the BALB/c-H-2dm2 mutant. Immunogenetics. 1982;15(5):461–466. doi: 10.1007/BF00345905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Ozato K., Melino M. R., Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J., Jandinski J. J., Sachs D. H. Immunochemical evidence in two haplotypes for at least three D region-encoded molecules, D, L, and R. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1713–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iványi D., Démant P. Molecular heterogeneity of D-end products detected by anti-H-2.28 sera. II. B10.D2(M504) (H-2dm1) mutant fails to express one of the two H-2.4-, 28 + Dd region molecules. Immunogenetics. 1982;15(5):467–476. doi: 10.1007/BF00345906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iványi D., Démant P. Serological characterization of previously unknown H-2 molecules identified in the products of the Kd and Dk region. Immunogenetics. 1981;12(3-4):397–408. doi: 10.1007/BF01561679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P. Aberrant Ae (E beta) Ia polypeptide chain in H-2g2 haplotype mice. Possible result of an intragenic recombination or mutation. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1453–1458. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P. Analysis of H-2 and Ia molecules by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1261–1279. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball E. S., Maloy W. L., Coligan J. E. Evidence for three carbohydrate prosthetic groups on mouse histocompatibility antigens H-2Kd and H-2Db. Mol Immunol. 1981 Jul;18(7):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Shreffler D. C. The H-2 model for the major histocompatibility systems. Transplant Rev. 1971;6:3–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1971.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer T., Hansen T. H., Camerini-Otero R. D., Sachs D. H. Analysis of the heterogeneity of the mouse H-2K, D, and L gene products. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2149–2156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Tanner W. The specific site of tunicamycin inhibition in the formation of dolichol-bound N-acetylglucosamine derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80922-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas J. M., King D. P., Jones P. P. Biosynthesis and expression of Ia and H-2 antigens on a macrophage cell line are stimulated by products of activated spleen cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):449–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moosic J. P., Sung E., Nilson A., Jones P. P., McKean D. J. The selective solubilization of different murine splenocyte membrane fractions with lubrol WX and triton X-100 distinguishes two forms of Ia antigens. A cell surface (alpha, beta) and an intracellular (alpha, Ii, beta). J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9684–9691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn R., Nathenson S. G., Coligan J. E. Isolation, characterization and amino acid sequence studies of the cyanogen bromide fragments of the H-2Dd glycoprotein. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Jul;10(7):495–503. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N. M., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse major histocompatibility complex antigens. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):113–120. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. III. Hybridoma antibodies reacting to antigens of the H-2b haplotype reveal genetic control of isotype expression. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A. A., Schöld M., Itakura K., Wallace R. B. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the murine transplantation antigen H-2Kb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3270–3274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A. C., Erb P., Gisler R. H. Ia-bearing bone marrow-cultured macrophages induce antigen-specific helper T cells for antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):612–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung E., Jones P. P. The invariant chain of murine Ia antigens: its glycosylation, abundance and subcellular localization. Mol Immunol. 1981 Oct;18(10):899–913. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., Lampen O. Tunicamycin inhibition of polyisoprenyl N-acetylglucosaminyl pyrophosphate formation in calf-liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin J. H., Kvist S., Dobberstein B. Identification of an H-2Kd gene using a specific cDNA probe. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):467–471. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01192.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]