Abstract
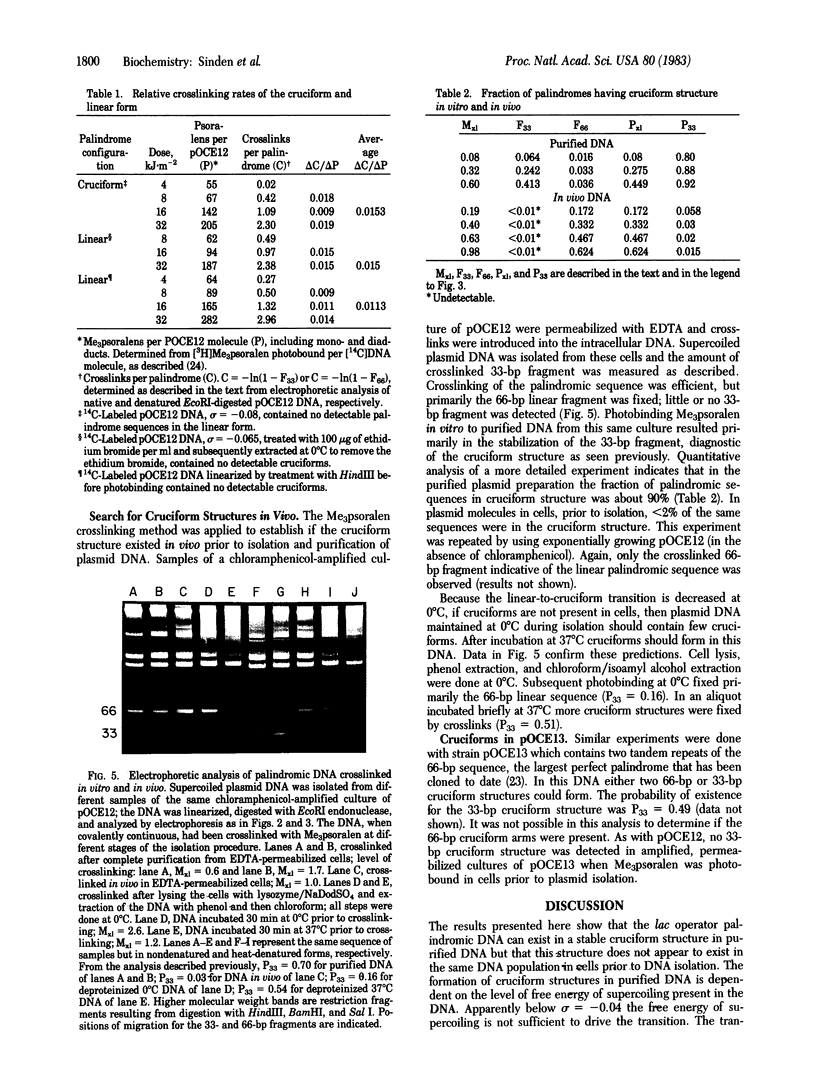
A perfect palindromic 66-base pair (bp) DNA sequence derived from the lac operator and cloned into plasmid pMB9 [Betz, J. L. & Sadler, J. R. (1981) Gene 13, 1-12] can exist in a 66-bp linear form or as two 33-bp cruciform arms. The fraction of the sequence in the cruciform depends on the superhelical density of the plasmid DNA. Relaxed DNA contains no cruciforms. The palindrome in the cruciform structure is cut by EcoRI endonuclease at the base of the cruciform arms, releasing 33-bp fragments; when in the linear form only 66-bp fragments are produced. The cruciform structure is fixed by trimethylpsoralen crosslinks in the cruciform arms. This together with the EcoRI cutting provides an assay for the cruciform structures in the DNA of living cells. Using this assay we show that the cruciform structure rarely if ever exists in vivo, but after DNA isolation greater than 90% of the sequence is in cruciforms. Results suggest that the plasmid DNA as organized in vivo either lacks sufficient torsional tension to form this cruciform or the palindrome is restrained in the linear form by other bound molecules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beerman T. A., Lebowitz J. Further analysis of the altered secondary structure of superhelical DNA. Sensitivity to methylmercuric hydroxide a chemical probe for unpaired bases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 25;79(3):451–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz J. L., Sadler J. R. Variants of a cloned synthetic lactose operator. I. A palindromic dimer lactose operator derived from one stand of the cloned 40-base pair operator. Gene. 1981 Jan-Feb;13(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Pardue M. L. Electron microscopy of DNA crosslinked with trimethylpsoralen: test of the secondary structure of eukaryotic inverted repeat sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2644–2648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. S. Light-induced cross-linking of DNA in the presence of a furocoumarin (psoralen). Studies with phage lambda, Escherichia coli, and mouse leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 17;217(1):30–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S., Ojala D., Posakony J., Nishiguchi J., Attardi G. Nucleotide sequence of a region of human mitochondrial DNA containing the precisely identified origin of replication. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):192–198. doi: 10.1038/277192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Müller-Hill B. Isolation of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1891–1898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T. S., Wang J. C. Thermodynamic properties of superhelical DNAs. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):527–535. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Studies on the permeability change produced in coliform bacteria by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2373–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. Hairpin-loop formation by inverted repeats in supercoiled DNA is a local and transmissible property. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1271–1289. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. In vivo consequences of plasmid topology. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):380–382. doi: 10.1038/292380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M., Backman K., Kield D., Flashman S., Jeffrey A., Maurer R. Recognition sequences of repressor and polymerase in the operators of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer M., Beck E., Hansen F. G., Bergmans H. E., Messer W., von Meyenburg K., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence of the origin of replication of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):580–584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Kemper B., Hays J., Weisberg R. A. T4 endonuclease VII cleaves holliday structures. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., Gellert M. Cruciform structures in palindromic DNA are favored by DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P. Structures and mechanisms of DNA restriction and modification enzymes. Q Rev Biophys. 1979 Aug;12(3):315–369. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannekoek H., Maat J., van den Berg E., Noordermeer I. Structure of a promotor on plasmid pMB9 derived from plasmid pSC101. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1535–1550. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E., Pfenninger O. Supercoils in prokaryotic DNA restrained in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by d(TA) oligomers. II. Analysis of the helix-coli transitions of linear and circular oligomers. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):145–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Carlson J. O., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in the DNA double helix measured with trimethylpsoralen in living E. coli cells: analogous measurements in insect and human cells. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):773–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Wells R. D. Relationship between superhelical density and cruciform formation in plasmid pVH51. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6292–6295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Griffin B. E. Sequence from early region of polyoma virus DNA containing viral replication origin and encoding small, middle and (part of) large T antigens. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalker D. M., Thomas C. M., Helinski D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the region of the origin of replication of the broad host range plasmid RK2. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(1):8–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00338997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M., Nishimura A., Yasuda Y., Hirota Y. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli K-12 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):575–579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of replication of human mitochondrial DNA. Localization of the 5' ends of nascent daughter strands. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5109–5115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Delta sequences and double symmetry in a yeast chromosomal replicator region. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):293–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Lukashin A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Fluctuations in superhelical DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):967–982. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesehahn G., Hearst J. E. DNA unwinding induced by photoaddition of psoralen derivatives and determination of dark-binding equilibrium constants by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth-Gutai M., Lebowitz J. Introduction of interrupted secondary structure in supercoiled DNA as a function of superhelix density: consideration of hairpin structures in superhelical DNA. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):195–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.195-204.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]