Abstract
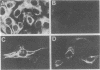
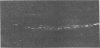
We describe reversible changes of intermediate filaments of fibroblastic cells associated with changes in the functional state of the cells. The changes are revealed by comparing the immunofluorescence patterns given by a monoclonal antibody and a polyclonal serum, both recognizing vimentin. The state of the filaments depends on culture density; this effect cannot be attributed to the nutritional state of the cells, their growth rate, or substances released into the medium. It seems to depend mainly on the aggregation of filaments during strong cell movements. The possible significance of these findings for the functional role of intermediate filaments is discussed.
Full text
PDF
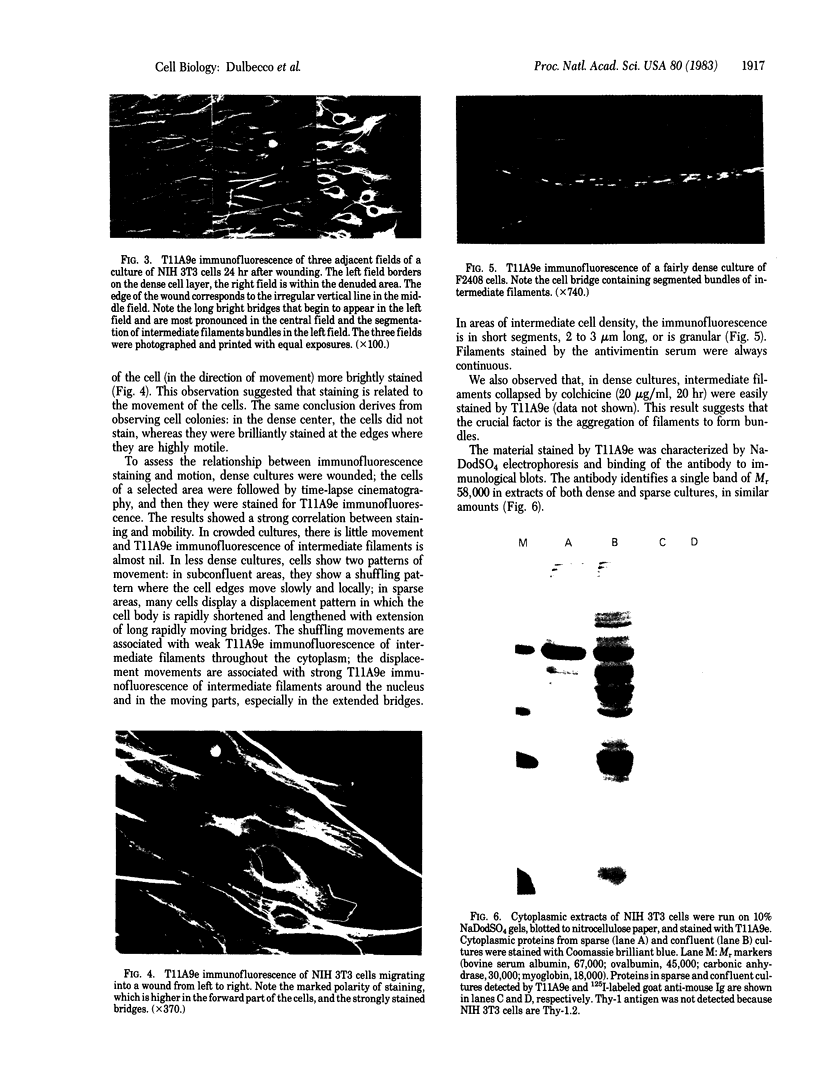

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellagi K., Brouet J. C. Redistribution of intermediate filaments during capping of lymphocyte surface molecules. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):284–286. doi: 10.1038/298284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R., Unger M., Bologna M., Battifora H., Syka P., Okada S. Cross-reactivity between Thy-1 and a component of intermediate filaments demonstrated using a monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):772–774. doi: 10.1038/292772a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fink L. M. An alteration in the phosphorylation of vimentin-type intermediate filaments is associated with mitosis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Winter S., Osborn M., Weber K. Widespread occurrence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):25–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Structural associations of synemin and vimentin filaments in avian erythrocytes revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Synemin: a new high molecular weight protein associated with desmin and vimentin filaments in muscle. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):727–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90549-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W. Intermediate filaments in 3T3 cells collapse after intracellular injection of a monoclonal anti-intermediate filament antibody. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):249–251. doi: 10.1038/291249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W. Vimentin and keratin intermediate filament systems in cultured PtK2 epithelial cells are interrelated. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):161–165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake P., Clark E. A., Khorshidi M., Sunshine G. H. Production and characterization of cytotoxic Thy-1 antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. Detection of T cell subsets. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Nov;9(11):875–886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B., Anderton B. Focus on filaments: embryology to pathology. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):706–707. doi: 10.1038/298706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Traub P. Properties of Ca2+-activated protease specific for the intermediate-sized filament protein vimentin in Ehrlich-ascites-tumour cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen-Hamilton M., Hamilton R. T., Allen W. R., Potter-Perigo S. Synergistic stimulation of S6 ribosomal protein phosphorylation and DNA synthesis by epidermal growth factor and insulin in quiescent 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins by cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. C., McConkey E. H., Guard N. L. Vimentin-derived proteins: differences between normal human fibroblasts and transformed human cells. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Oct;135(2):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Mirsky R., Raff M. C., Thorpe R., Dowding A. J., Anderton B. H. All classes of intermediate filaments share a common antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Dunia I., Dodemont H. J., Benedetti E. L., Bloemendal H. Lenticular intermediate-sized filaments: biosynthesis and interaction with plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Chen L. B., Murphy J. R., Fields B. N. Specific disruption of vimentin filament organization in monkey kidney CV-1 cells by diphtheria toxin, exotoxin A, and cycloheximide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7267–7271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Cantieri J. S., Teller D. C., Lonsdale-Eccles J. D., Dale B. A. Characterization of a class of cationic proteins that specifically interact with intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4097–4101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven A. C., Wall J., Hainfeld J., Steinert P. M. Structure of fibroblastic intermediate filaments: analysis of scanning transmission electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3101–3105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Choppin P. W. Effect of vanadate on intracellular distribution and function of 10-nm filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2363–2367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock C. L. Nucleus-associated intermediate filaments from chicken erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):881–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Heidemann S. R., McIntosh J. R. Isolation and partial characterization of a cage of filaments that surrounds the mammalian mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):160–169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]