Abstract
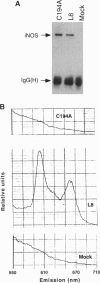
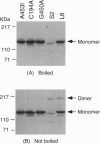
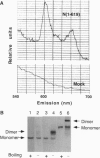
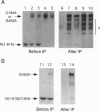
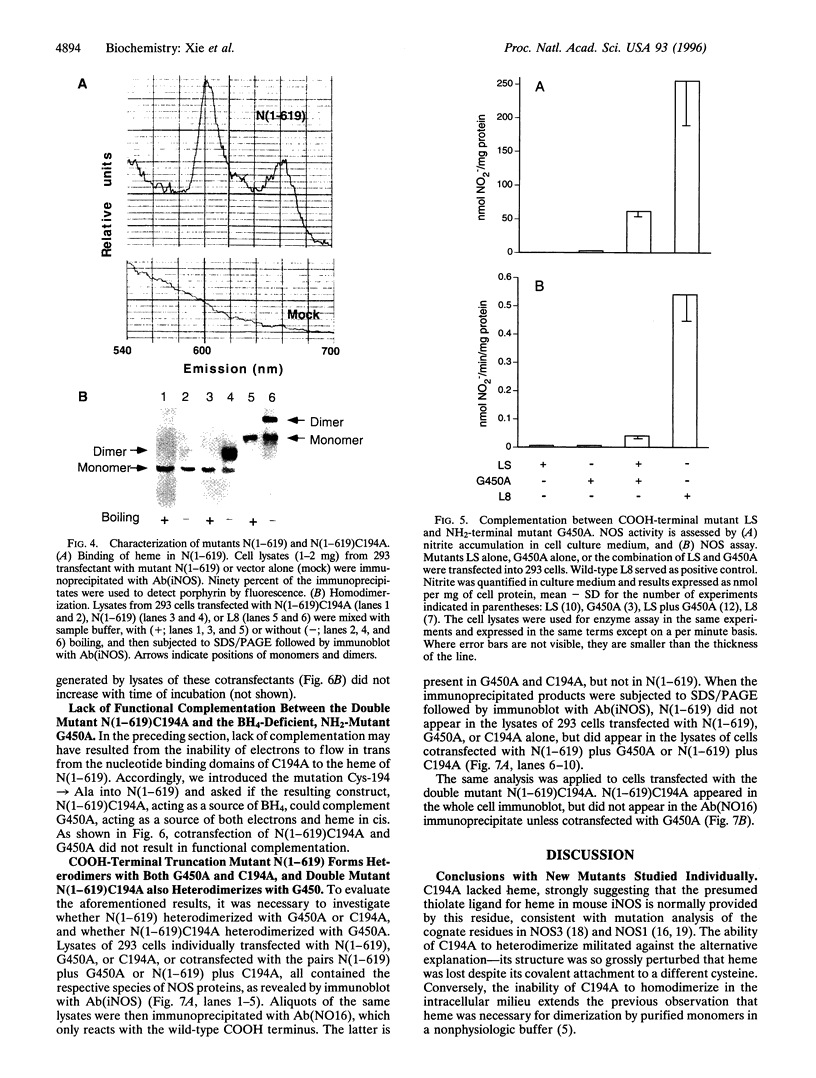
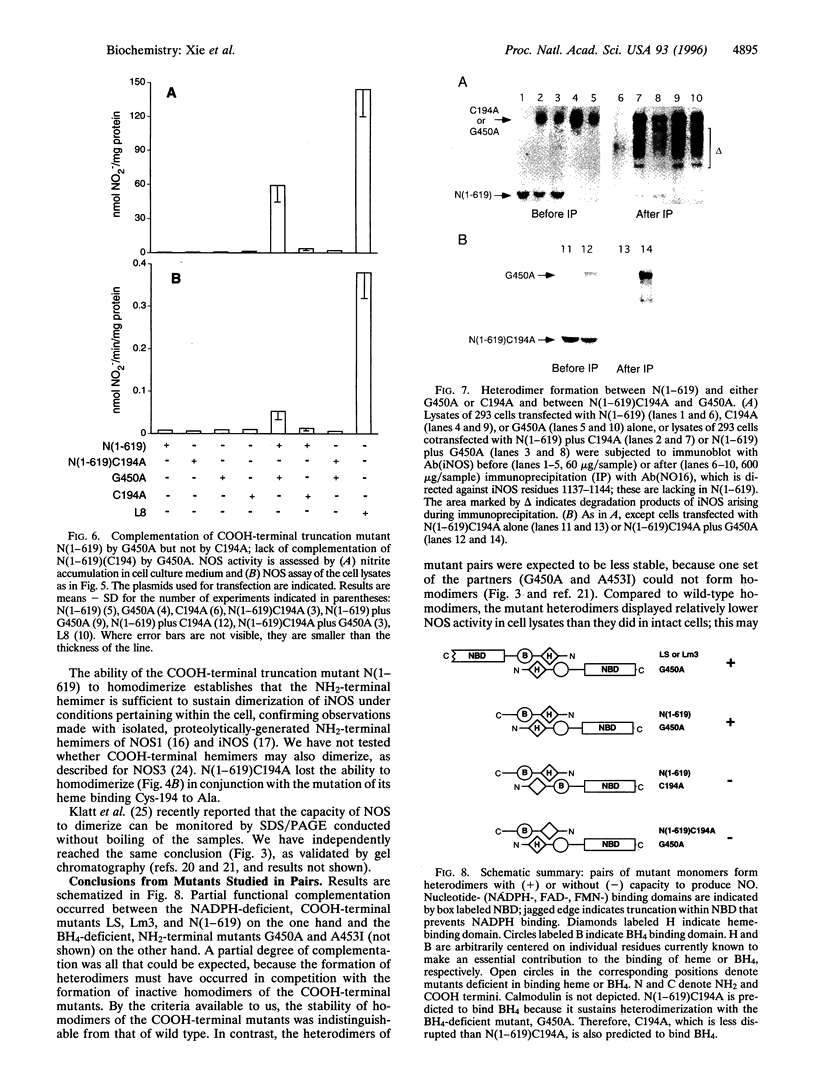
For catalytic activity, nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) must be dimeric. Previous work revealed that the requirements for stable dimerization included binding of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), arginine, and heme. Here we asked what function is served by dimerization. We assessed the ability of individually inactive mutants of mouse inducible NOS (iNOS; NOS2), each deficient in binding a particular cofactor or cosubstrate, to complement each other by generating NO upon cotransfection into human epithelial cells. The ability of the mutants to homodimerize was gauged by gel filtration and/or PAGE under partially denaturing conditions, both followed by immunoblot. Their ability to heterodimerize was assessed by coimmunoprecipitation. Heterodimers that contained only one COOH-terminal hemimer and only one BH4-binding site could both form and function, even though the NADPH-, FAD-, and FMN-binding domains (in the COOH-terminal hemimer) and the BH4-binding sites (in the NH2-terminal hemimer) were contributed by opposite chains. Heterodimers that contained only one heme-binding site (Cys-194) could also form, either in cis or in trans to the nucleotide-binding domains. However, for NO production, both chains had to bind heme. Thus, NO production by iNOS requires dimerization because the active site requires two hemes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baek K. J., Thiel B. A., Lucas S., Stuehr D. J. Macrophage nitric oxide synthase subunits. Purification, characterization, and role of prosthetic groups and substrate in regulating their association into a dimeric enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21120–21129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: a physiologic messenger molecule. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:175–195. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. F., Tsai A. L., Wu K. K. Cysteine 184 of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is involved in heme coordination and catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):25062–25066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Martin E., Xie Q. W., Sassa S., Nathan C. Inducible nitric oxide synthase: identification of amino acid residues essential for dimerization and binding of tetrahydrobiopterin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 5;92(25):11514–11518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D. K., Stuehr D. J. Macrophage NO synthase: characterization of isolated oxygenase and reductase domains reveals a head-to-head subunit interaction. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 24;34(3):801–807. doi: 10.1021/bi00003a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griscavage J. M., Fukuto J. M., Komori Y., Ignarro L. J. Nitric oxide inhibits neuronal nitric oxide synthase by interacting with the heme prosthetic group. Role of tetrahydrobiopterin in modulating the inhibitory action of nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21644–21649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatt P., Schmidt K., Lehner D., Glatter O., Bächinger H. P., Mayer B. Structural analysis of porcine brain nitric oxide synthase reveals a role for tetrahydrobiopterin and L-arginine in the formation of an SDS-resistant dimer. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3687–3695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00038.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Robinson L. J., Michel T. Oligomerization of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Evidence for a dominant negative effect of truncation mutants. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 17;270(46):27403–27406. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.46.27403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide synthase structure and mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12231–12234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan K., Bredt D. S., Hirsch D. J., Snyder S. H., Clark J. E., Masters B. S. Cloned, expressed rat cerebellar nitric oxide synthase contains stoichiometric amounts of heme, which binds carbon monoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11141–11145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan K., Masters B. S. Prokaryotic expression of the heme- and flavin-binding domains of rat neuronal nitric oxide synthase as distinct polypeptides: identification of the heme-binding proximal thiolate ligand as cysteine-415. Biochemistry. 1995 Mar 21;34(11):3686–3693. doi: 10.1021/bi00011a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Xie Q. W. Regulation of biosynthesis of nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13725–13728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulski M., Tully T. Molecular and biochemical characterization of dNOS: a Drosophila Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9072–9076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. K., Marletta M. A. Characterization of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and a C415H mutant, purified from a baculovirus overexpression system. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 13;33(49):14723–14732. doi: 10.1021/bi00253a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Pollock J. S., Nakane M., Gorsky L. D., Förstermann U., Murad F. Purification of a soluble isoform of guanylyl cyclase-activating-factor synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):365–369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Walter U. NO at work. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):919–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Cho H. J., Kwon N. S., Weise M. F., Nathan C. F. Purification and characterization of the cytokine-induced macrophage nitric oxide synthase: an FAD- and FMN-containing flavoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Ikeda-Saito M. Spectral characterization of brain and macrophage nitric oxide synthases. Cytochrome P-450-like hemeproteins that contain a flavin semiquinone radical. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20547–20550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K. A., Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide synthase is a cytochrome P-450 type hemoprotein. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6627–6631. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q. W., Cho H. J., Calaycay J., Mumford R. A., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Ding A., Troso T., Nathan C. Cloning and characterization of inducible nitric oxide synthase from mouse macrophages. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):225–228. doi: 10.1126/science.1373522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q. W., Cho H., Kashiwabara Y., Baum M., Weidner J. R., Elliston K., Mumford R., Nathan C. Carboxyl terminus of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Contribution to NADPH binding and enzymatic activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28500–28505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]